Pediatric Echocardiography
Technique
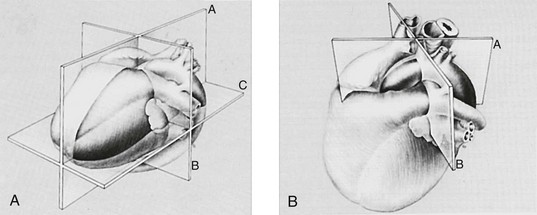
Transthoracic echocardiography is an ultrasound technique that is optimized for imaging the moving heart. Standard imaging windows that are free of interference from the lungs are illustrated in Figure 64-1. These windows allow imaging of the heart in multiple planes. These planes are based on the axes of the heart and not on the axes of the body (Fig. 64-2).
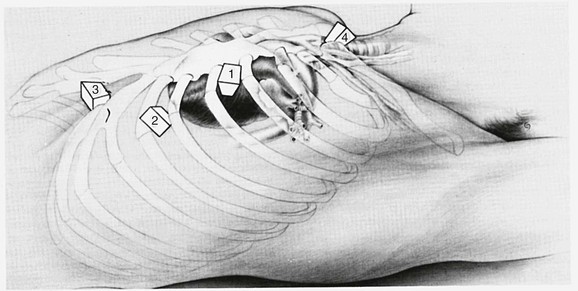
Figure 64-1 Probe positions for the four standard windows used in transthoracic echocardiography.
Position 1, parasternal; position 2, apical; position 3, subcostal; position 4, suprasternal. (From Snider AR, Serwer GA, Ritter SB: Echocardiography in pediatric heart disease. 2nd ed. St Louis: Mosby–Year Book; 1997.)
Assessment of ventricular systolic function is performed in every echocardiographic examination. Among the various techniques of quantifying left ventricular systolic function, the left ventricular shortening fraction is the most easily accomplished and universally used. Figure 64-3 illustrates this technique. Standards for left ventricular dimensions and shortening fraction according to body surface area are available in standard references. Assessment of left ventricular diastolic function is less exact, and techniques continue to be developed to evaluate this rather elusive entity. The method with the most promise is tissue Doppler imaging, which uses the Doppler principle to measure the high amplitude but low velocity signals derived from myocardial motion.
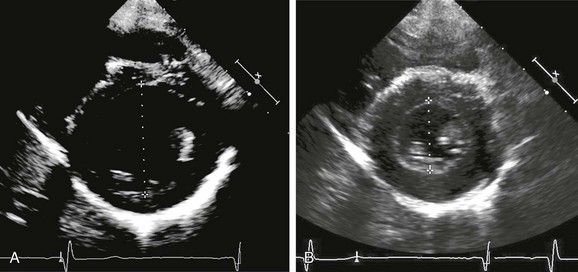
Figure 64-3 Parasternal short-axis views of the left ventricle at the midventricular level.
A, End-diastolic frame. B, End-systolic frame. Measurements of left ventricular end-diastolic dimension (LVEDD) (A) and left ventricular end-systolic dimension (LVESD) (B) are depicted. The cursor is placed perpendicular to the ventricular septum and the left ventricular free wall. Left ventricular shortening fraction is defined as (LVEDD – LVESD)/LVEDD × 100.
Formulating a Diagnosis
Once the images have been obtained, a comprehensive diagnosis must be constructed, which is accomplished by using the segmental approach to cardiac anatomy (see Chapter 63). A common template for reporting the findings of an echocardiogram is presented in Box 64-1. Note that the scheme is logical and largely follows the blood flow through the various segments of the heart.
Ayers, NA, Miller-Hance, W, Fyfe, DA, et al. Indications and guidelines for performance of transesophageal echocardiography in the patient with pediatric acquired or congenital heart disease: a report from the Task Force of the Pediatric Council of the American Society of Echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2005;18:91–98.
Eidem BW, Cetta F, O’Leary PW, eds. Echocardiography in pediatric and adult congenital heart disease. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2010.
Lai, WW, Geva, T, Shirali, GS. Guidelines and standards for the performance of a pediatric echocardiogram: a report from the Task Force of the Pediatric Council of the American Society of Echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2006;19:1413–1430.
Lai WW, Mertens L, Cohen MS, et al, eds. Echocardiography in pediatric and congenital heart disease: from fetus to adult. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley-Blackwell, 2009.
Lopez, L, Colan, SD, Frommelt, PC, et al. Recommendations for quantification methods during the performance of a pediatric echocardiogram: a report from the Pediatric Measurements Writing Group of the American Society of Echocardiography Pediatric and Congenital Heart Disease Council. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2010;23:465–495.