Pharmacogenomics of Cardiac Arrhythmias
Individuals vary widely in their responses to therapy with most drugs. Indeed, response to cardiovascular drug therapy and antiarrhythmics in particular is so highly variable that study of the underlying mechanisms has elucidated important lessons for understanding variable responses to drug therapy in general.1,2
Principles of Pharmacogenomics
Definitions
Two key steps are included in the series of events that take place between administration of a drug and manifestation of its beneficial or adverse effects (Figure 55-1). First, drug must be delivered to its molecular site of action (e.g., receptor, ion channel). The magnitude of the effect at the target is determined by drug concentration, and the study of the time dependence of the concentration of drug (and metabolites) achieved in plasma, tissue, or other sites such as urine or bile is termed pharmacokinetics. The second major process that determines drug action has been termed pharmacodynamics and broadly includes the processes that must occur between the interaction of a drug with a specific molecular target and the manifestation of drug action at the molecular, cellular, whole-organ, and whole-patient levels. Because drugs act in a complex (and often abnormal) biological milieu, considerable intersubject variability in drug effects can arise from pharmacodynamic mechanisms.
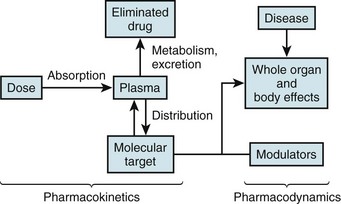
Figure 55-1 Mechanisms modulating drug actions
The left side illustrates pharmacokinetic variables that determine absorption, distribution, metabolism, and elimination (often abbreviated ADME). Variability in interactions between drugs and their molecular targets, along with variability in underlying pathophysiologies including disease processes, modulates pharmacodynamic mechanisms (right) that contribute to net drug responses. Understanding the molecular determinants of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics is the first step toward identifying genetic variants that contribute to drug responses.
These principles of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics have been recognized for decades, and it is now apparent that they are manifestations of the highly regulated function of individual molecules. Thus, metabolism of a drug occurs by interaction of the drug with specific drug-metabolizing molecules, and absorption, distribution, and renal and biliary excretion reflect cellular drug uptake and efflux by specific transporter3 molecules. It is variability in function and expression of metabolizing and transport molecules, regulated by a host of genetic and environmental factors, that determines pharmacokinetic variability. Similarly, variability in the biological milieu in which drugs act can be conceptualized as variability in the function of multiple molecules, including the target molecules with which drugs interact to produce their beneficial and adverse effects, whose integrated behavior determines normal and abnormal cellular and whole-organ function.
Some DNA variants are rare, cause specific “monogenic” diseases, and have conventionally been termed mutations. More common variants are termed polymorphisms and might or might not alter function or expression of the encoded protein. As we begin to understand that each human harbors thousands of DNA variants4,5—some common and some extremely rare—the distinction between “mutation” and “rare variant” becomes increasingly unclear, and more generic language like rare and common polymorphisms is being adopted. One critical aspect of modern genomics is that DNA tends to be highly ancestry specific. Variants implicated in traits like variable drug responses in one ethnic group may be absent in another, or different variants in the same gene may contribute.
Approaches to Identifying Pharmacogenetic Variants
Associating genetic variants with clinical phenotypes, including drug response, in humans has taken one of two broad approaches. The first is predicated on a perceived understanding of the fundamental physiology, pathophysiology, or pharmacology of the phenotype under study; this is termed a candidate gene approach (see Figure 55-1). The second takes advantage of emerging high-throughput technologies by genotyping or by direct sequencing of large regions of DNA (up to whole exomes and genomes) to then determine whether there is an association between any locus interrogated and the phenotype under study. To date, the most widely used method in this unbiased or hypothesis-free approach is the genome-wide association study (GWAS) paradigm.6 One clear emerging lesson of these genetic association studies is that any result requires further validation both by replication and by further experiments testing the underlying biology.
Candidate Gene Approaches
Although the candidate gene approach is intuitively very appealing, repeated experience over the past decade has demonstrated that initially identified associations frequently failed to replicate.7 The reasons for this failure of replication are multiple: (1) The candidate variant may not, in fact, explain a large proportion of the variance in the phenotype under study; (2) the studies generally involve small numbers and so are underpowered; and (3) a publication bias is associated with positive results, so attempts to replicate generally regress to the mean.
