Antrectomy with gastroduodenostomy
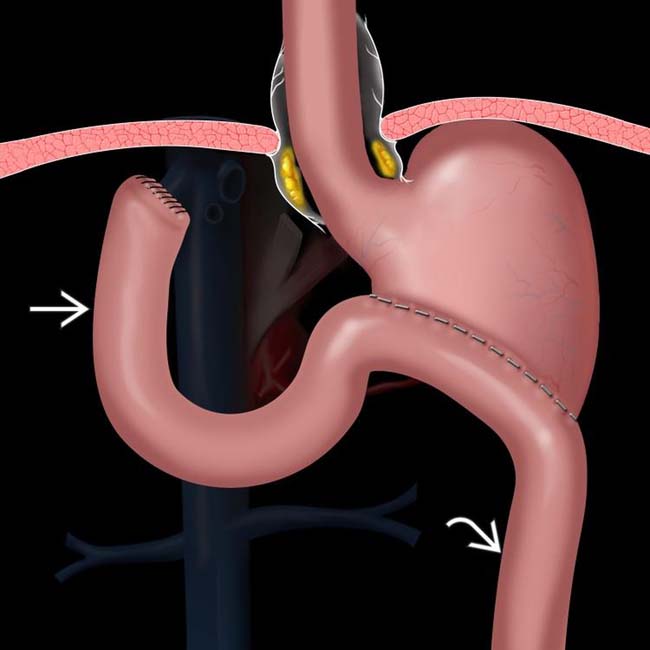
 , composed of the duodenum and a variable length of jejunum, carries pancreaticobiliary secretions toward the stomach, while the efferent limb
, composed of the duodenum and a variable length of jejunum, carries pancreaticobiliary secretions toward the stomach, while the efferent limb  carries fluid and food downstream.
carries fluid and food downstream.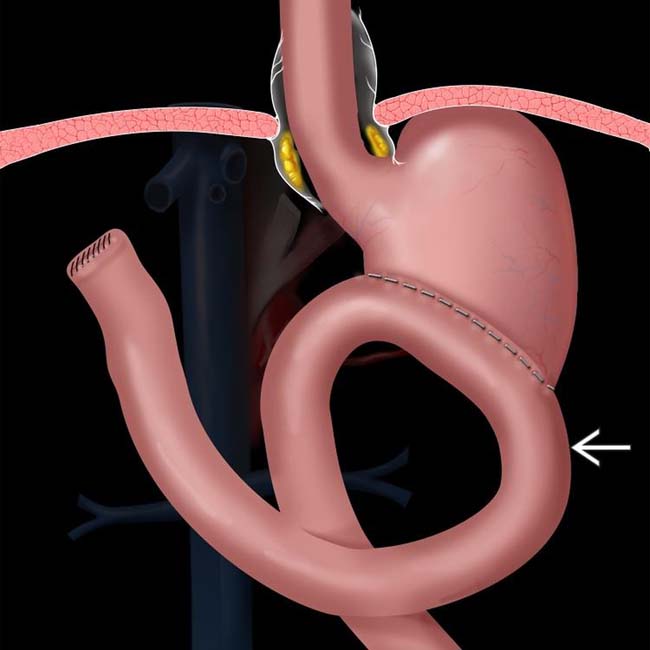
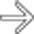 enters the anastomosis from a left-to-right direction. This procedure is intended to reduce the prevalence of bile gastritis.
enters the anastomosis from a left-to-right direction. This procedure is intended to reduce the prevalence of bile gastritis.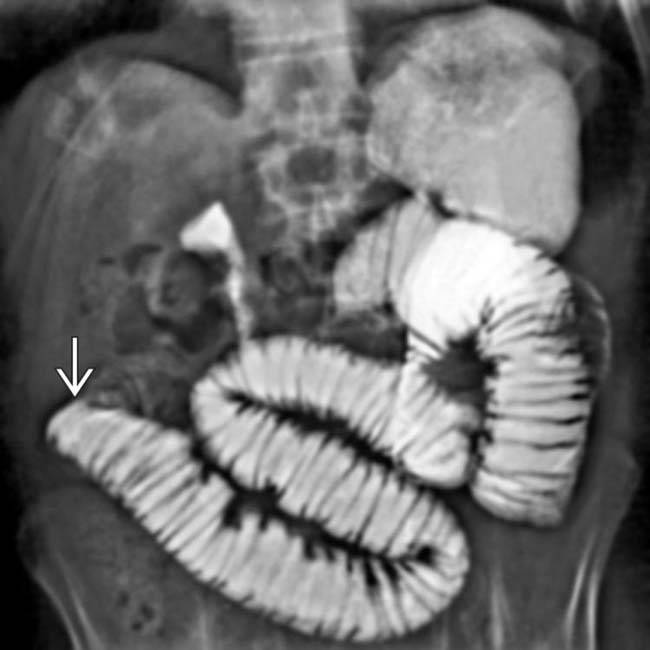
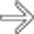 . At surgery, a phytobezoar was removed, which corresponded to the shape and size of the gastric remnant.
