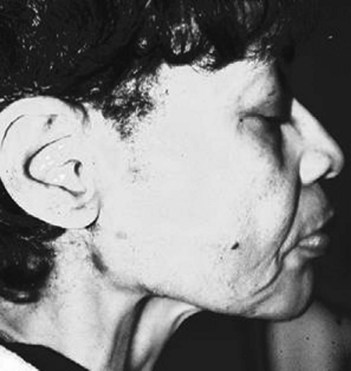
230 Parotid enlargement
Salient features
Questions
Advanced-level questions
Mention a few causes of keratoconjunctivitis sicca
• Primary keratoconjunctivitis sicca is common and characterized by involvement of the lacrimal gland alone.
• Primary Sjögren syndrome is an autoimmune disorder that is usually positive for rheumatoid factor, anti-nuclear antibodies and hypergammaglobulinaemia. Less frequently, autoantibodies to DNA, salivary gland, smooth muscle and gastric parietal cells are present. There may be associated dry mouth and bronchial epithelium, and the vagina may also be affected. Histopathogically the glands show intralobar ductal epithelial hyperplasia and lymphocytic infiltration of the gland.
• Secondary Sjögren syndrome is the presence of keratoconjunctivitis sicca in association with a systemic disorder such as the following:
How are parotid secretions carried into the oral cavity?
By Stensen’s duct, which opens just opposite the upper second molar tooth.