Chapter 31 Percutaneous Translaminar Facet Pedicle Screw Fixation
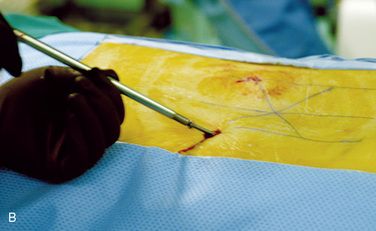
Percutaneous translaminar facet pedicle screw fixation is a minimally invasive posterior supplementary fixation method to anterior lumbar interbody fusion (ALIF) [1–3]. The screws are inserted percutaneously through stab wounds under fluoroscopic guidance.
Biomechanical studies of ALIF revealed that it does not limit extension and axial rotation of the spinal motion segment [4–6]. However, supplementary translaminar facet fixation has been shown to be an effective method to stabilize extension and axial rotation [7,8]. Translaminar facet screw fixation has also been demonstrated to enhance fusion [9–16].
The percutaneous translaminar facet pedicle screw fixation method described here is a modification of the translaminar facet fixation method first described by Magerl [17], in which the screw is inserted into the pedicle through the facet joints. Transfacet pedicle screw fixation showed biomechanical stability equivalent to that of conventional pedicle screw fixation when it is used to augment to ALIF [18].
Percutaneous translaminar facet pedicle screw fixation gives immediate postoperative spinal stabilization after ALIF and therefore enhances fusion while preserving posterior spinal elements [1,2,15]. The advantages of percutaneous translaminar facet screw fixation are that it is a safe, economical, efficient, and minimally invasive procedure [3].