. At surgery, a phytobezoar was removed, which corresponded to the shape and size of the gastric remnant.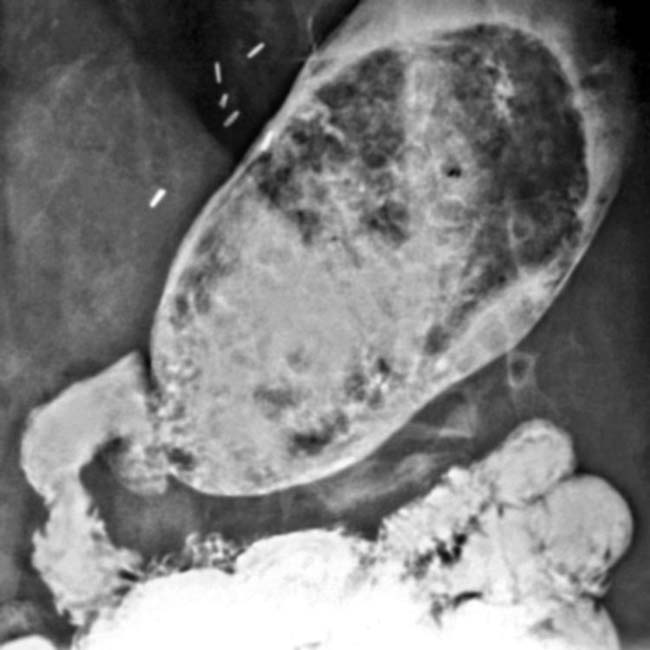
IMAGING
General Features
• Many to most fluoroscopic exams of esophagus, stomach, and duodenum are now performed for patients who have surgically altered anatomy
Surgical Procedures
• Billroth 2 (B2) procedure
Complications
• Recurrent or new carcinoma
• Anastomotic leak
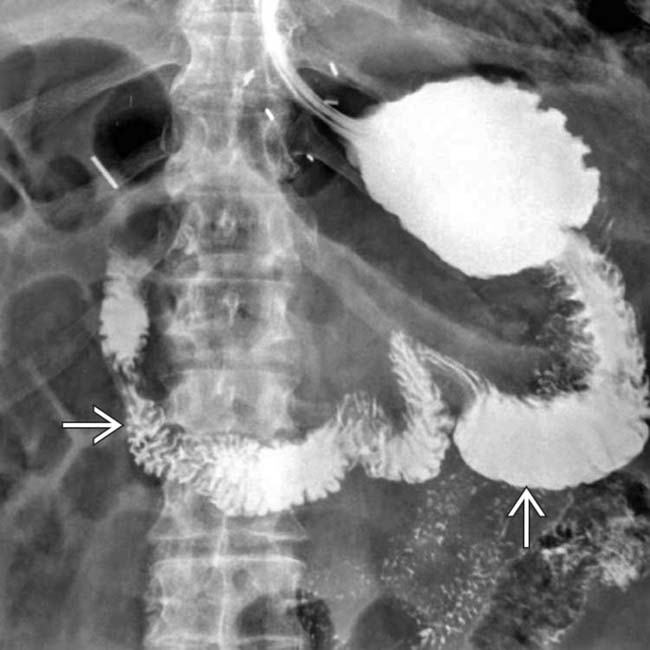
 and delayed and decreased filling of the efferent limb.