A major exception to the general “rule” that candidate gene studies fail to replicate in a robust fashion is seen in pharmacogenomics.8 Here, single variants that alter the function of drug-metabolizing or transport molecules may confer a very high likelihood of developing aberrantly high (or low) plasma drug concentrations—and thus highly variable drug responses—during treatment. In addition, genetically determined variations in drug targets (molecules with which drugs interact to achieve their therapeutic or adverse effects) may strongly modulate the outcomes of drug therapy. Specific examples are discussed in the following sections.
Unbiased Approaches: The Genome-Wide Association Study Paradigm
In arrhythmia science, GWASs have been used to identify new genes and pathways involved in physiological traits (like electrocardiographic [ECG] intervals) and susceptibility to common arrhythmias like atrial fibrillation (AF) or sudden cardiac death.9,10 These results, in turn, are being used to explore the role of variants in these genes in variable drug response. In addition, GWASs have been used to directly analyze drug responses, as described later.11
The GWAS experiment starts by identifying cases and controls for a specific phenotype. These can be categorical (e.g., premature heart disease, breast cancer, drug-induced adverse effect, AF, restless leg syndrome) or continuous (e.g., PR duration, warfarin steady state dose).6 High-throughput platforms are then used to determine genotypes at hundreds of thousands or millions of SNP sites in cases and controls, and tests of association are performed at each SNP to identify those associated with the phenotype under study (Figure 55-2). Evidence that the experiment has yielded a positive result may include very low P values (after correction for multiple comparisons), replication, and ultimately biological plausibility. SNPs are chosen because they tag blocks of linkage disequilibrium; therefore, there is little expectation that those associated with low P values are functional themselves. Rather, they act as sign posts within the genome, identifying specific loci at which functional variants may reside.
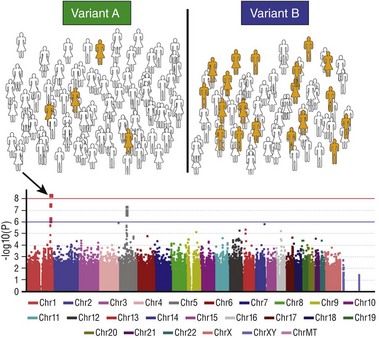
Figure 55-2 The genome-wide association study paradigm
The first step (top panel) is to assign each subject in a large cohort to case (orange) or control (white) status. The entire cohort is then genotyped at hundreds of thousands to millions of common polymorphic sites. The figure illustrates how a hypothetical polymorphism predicting the phenotype in question might segregate: In this case, variant B is associated with the phenotype. A statistical test of association is then performed for each polymorphism and the results displayed on a Manhattan plot (bottom): The x-axis is the chromosomal location of the polymorphism, and the y-axis is the exponent of the P value for the individual statistical test (higher values denote lower P values). In the example shown, a cluster of polymorphisms in chromosome 1 (arrow) achieves P values less than 10−8. The red horizontal line denotes an arbitrary level of statistical significance after correction for multiple testing.
GWAS analyses of the distribution of normal ECG intervals (e.g., PR, QRS, QT) have been conducted in tens of thousands of patients and have identified genomic loci that contribute to variability in these traits.12–18 Some of these are, in retrospect, obvious from an understanding of underlying physiology. Thus, for example, strong signals are present in the KCNQ1 and KCNH2 loci (encoding potassium channels important for cardiac repolarization) in GWAS analyses of variability in the QT interval. Mutations in these genes are the most common causes of the congenital long QT syndrome; the GWAS result demonstrates that common variants in these genes contribute to physiological variability of QT intervals in a normal population.
Other signals identified by GWAS identify genes whose role in the phenotype under study is completely unsuspected. In the QT analyses, the strongest signal has consistently been noted near NOS1AP, which encodes an ancillary protein for the neuronal isoform of nitric oxide synthase. Initial studies suggest that NOS1AP encodes a regulator of cardiac potassium and calcium function.19 Follow-up studies have now implicated NOS1AP variants in phenotypes beyond normal QT variability: These include risk for sudden cardiac death in populations,20 risk for events in patients with congenital long QT syndrome,21,22 and risk of sudden death during treatment with some drugs.23 The strongest GWAS signal for variability in PR and QRS is seen in SCN10A, which encodes a sodium channel previously implicated only in pain perception and not known to play a role in the heart. Preliminary studies have suggested multiple roles for the gene in the heart: A contribution to late sodium current,24 regulation of the canonical cardiac sodium channel SCN5A,25,26 and a role in neural regulation of conduction27 have been suggested.
GWASs of patients with and without AF have consistently implicated SNPs at chromosome 4q25.28–30 The nearest gene encodes the transcription factor PITX2; initial studies suggest that PITX2c, a cardiac-specific isoform, regulates both development of the pulmonary myocardium31 and expression of other genes (e.g., NPPA, KCNQ1) that have been implicated in AF susceptibility.32 These data are also being used to inform additional studies of variable response to AF therapy. Thus, for example, reports have suggested that SNPs at Chr4q25 predict response to drug33 or ablation34 therapy in AF.
In addition to analysis of phenotypes such as ECG intervals or disease susceptibility, the GWAS paradigm has been used to directly study variability in drug response. Here, the problem is that precise definitions of drug response phenotypes are needed, and the numbers of patients that can be accrued is by nature of the experiment much smaller than analyses of ECG intervals or of arrhythmias themselves.11 Nevertheless, as is described further later, initial attempts have been made to analyze phenotypes such as warfarin steady state dose requirement or susceptibility to drug-induced torsades de pointes.
Other Experimental Approaches
A design intermediate between a single candidate gene interrogation and an unbiased GWAS approach is a multiplexed candidate gene study. In this approach, hundreds of SNPs, chosen because they tag major haplotype blocks within logically chosen candidate genes, are interrogated to identify specific loci that may associate with the phenotype of choice.35 This approach offers the advantage of shifting the focus away from single variants, along with the disadvantage that it remains a candidate gene approach albeit using candidates chosen often through unbiased approaches. The hypothesis that combinations of genetic variants contribute to a trait can be addressed using this method.36 Another emerging approach is to combine the results of genomic studies with those of other studies yielding complementary datasets. Examples include expression profiling in cell lines or specific tissues, informatics approaches,37 and evaluation of drug response in model organisms with known genetic backgrounds, such as mice or zebrafish.9,38
An emerging approach in modern genomics is direct sequencing of candidate genes, of loci implicated as modulators of a phenotype by GWAS, of large candidate gene sets, and ultimately of the whole genome. New technologies have enabled the development of very high throughput and reasonably accurate genotyping for such experiments. The challenge is that the larger the region of the genome interrogated, the larger the number of genetic variants identified, and the ability to relate specific variants to phenotypes under study remains a major challenge in this area. Nevertheless, these approaches are being explored in genomics and have been applied to electrophysiological phenotypes.39,40
Pharmacokinetic Mechanisms
Most drug metabolism occurs in the hepatocyte, where drugs are biotransformed to one or more metabolites, usually by oxidation. Drug metabolites are generally more polar than the parent drug and are themselves excreted or conjugated (most commonly as glucuronides) before renal or biliary excretion. Oxidation is usually accomplished by members of the cytochrome P-450 (CYP) superfamily, the most important members of which for drug metabolism are the CYP3A family (CYP3A4 and CYP3A5), CYP2D6, CYP2C9, and CYP2C19. Conjugation is accomplished by uridine glucuronyl transferase, N-acetyltransferase, or a group of methyltransferases.8
High-Risk Pharmacokinetics
The term high-risk pharmacokinetics has been used to describe specific clinical settings in which variation in normal metabolism or excretory pathways can confer especially important clinical effects.41 Such variation most often arises because of genetic polymorphisms in the pathway or because of coadministration of drugs that inhibit the pathway. One high-risk setting involves use of a drug that has a narrow margin between effective dose and toxic dose, and that has a single predominant route of elimination. A second setting involves administration of a prodrug, a drug that requires a specific metabolic pathway for its bioactivation. Examples of prodrugs whose bioactivation depends on drug metabolism pathways with known polymorphisms include clopidogrel and codeine. Table 55-1 presents examples of antiarrhythmic drugs for which variants in single genes produce large effects.
Table 55-1
Pharmacogenetics of Antiarrhythmic Drugs
| Drug | Genes With Polymorphisms Possibly Affecting Response | Inhibitor of |
| Quinidine | CYP2D6, ABCB1 | |
| Procainamide | NAT2 | |
| Amiodarone | CYP3A4, ABCB1, CYP2C9 | |
| Flecainide | CYP2D6 | |
| Propafenone | CYP2D6 | |
| Sotalol | ||
| Dofetilide | ||
| Dronedarone | ABCB1 | |
| Metoprolol, timolol | CYP2D6, ADR1 | |
| β-Blockers | ADR1 | |
| Verapamil | CYP3A4, ABCB1 | |
| Diltiazem | CYP3A4, ABCB1 | |
| Warfarin | CYP2C9, VKORC1 | |
| Adenosine | ||
| Digoxin | ABCB1 |
A spectacular example of high-risk pharmacokinetics has been drug interactions involving substrates of CYP3A4, notably the antihistamine terfenadine and the pro-motility agent cisapride.42 These compounds are high-potency QT-prolonging agents (resulting from block of the potassium current IKr) and ordinarily undergo very extensive presystemic metabolism by CYP3A (and no other major pathway) to non–IKr-blocking metabolites. When drugs that inhibit CYP3A are coadministered, presystemic metabolism is inhibited, concentrations of terfenadine or cisapride entering the systemic circulation can increase by several orders of magnitude, and torsades de pointes due to IKr block becomes a real risk. These risks led to withdrawal of these drugs from the market. Although the activity of CYP3A4 varies among individual patients, the reasons for this are not completely understood. No common nonsynonymous SNPs are present in the gene, although noncoding SNPs regulating function have been described.43,44 Functionally important polymorphisms in the coding region of the very closely related gene for CYP3A5 are expressed in enterocytes and hepatocytes. Loss-of-function alleles are more common in white or Asian patients than in African American patients.
Another widely used drug that is eliminated largely by a single molecular mechanism is digoxin, whose hepatic and renal excretion is mediated by the drug efflux transporter P-glycoprotein encoded by ABCB1.3 The well-recognized effects of quinidine, amiodarone, verapamil, and numerous other drugs (erythromycin, itraconazole, cyclosporine) in elevating digoxin concentrations likely reflect interference with this P-glycoprotein elimination pathway. Similarly, sotalol and dofetilide are eliminated largely by renal excretion of unchanged drug, so marked QT prolongation is a real risk in patients with renal dysfunction given usual drug dosages; the specific transporter is unknown. Patients with entirely defective P-glycoprotein have not been described, although mice in which the gene is disrupted have no manifest baseline phenotype. However, because of the very prominent role of P-glycoprotein in maintenance of an effective blood-brain barrier, these mice display striking accumulation in the central nervous system and resulting toxicity when exposed to certain drugs, including digoxin. Polymorphisms have been described that modulate the function of drug transport molecules in vitro; these have been linked to variability in plasma and tissue concentrations and effects of digoxin, simvastatin, and many other drugs.
Pharmacodynamic Mechanisms
DNA polymorphisms can result in important functional changes in drug target molecules.1,2 One example is the common R389G (substitution of glycine for arginine at position 389) variant in ADR1 encoding the β1-adrenergic receptor. The R389 variant demonstrated a twofold to fourfold greater increase in myocyte contractility during exposure to β-agonists and predicted a beneficial response of patients with heart failure receiving bucindolol; in fact, clinical response in G389 carriers was no different from response to placebo. Recent studies implicate this polymorphism as a modulator of rate control in atrial fibrillation.45 Another example may be polymorphisms in the KCNE2 gene. Some, but not all, studies suggest that KCNE2 can partner with and modify the function of HERG, the protein whose expression results in IKr. A KCNE2 polymorphism resulting in T8A increases sensitivity to IKr blockers approximately threefold and has been linked to susceptibility to drug-induced torsades de pointes. A variant in the SCN5A promoter has been described that reduces promoter activity and is associated with longer QRS duration (slower conduction) at baseline,46 and, as has been discussed, SCN10A variants also modulate QRS. The SCN5A variant predicted greater QRS prolongation with sodium channel-blocking drug challenge in Asian patients with Brugada syndrome46 and thus becomes a candidate for modulating risk of sudden death seen when conduction is slowed by drugs, disease, or genetic syndromes.
Variable responses to warfarin reveal that this is an example of a drug in which two genes play an important role.1,47 One is CYP2C9, which is responsible for the bioinactivation of S-warfarin, the active enantiomer of the drug. Patients with CYP2C9 variants that result in loss of function have higher plasma drug levels, increased drug effect, excessive risk of bleeding at ordinary doses, and decreased steady state dose requirements. The specific variants and their frequencies vary by ancestry. The second gene is VKORC1, which encodes an important component of the warfarin drug target (the vitamin K complex). Very rare patients have VKORC1 coding region mutations, resulting in warfarin resistance. In addition, however, common variation in the promoter clearly modulates VKORC1 hepatic mRNA abundance and can be related to warfarin sensitivity. In fact, the initial warfarin dose requirement appears more dependent on VKORC1 variants than on those in CYP2C9. Steady state warfarin dose requirements vary strikingly across ethnicities, and higher dose requirements in African subjects and lower ones in Asian subjects have been associated with VKORC1 variation. GWASs of warfarin steady state dose have confirmed a prominent contribution by common variants in CYP2C9 and VKORC1 and have suggested a role for at least one other gene, CYP4F2, which is thought to be involved in vitamin K oxidation.48,49
The Example of Drug-Induced Long QT Syndrome
A range of genetic approaches have been used to study the potential contributions of DNA variants to risk for drug-induced torsades de pointes (diTdP). This serious adverse drug event occurs in 1% to 5% of patients treated with QT-prolonging antiarrhythmics, such as sotalol, dofetilide, or quinidine, and to a much lesser extent in patients exposed to noncardiovascular drugs such as terfenadine, cisapride, erythromycin, haloperidol, methadone, and many others. The mechanism whereby patients receiving antiarrhythmic drugs are at so much higher risk than those receiving the noncardiovascular drugs remains unexplained and may reflect a contribution by concomitant disease, notably atrial fibrillation, which is frequently the indication for prescribing QT-prolonging antiarrhythmics; data suggest that the period of conversion from atrial fibrillation to sinus rhythm is one of high risk for QT interval dysregulation because of mechanisms that are not well understood.42
An understanding of normal and abnormal cardiac repolarization informs a set of candidate genes that may modulate QT and diTdP risk. Virtually all drugs that cause torsades de pointes are IKr blockers. The biological context in which IKr blockers act includes other elements of the action potential (e.g., IKr, INa, ICa), as well as mechanisms that control normal autonomic function and serum potassium. One recent study suggested that PI3 kinase inhibition (a property of some anticancer drugs that have been linked to diTdP) affects multiple ionic currents, suppressing IKr and IKs and increasing late sodium current—effects that may prolong QT.50 This complexity is consistent with the notion that the mechanisms that maintain a short QT interval vary among individual patients, and patients with reduced repolarization reserve as the result of genetic or environmental factors are at increased risk for developing torsades de pointes on challenge with an IKr blocker. Several studies have implicated variable IKs as playing an important role in maintaining this reserve.51 One report indicated that in vitro exposure to an IKr-blocking drug paradoxically shortened action potentials. The proposed explanation was decreased expression of a microRNA (miRNA), whose ordinary role is to inhibit translation of KCNQ1, a key gene in the IKs complex; the decrease in miRNA thus resulted in increased IKs expression and unexpectedly shortened action potentials.52 This experiment highlights the way in which complex regulation of multiple ion currents control cardiac repolarization, as well as a potential role for miRNAs as modulators of these processes.
Because two common clinical situations in which marked QT prolongation and torsades de pointes are observed are diTdP and the congenital long QT syndromes, one obvious set of candidate genes for mediating diTdP risk consists of the congenital long QT syndrome disease genes. A second set of candidates are those, such as NOS1AP, that have been implicated in variability in normal QT intervals by GWASs. A third set includes genes implicated by physiological studies,38 informatics approaches,37 or in silico modeling as modulators of the QT: Genes involved in autonomic function, potassium homeostasis, or PI3 kinase signaling are examples. A fourth set of candidate genes are those responsible for metabolism and elimination of the QT-prolonging drug; in this case, genetic variants will be specific to individual culprit drugs. For example, the antipsychotic thioridazine is metabolized by CYP2D6, and evidence suggests that poor metabolizers are at increased risk for diTdP with this drug.53
Individual case reports and series have provided evidence that some patients with previously unrecognized congenital long QT syndrome may present with torsades de pointes when challenged with a QT-prolonging drug. In addition, common variants in these genes could contribute: One example is a common nonsynonymous SNP in the cardiac sodium channel gene resulting in S1103Y, detected only in African Americans and reported to modulate the risk of a range of arrhythmias, including diTdP and sudden infant death syndrome.54,55 Systematic evaluations of patients with diTdP, surveying increasingly large sets of congenital long QT syndrome and other congenital arrhythmia syndrome genes, have identified potentially contributory variants in patients with diTdP in up to 65% of cases.39,56 Another set of candidate variants that might modulate risk are those in the β1-adrenergic receptor gene, but systematic surveys have not supported this contention.
A large candidate gene survey studied 1424 SNPs in 18 high-priority candidate genes (including congenital long syndrome disease genes and NOS1AP) in a set of 176 European ancestry patients with diTdP and two sets of controls: 837 population controls and 207 patients exposed to QT-prolonging drugs and not developing marked QT interval changes.35 This study identified a single nonsynonymous SNP in KCNE1 that predicted diTdP with a relatively high odds ratio, 9.0. KCNE1 encodes a key subunit necessary for physiological IKs function, and the variant, D85N, has been implicated as a modulator of normal QT interval and as a risk factor in modulating the phenotype in both congenital and drug-induced TdP. A preliminary report of a GWAS using a very similar set did not identify common genetic variants with large effect sizes.57
The Future: Using Pharmacogenetic Information in Patient Management
One goal of pharmacogenetic studies is to identify mechanisms leading to large variability with existing drug therapies. These results, in turn, could be used to tailor therapy with existing drugs and to evaluate new drugs to ensure that high-risk situations are avoided.1,2 Another possible outcome of pharmacogenomic studies is the development of readily measurable biomarkers to predict individual patient responses. In addition, identification of new pathways to variable physiological and drug responses may be the first clue to the development of new drug targets.
Rapid advances in genotyping technology are now raising the possibility that testing for pharmacogenomic variation can be accomplished in a “preemptive” fashion, that is, genetic information related to drug response and perhaps to other important pathophysiological phenotypes such as susceptibility to disease can be embedded in patients’ electronic medical records, to be accessed when a culprit drug is prescribed. Electronic systems would then advise the physician at the point of care whether the choice of drug or the drug dosage needs to be altered. This potential approach to incorporating genomic variant data into the flow of health care is now being explored at various academic medical centers.58
References
1. Roden, DM, Johnson, JA, Kimmel, SE, et al. Cardiovascular pharmacogenomics. Circ Res. 2011; 109:807–820.
2. Roden, DM, Wilke, RA, Kroemer, HK, et al. Pharmacogenomics: the genetics of variable drug responses. Circulation. 2011; 123:1661–1670.
3. DeGorter, MK, Xia, CQ, Yang, JJ, et al. Drug transporters in drug efficacy and toxicity. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2012; 52:249–273.
4. Tennessen, JA, Bigham, AW, O’Connor, TD, et al. Evolution and functional impact of rare coding variation from deep sequencing of human exomes. Science. 2012; 337:64–69.
5. Nelson, MR, Wegmann, D, Ehm, MG, et al. An abundance of rare functional variants in 202 drug target genes sequenced in 14,002 people. Science. 2012; 337:100–104.
6. Manolio, TA. Genomewide association studies and assessment of the risk of disease. N Engl J Med. 2010; 363:166–176.
7. Ioannidis, JP, Ntzani, EE, Trikalinos, TA, et al. Replication validity of genetic association studies. Nat Genet. 2001; 29:306–309.
8. Wang, L, McLeod, HL, Weinshilboum, RM. Genomics and drug response. N Engl J Med. 2011; 364:1144–1153.
9. Milan, DJ, Lubitz, SA, Kaab, S, et al. Genome-wide association studies in cardiac electrophysiology: recent discoveries and implications for clinical practice. Heart Rhythm. 2010; 7:1141–1148.
10. Bezzina, CR, Pazoki, R, Bardai, A, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies a susceptibility locus at 21q21 for ventricular fibrillation in acute myocardial infarction. Nat Genet. 2010; 42:688–691.
11. Motsinger-Reif, AA, Jorgenson, E, Relling, MV, et al. Genome-wide association studies in pharmacogenomics: Successes and lessons. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2013; 23:333–340.
12. Holm, H, Gudbjartsson, DF, Arnar, DO, et al. Several common variants modulate heart rate, PR interval and QRS duration. Nat Genet. 2010; 42:117–122.
13. Pfeufer, A, Sanna, S, Arking, DE, et al. Common variants at ten loci modulate the QT interval duration in the QTSCD study. Nat Genet. 2009; 41:407–414.
14. Newton-Cheh, C, Eijgelsheim, M, Rice, KM, et al. Common variants at ten loci influence QT interval duration in the QTGEN study. Nat Genet. 2009; 41:399–406.
15. Pfeufer, A, van Noord, C, Marciante, KD, et al. Genome-wide association study of PR interval. Nat Genet. 2010; 42:153–159.
16. Sotoodehnia, N, Isaacs, A, de Bakker, PI, et al. Common variants in 22 loci are associated with QRS duration and cardiac ventricular conduction. Nat Genet. 2010; 42:1068–1076.
17. Chambers, JC, Zhao, J, Terracciano, CMN, et al. Genetic variation in SCN10A influences cardiac conduction. Nat Genet. 2010; 42:149–152.
18. Denny, JC, Ritchie, MD, Crawford, DC, et al. Identification of genomic predictors of atrioventricular conduction: Using electronic medical records as a tool for genome science. Circulation. 2010; 122:2016–2021.
19. Chang, KC, Barth, AS, Sasano, T, et al. CAPON modulates cardiac repolarization via neuronal nitric oxide synthase signaling in the heart. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008; 105:4477–4482.
20. Kao, WH, Arking, DE, Post, W, et al. Genetic variations in nitric oxide synthase 1 adaptor protein are associated with sudden cardiac death in US white community-based populations. Circulation. 2009; 119:940–951.
21. Crotti, L, Monti, MC, Insolia, R, et al. NOS1AP is a genetic modifier of the long-QT syndrome. Circulation. 2009; 120:1657–1663.
22. Tomás, M, Napolitano, C, De Giuli, L, et al. Polymorphisms in the NOS1AP gene modulate QT interval duration and risk of arrhythmias in the long QT syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010; 55:2745–2752.
23. Becker, ML, Visser, LE, Newton-Cheh, C, et al. A common NOS1AP genetic polymorphism is associated with increased cardiovascular mortality in users of dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers. Br J ClinPharmacol. 2009; 67:61–67.
24. Yang, T, Atack, TC, Stroud, DM, et al. Blocking SCN10A channels in heart reduces late sodium current and is antiarrhythmic. Circ Res. 2012; 111:322–332.
25. Arnolds, DE, Liu, F, Fahrenbach, JP, et al. TBX5 drives Scn5a expression to regulate cardiac conduction system function. J Clin Invest. 2012; 122:2509–2518.
26. van den Boogaard, M, Wong, LYE, Tessadori, F, et al. Genetic variation in T-box binding element functionally affects SCN5A/SCN10A enhancer. J Clin Invest. 2012; 122:2519–2530.
27. Verkerk, AO, Remme, CA, Schumacher, CA, et al. Functional Nav1. 8 channels in intracardiac neurons: the link between SCN10A and cardiac electrophysiology. Circ Res. 2012; 111:333–343.
28. Gudbjartsson, DF, Arnar, DO, Helgadottir, A, et al. Variants conferring risk of atrial fibrillation on chromosome 4q25. Nature. 2007; 448:353–357.
29. Kaab, S, Darbar, D, van Noord, C, et al. Large scale replication and meta-analysis of variants on chromosome 4q25 associated with atrial fibrillation. Eur Heart J. 2009; 30:813–819.
30. Ellinor, PT, Lunetta, KL, Albert, CM, et al. Meta-analysis identifies six new susceptibility loci for atrial fibrillation. Nat Genet. 2012; 44:670–675.
31. Mommersteeg, MTM, Brown, NA, Prall, OWJ, et al. Pitx2c and Nkx2-5 are required for the formation and identity of the pulmonary myocardium. Circ Res. 2007; 101:902–909.
32. Wang, J, Klysik, E, Sood, S, et al. Pitx2 prevents susceptibility to atrial arrhythmias by inhibiting left-sided pacemaker specification. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010; 107:9753–9758.
33. Parvez, B, Vaglio, J, Rowan, S, et al. Symptomatic response to antiarrhythmic drug therapy is modulated by a common single nucleotide polymorphism in atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012; 60:539–545.
34. Husser, D, Adams, V, Piorkowski, C, et al. Chromosome 4q25 variants and atrial fibrillation recurrence after catheter ablation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010; 55:747–753.
35. Kaab, S, Crawford, DC, Sinner, MF, et al. A large candidate gene survey identifies the KCNE1 D85N polymorphism as a possible modulator of drug-induced torsades de pointes. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2012; 5:91–99.
36. Lubitz, SA, Sinner, MF, Lunetta, KL, et al. Independent susceptibility markers for atrial fibrillation on chromosome 4q25. Circulation. 2010; 122:976–984.
