24 Patent ductus arteriosus
Salient features
History
• Bronchitis or dyspnoea on exertion in severe cases
• Take a maternal history of rubella, particularly in the first trimester
• Determine whether the patient was a premature baby or had a low birth weight. Remember the frequency of patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) in infants weighing 501–1500 g is 31% (Pediatrics 1993;91:540–5)
• Determine whether the patient was born in a place located at a high altitude.
Examination
• Collapsing pulse (caused by an aortic diastolic run-off)
• Systolic and/or diastolic thrill in the left second interspace
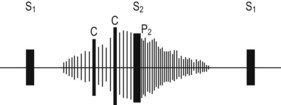
• Loud, continuous ‘machinery’ murmur, i.e. pansystolic and extending into early diastole—known as Gibson murmur—is heard along the left upper sternal border and outer border of the clavicle. The murmur begins after the first heart sound, peaks with the second sound, and trails off in diastole (Edinb Med 1890;8:1) (Fig. 24.1)
Advanced-level questions
Mention a few causes of continuous murmurs
How would you investigate this patient?
• ECG may be normal or shows left ventricular hypertrophy.
• Chest radiograph may be normal, or there may be left ventricular and left atrial enlargement. The chest film shows pulmonary plethora, proximal pulmonary arterial dilatation and a prominent ascending aorta. The ductus arteriosus may be visualized as an opacity at the confluence of the descending aorta and the aortic knob. If pulmonary hypertension develops, right ventricular hypertrophy is noted.
• Echocardiography can usuually visualize the ductus arteriosus. Doppler studies demonstrate continuous flow in the pulmonary trunk.
• Cardiac catheterization is useful to determine the presence and severity of the shunt and determines pulmonary vascular resistance. Angiography defines its anatomy.
What are complications?
• Congestive cardiac failure is the commonest complication.
• Infective endocarditis or endarteritis (involves the pulmonary side of the ductus arteriosus or the pulmonary artery opposite the duct orifice, from which septic pulmonary emboli may arise).
• Pulmonary hypertension and reversal of shunt (causes differential cyanosis and clubbing, i.e. toes—not fingers—are clubbed and cyanosed).
• Substantial left-to-right shunting through the ductus in infants may increase the risk of intraventricular haemorrhage, necrotizing enterocolitis, bronchopulmonary dysplasia and death.
• The ductus may become aneurysmal and calcified, which may lead to its rupture
How would you manage such patients?
• Within 1–3 weeks of birth: administer a prostaglandin E synthesis inhibitor such as indometacin or ibuprofen. Ibuprofen is as effective as indometacin but is associated with a lower incidence of renal toxic effects (N Engl J Med 2000;343:674–81).
• PDA can be closed percutaneously by two types of device: coils (e.g. Gianturco-Grifka Vascular Occlusion Device, Nit-Occlud PDA occluder) or occluders (e.g. Amplatzer PDA occluder).
• Surgery is required in children or adults with large shunts: ligation or division of the PDA.
Notes
• Because of the risk of endarteritis associated with unrepaired PDA (estimated at 0.45% annually after the second decade of life) and the low risk associated with ligation (mortality of <0.5%), it is recommended that even a small PDA be ligated surgically or occluded with a percutaneously placed closure device.
• Once severe pulmonary vascular obstructive disease develops, surgical ligation or percutaneous closure is contraindicated.