and delayed and decreased filling of the efferent limb.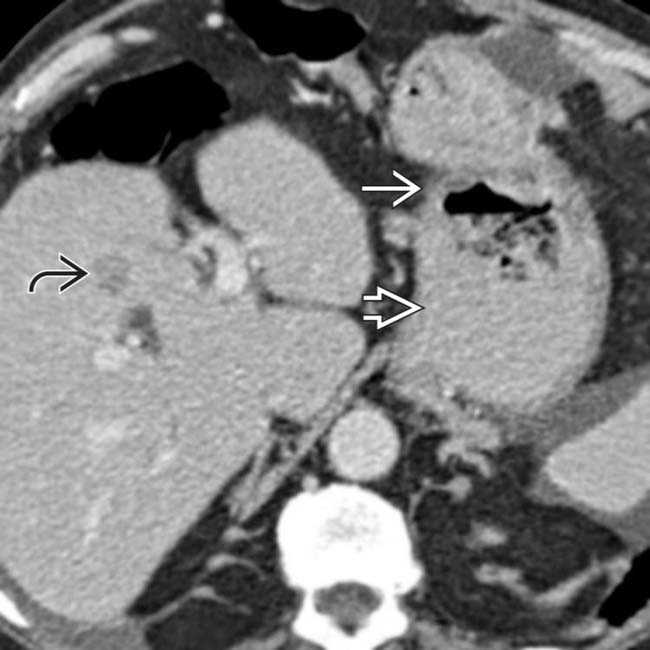
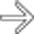
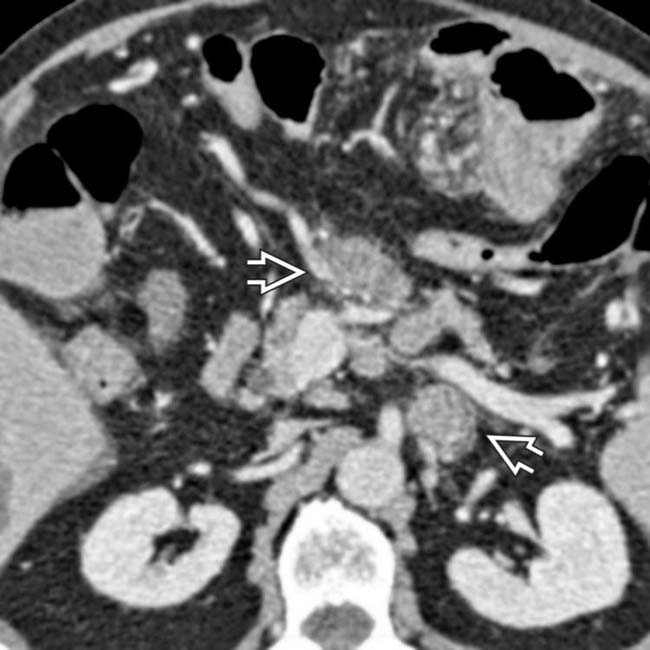
 near the gastroenteric anastomosis
near the gastroenteric anastomosis  , due to gastric carcinoma. Liver metastases are evident
, due to gastric carcinoma. Liver metastases are evident  .
.
 from lymphatic metastases.
from lymphatic metastases.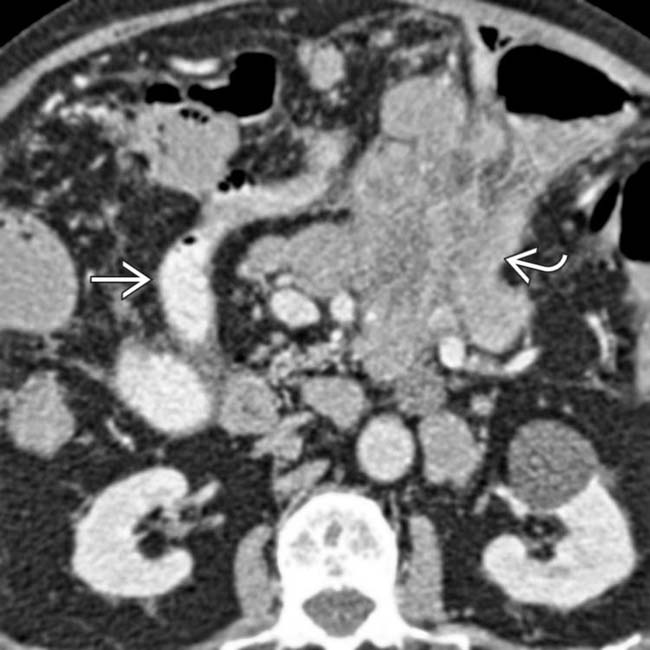
 . The contrast-filled lumen of the afferent limb is seen
. The contrast-filled lumen of the afferent limb is seen  . Gastric cancer occurs with increased frequency following this type of ulcer surgery, usually 15 or more years later.
