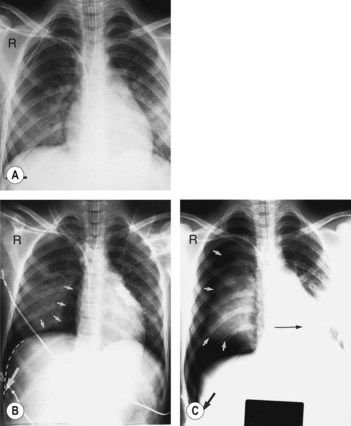
108 Pneumothorax
Salient features
History
Examination
Questions
How would you investigate this patient?
• Chest radiography, both inspiratory and expiratory phases. In critically ill patients, pneumothorax is suspected when:
• Blood gases if the patient is breathless: hypoxaemia depending on the shunting, whereas hypercapnia does not develop.
Advanced-level questions
How would you grade the degree of collapse?
British Thoracic Society of grading:
• Small: where there is a small rim of air around the lung
• Moderate: when the lung is collapsed towards the heart border
• Complete: airless lung, separate from the diaphragm (aspiration is necessary)
• Tension: any pneumothorax with cardiorespiratory distress (rare and requires immediate drainage).
How would you manage this patient?
• Small pneumothoraces (<20% in size) spontaneously resolve within weeks.
• Larger ones (irrespective of size) with normal lungs are managed by simple aspiration rather than an intercostal tube as the initial drainage procedure. Aspiration is less painful than intercostal drainage, leads to a shorter admission and reduces the need for pleurectomy, and has no increase in recurrence rate at 1 year.
• When there is rapid re-expansion following simple aspiration, an intercostal tube with underwater seal drainage is used. The tube should be left in for at least 24 h. When the lung re-expands, clamp the tube for 24 h. If repeat radiography shows that the lung remains expanded, the tube can be removed. If not, suction should be applied to the tube. If it fails to resolve within 1 week, surgical pleurodesis should be considered. Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery with several chest ports allows clear visualization of the pleural cavity for resection of bullae and pleurodesis.
What are the causes of pneumothorax?
• Spontanenous (usually in thin males)
• COPD: emphysematous bulla (JAMA 1975;234:389–93)
• TB (the original descriptions of pneumothorax is commonly associated with TB, JAMA 1931;96:653–7)
• Marfan syndrome, Ehlers–Danlos syndrome
• Catamenial pneumothorax: pneumothorax that occurs in association with menstruation.
When would you suspect a tension pneumothorax?
Tension pneumothorax should be suspected in the presence of any of the following:
When should open thoracotomy be considered?
It should be considered if there is one of the following present: