Chapter 17 Peroneal Nerve
Anatomy
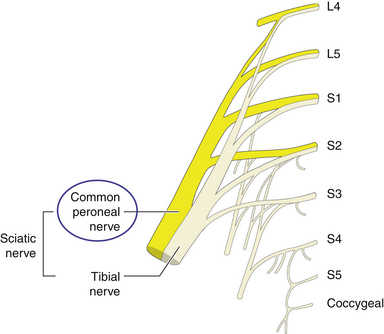
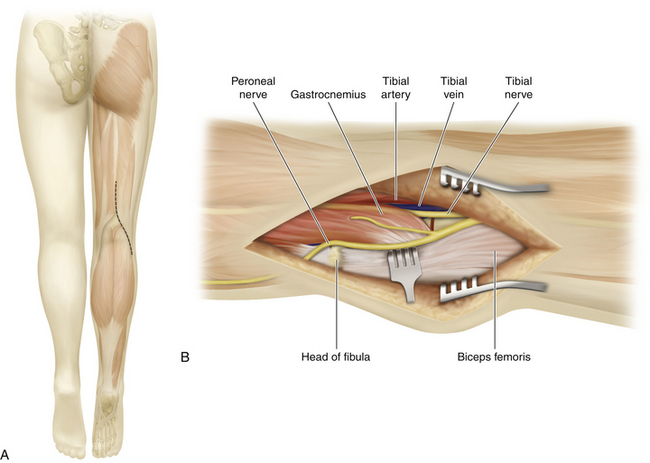
• The peroneal nerve is a distinct component of the sciatic nerve from its point of origin (Figure 17-1). The nerve diverges from the tibial nerve at the upper end of the popliteal fossa (Figure 17-2). The nerve runs downward and laterally toward the neck of the fibula. The nerve can be palpated against the neck of the fibula (Figure 17-3).
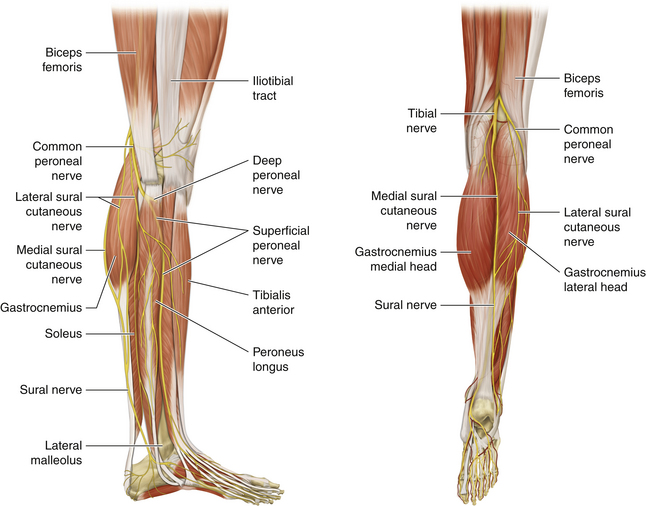
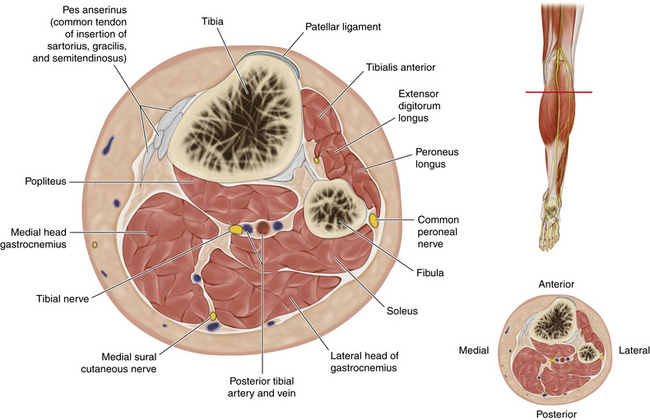
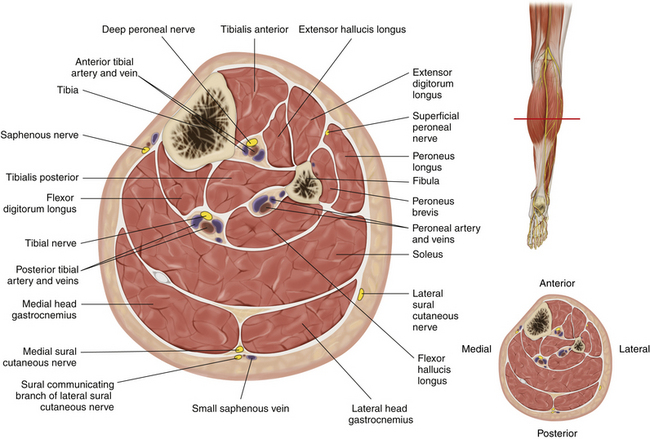
• The peroneal nerve is immediately deep to the investing fascia; it runs along the upper border of the lateral head of the gastrocnemius, medial to the biceps tendon (which inserts into the fibular head).
• The medial side of the biceps tendon can be similar in appearance to the peroneal nerve.
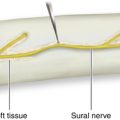
• The peroneal component of the sural nerve complex is given off at a variable point in the peroneal nerve’s passage through the popliteal fossa. The caliber of this branch varies, and it is impossible to predict the relative contributions of the tibial and peroneal contributions to the sural nerve complex.
• At the neck of the fibula the nerve runs under arching peroneus longus fibers. The edge of this arch may be fibrous and is the site of potential entrapment of the nerve.
• Within the substance of peroneus longus, at the level of the neck of the fibula, the nerve divides into superficial and deep branches and gives off three articular branches (Figure 17-4).
• The superficial nerve spirals around the neck of the fibula and supplies the peroneal compartment, which is bounded by the fibula, the investing fascia, and two fascial septa. Having supplied the peroneal muscles, the superficial peroneal nerve pierces the investing fascia. Its cutaneous branches can frequently be seen or palpated on the dorsal aspect of the ankle joint.
• The deep branch supplies the tibialis anterior, extensor hallucis longus, extensor digitorum longus, and peroneus tertius muscles (primarily with axons derived from the L5 spinal nerve).
• From its origin at the neck of the fibula, the deep branch runs deep to the extensor digitorum longus and runs between that muscle and the tibialis anterior with the anterior tibial vessels. (Figure 17-5)
Technique
• The head of the fibula is easily palpable, and the relationship of the peroneal nerve to the neck of the fibula is constant. The nerve can be palpated against the neck and, frequently, for several inches proximal to that point.
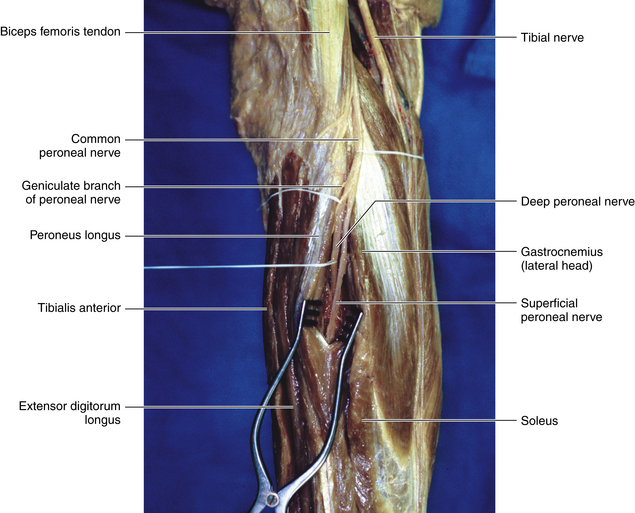
• The dissection of the peroneal nerve in the popliteal fossa is straightforward, and it is important to identify both the peroneal nerve and the medial edge of the biceps tendon. Surgeons who have not seen this before may think they have found the peroneal nerve when, in fact, they are looking at the medial portion of the biceps tendon, and thus may inadvertently divide the nerve during the dissection.
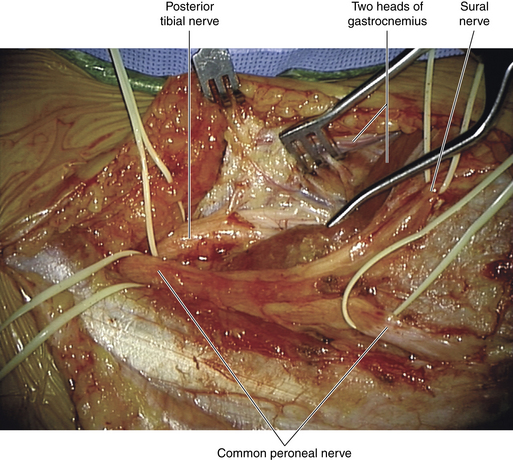
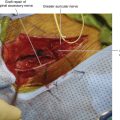
• The proximal nerve is usually separated from the tibial nerve at the point of bifurcation of the sciatic nerve, thus gaining the surgeon some length for a proximal stump (Figure 17-6). The sural branch can also be lysed from the peroneal nerve if needed, to free up a proximal stump (Figure 17-7).
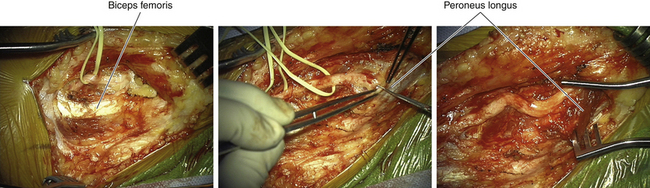
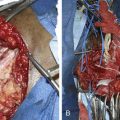
• The arching fibers of the peroneus longus may constitute an entrapment point of the nerve. This arch is divided to display the two main terminal branches of the nerve, as well as the articular branches (Figure 17-8). If the peroneal nerve contains a ganglion cyst, the articular branches must be dissected with care, because they constitute the connection to the synovial cavities of the joint.
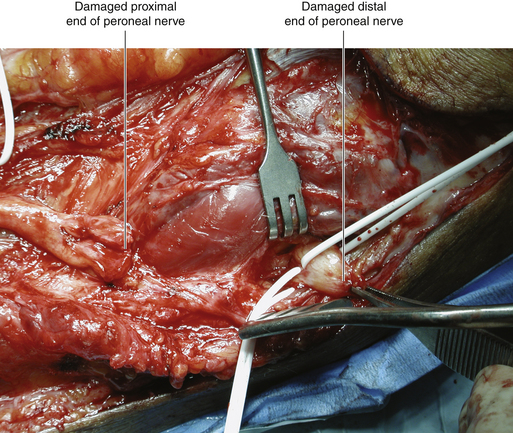
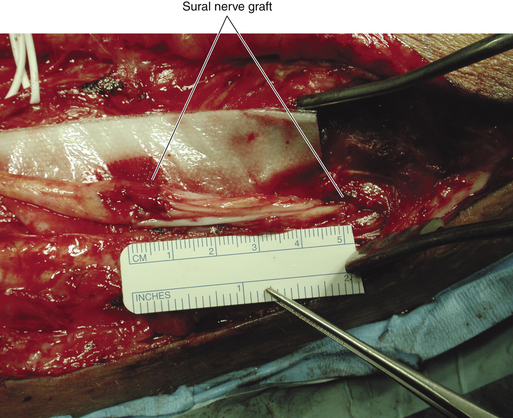
• Direct nerve injury at the neck of the fibula may present a challenge, because the viable distal stumps of both the superficial and deep nerves have to be dissected out of the scar tissue before nerve grafts can be placed. The entrapment point is opened to gain access to viable distal fascicles (Figure 17-9).
• For reasons not fully understood, the results of peroneal surgery for significant nerve injury are variable. There is little chance of success unless viable distal stumps are found, and it is pointless to sew grafts to wisps of fascicles and scar tissue (Figure 17-10). It is better in such cases to retreat in favor of reconstructive procedures.