. Gastric cancer occurs with increased frequency following this type of ulcer surgery, usually 15 or more years later.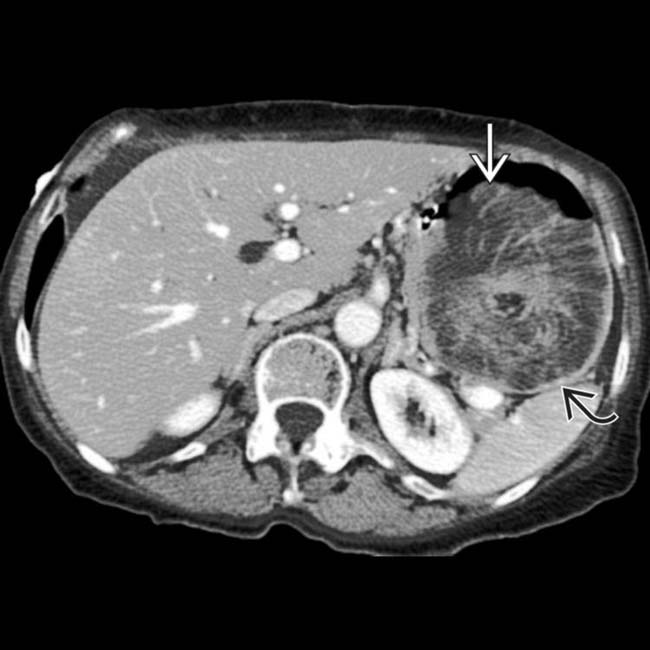
 within the distended gastric remnant
within the distended gastric remnant  .
.






















































































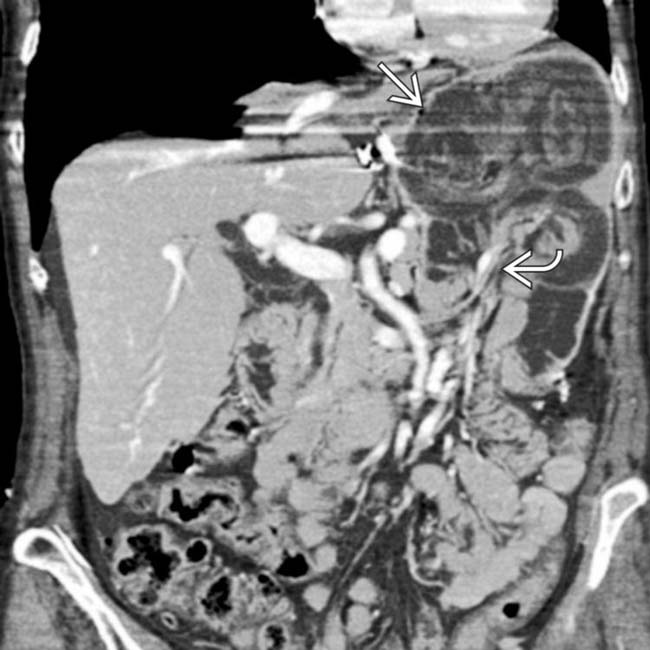
 with invagination of bowel, mesenteric fat, and vessels
with invagination of bowel, mesenteric fat, and vessels  into the gastric remnant (intussuscipiens). This is a rare complication but may result in bowel obstruction and ischemia.
into the gastric remnant (intussuscipiens). This is a rare complication but may result in bowel obstruction and ischemia.