Indications and contraindications
Box 31.1 lists the indications for and contraindications to percutaneous translaminar facet screw fixation.
Procedures
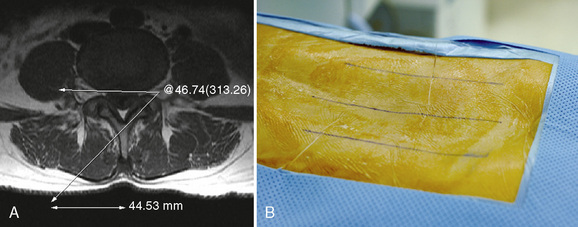
Preoperative Measurement of Laminar Angles
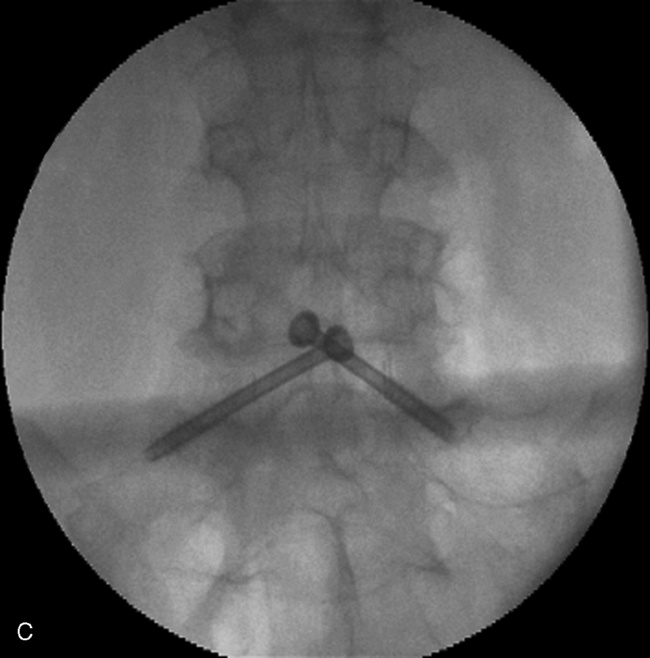
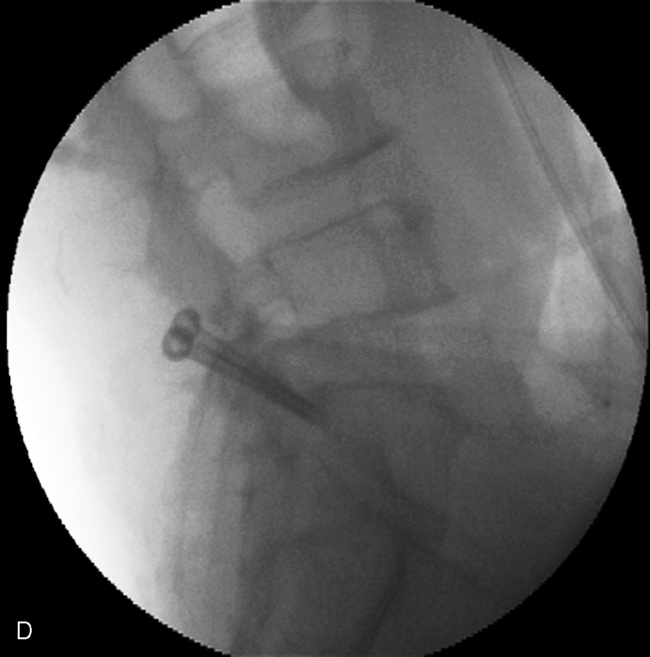
Intraoperative Measurement of Caudal Angle
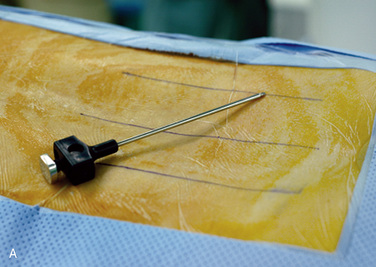
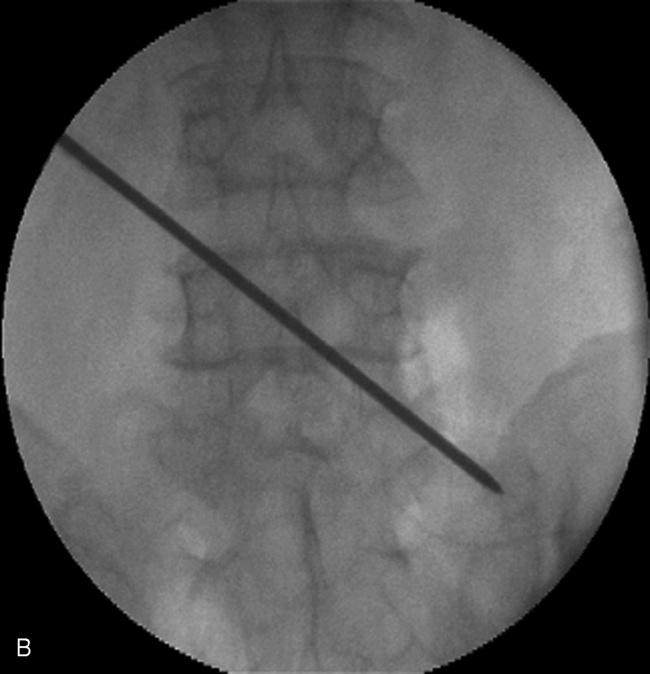
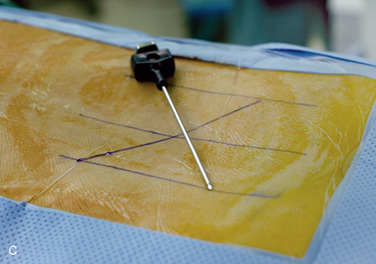
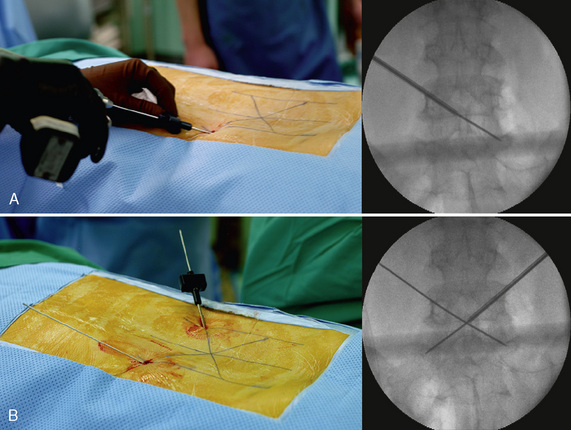
Insertion of the Translaminar Facet Screw
Postoperative management
CASE STUDY 31.1 Degenerative Spondylolisthesis At L4-L5 Treated With Mini-Open Alif Followed By Percutaneous Translaminar Facet Pedicle Screw Fixation
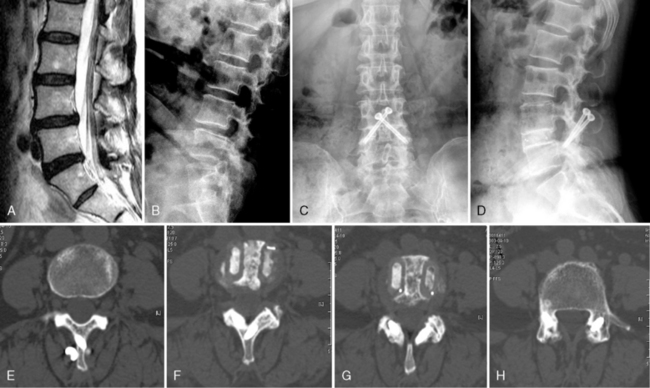
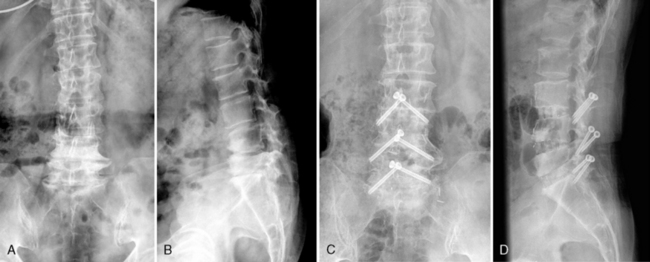
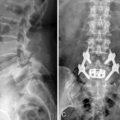
A 64-year-old woman with degenerative spondylolisthesis at L4-L5 was treated with mini-open ALIF followed by percutaneous translaminar facet pedicle screw fixation. Assessment computed tomography performed 2 years after the operation confirmed solid bony union in the cages and the grafts between them (Fig. 31-6).
CASE STUDY 31.2 Lumbar Degenerative Kyphosis Treated With Alif At L3-L4, L4-L5, and L5-S1 With Percutaneous Translaminar Facet Pedicle Screw Fixation
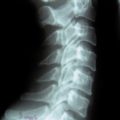
A 57-year-old woman with lumbar degenerative kyphosis was treated with ALIF at L3-L4, L4-L5, and L5-S1 with percutaneous translaminar facet pedicle screw fixation. Plain radiographs taken 1 year postoperatively showed restoration of the lumbar lordosis from the kyphotic deformity and solid bony union at the interbody spaces (Fig. 31-7).
CASE STUDY 31.3
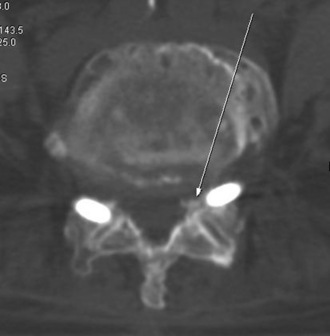
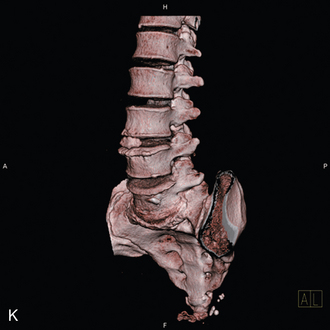
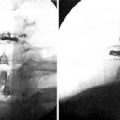
A 65-year-old woman with degenerative flat back deformity was treated with ALIF and percutaneous translaminar facet pedicle screw fixation at L5-S1. During the insertion of the Kirschner wire, repeated drilling was done to make a perfect path for the screw. The patient awoke with radicular pain and a fracture of the tip of the superior articular process of the sacrum. After a postoperative computed tomography scan showed compression of the exiting L5 root, revision surgery was performed to remove the fractured bony fragment. The screw was removed, and pedicle screw fixation was performed (Fig. 31-8).
1 Jang J.S., Lee S.H., Lim S.R. Guide device for percutaneous placement of translaminar facet screws after anterior lumbar interbody fusion. J Neurosurg. 2003;98:100-103.
2 Jang J.S., Lee S.H. Clinical analysis of percutaneous facet screw fixation after anterior lumbar interbody fusion. J Neurosurg Spine. 2005;3:40-46.
3 Shim C.S., Lee S.H., Jung B., et al. Fluoroscopically assisted percutaneous translaminar facet screw fixation following anterior lumbar interbody fusion: technical report. Spine. 2005;30:838-843.
4 Lund T., Oxland T.R., Jost B., et al. Interbody cage stabilization in the lumbar spine: biomechanical evaluation of cage design, posterior instrumentation and bone density. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1998;80:351-359.
5 Nibu K., Panjabi M.M., Oxland T., et al. Multidirectional stabilizing potential of BAK interbody spinal fusion system for anterior surgery. J Spinal Disord. 1997;10:357-362.
6 Oxland T.R., Hoffer Z., Nydegger T., et al. A comparative biomechanical investigation of anterior lumbar interbody cages: central and bilateral approaches. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000;82:383-393.
7 Rathonyi G.C., Oxland T.R., Gerich U., et al. The role of supplemental translaminar screws in anterior lumbar interbody fixation: a biomechanical study. Eur Spine J. 1998;7:400-407.
8 Volkman T., Horton W.C., Hutton W.C. Transfacet screws with lumbar interbody reconstruction: biomechanical study of motion segment stiffness. J Spinal Disord. 1996;9:425-432.
9 Benini A., Margerl F. Selective decompression and translaminar articular facet screw fixation for lumbar canal stenosis and disc protrusion. Br J Neurosurg. 1993;7:413-418.
10 Grob D., Humke T. Translaminar screw fixation in the lumbar spine: technique, indications, results. Eur Spine J. 1998;7:178-186.
11 Grob D., Rubeli M., Scheier H.J.G., et al. Translaminar screw fixation of the lumbar spine. Int Orthop. 1992;16:223-226.
12 Heggeness M.H., Esses S.I. Translaminar facet joint screw fixation for lumbar and lumbosacral fusion: a clinical and biomechanical study. Spine. 1991;16:S266-S269.
13 Humpke T., Grob D., Dvorak J., et al. Translaminar screw fixation of the lumbar and lumbosacral spine: a 5-year follow-up. Spine. 1998;23:1180-1184.
14 Jacobs R.R., Montesano P.X., Jackson R.P. Enhancement of lumbar spine fusion by use of translaminar facet joint screws. Spine. 1989;14:12-15.
15 Reich S.M., Kuflik P., Neuwirth M. Translaminar facet screw fixation in lumbar spine fusion. Spine. 1993;18:444-449.
16 Stonecipher T., Wright S. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion with facet-screw fixation. Spine. 1989;14:468-471.
17 Magerl F.P. Stabilization of the lower thoracic and lumbar spine with external skeletal fixation. Clin Orthop Relat Res.. 1984;189:125-141.
18 Ferrara L.A., Secor J.L., Jin B., et al. A biomechanical comparison of facet screw fixation and pedicle screw fixation: effect of short-term and long-term repetitive cycling. Spine. 2003;28:1226-1234.