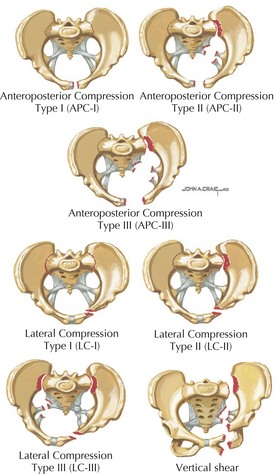
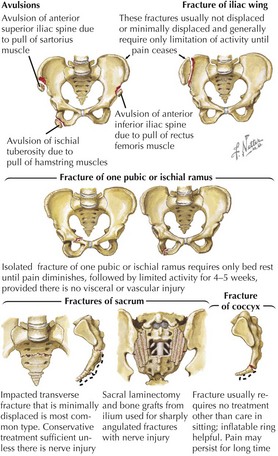
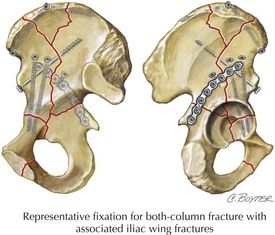
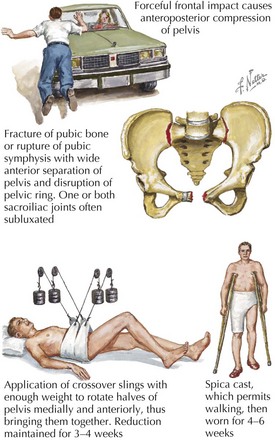
17 Pelvic Fractures
Anatomy of the Pelvic Skeleton
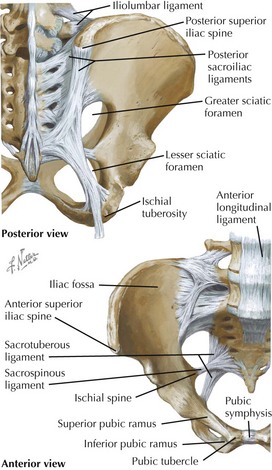
Coxal Bones (Os Coxae; 2)
Ilium: Parts and Landmarks
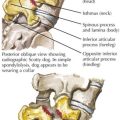
Sacrum
• Parts and landmarks: ala, sacroiliac articular surfaces, lumbosacral articular (disc) surface, promontory, fused bodies (5), anterior and posterior foramina, coccyx (~4 segments)
Neurovascular Supply
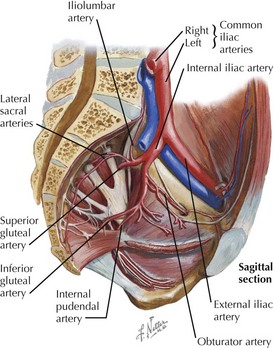
Nerves of the Pelvis
• Hilton’s law: nerves supplying a joint also innervate muscles acting across it, as well as skin over distal insertions of those muscles
• Sciatic nerve: anterior rami of L4, L5 (lumbosacral trunk), S1-S4, collect as trunk and pass out of greater sciatic foramen
• Sacral plexus
Arteries of the Pelvis
• Common iliac arteries and their internal and external iliac branches supply bones and viscera within the pelvic cavity.
Venous Drainage
• Pelvic walls and viscera drain largely into branches of internal and external iliac veins (caval venous return).
• Rectal plexus blood also drains into inferior mesenteric vein via superior rectal vein (portal venous return).