37. Berger, SI, Ma’ayan, A, Iyengar, R. Systems pharmacology of arrhythmias. SciSignal. 2010; 3:ra30.
38. Milan, DJ, Kim, AM, Winterfield, JR, et al. A drug-sensitized zebrafish screen identifies multiple genes, including GINS3, as regulators of myocardial repolarization. Circulation. 2009; 120:553–559.
39. Ramirez, AH, Shaffer, CM, Delaney, JT, et al. Novel rare variants in congenital cardiac arrhythmia genes are frequent in drug-induced torsades de pointes. Pharmacogenomics J. 2012.
40. Refsgaard, L, Holst, AG, Sadjadieh, G, et al. High prevalence of genetic variants previously associated with LQT syndrome in new exome data. Eur J Hum Genet. 2012; 20:905–908.
41. Roden, DM, Stein, CM. Clopidogrel and the concept of high risk pharmacokinetics. Circulation. 2009; 119:2127–2130.
42. Roden, DM. Drug-induced prolongation of the QT interval. N Engl J Med. 2004; 350:1013–1022.
43. Wang, D, Guo, Y, Wrighton, SA, et al. Intronic polymorphism in CYP3A4 affects hepatic expression and response to statin drugs. Pharmacogenomics J. 2011; 11:274–286.
44. Lamba, V, Panetta, JC, Strom, S, Schuetz, EG. Genetic predictors of interindividual variability in hepatic CYP3A4 expression. J Pharmacol ExpTher. 2010; 332:1089–1099.
45. Parvez, B, Chopra, N, Rowan, S, et al. A common beta1-adrenergic receptor polymorphism predicts favorable response to rate-control therapy in atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012; 59:49–56.
46. Bezzina, CR, Shimizu, W, Yang, P, et al. Common sodium channel promoter haplotype in Asian subjects underlies variability in cardiac conduction. Circulation. 2006; 113:338–344.
47. Klein, TE, Altman, RB, Eriksson, N, et al. Estimation of a warfarin dose with clinical and pharmacogenetic data: International Warfarin Pharmacogenetics Consortium. N Engl J Med. 2009; 360:753–764.
48. Cooper, GM, Johnson, JA, Langaee, TY, et al. A genome-wide scan for common genetic variants with a large influence on warfarin maintenance dose. Blood. 2008; 112:1022–1027.
49. Takeuchi, F, McGinnis, R, Bourgeois, S, et al. A genome-wide association study confirms VKORC1, CYP2C9, and CYP4F2 as principal genetic determinants of warfarin dose. PLoS Genet. 2009; 5:e1000433.
50. Lu, Z, Wu, CY, Jiang, YP, et al. Suppression of phosphoinositide 3-kinase signaling and alteration of multiple ion currents in drug-induced long QT syndrome. Sci Transl Med. 2012; 4:131ra50.
51. Roden, DM. Repolarization reserve: a moving target. Circulation. 2008; 118:981–982.
52. Xiao, L, Xiao, J, Luo, X, et al. Feedback remodeling of cardiac potassium current expression: A novel potential mechanism for control of repolarization reserve. Circulation. 2008; 118:983–992.
53. Llerena, A, Berecz, R, de la Rubia, A, et al. QTc interval lengthening is related to CYP2D6 hydroxylation capacity and plasma concentration of thioridazine in patients. J Psychopharmacol. 2002; 16:361–364.
54. Splawski, I, Timothy, KW, Tateyama, M, et al. Variant of SCN5A sodium channel implicated in risk of cardiac arrhythmia. Science. 2002; 297:1333–1336.
55. Plant, LD, Bowers, PN, Liu, Q, et al. A common cardiac sodium channel variant associated with sudden infant death in African Americans, SCN5A S1103Y. J Clin Invest. 2006; 116:430–435.
56. Itoh, H, Sakaguchi, T, Ding, WG, et al. Latent genetic backgrounds and molecular pathogenesis in drug-induced long QT syndrome. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2009; 2:511–523.
57. Kaab, S, Ritchie, MD, Crawford, DC, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies novel genomic regions associated with drug-induced long QT syndrome. Circulation. 2009; 120:S580.
58. Pulley, JM, Denny, JC, Peterson, JF, et al. Operational implementation of prospective genotyping for personalized medicine: the design of the Vanderbilt PREDICT project. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2012; 92:87–95.