10 Palpitations
Salient features
History
• How old are you? Supraventricular tachycardias (SVT), particularly ones that use a bypass tract (atrioventricular re-entry tachycardia) may be experienced in earlier life. Atrial fibrillation, flutter, atrial tachycardia and ventricular tachycardia (VT) tend to occur later in life associated with structural heart disease.
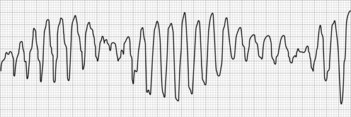
• Are the palpitations regular or irregular? Patients should be asked to tap out the rhythm or choose from cadences tapped by the clinician. (Rapid regular rhythms suggest SVT or VT whereas rapid, irregular rhythms suggest atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter or tachycardia with varying block.)
• Is the onset abrupt (paroxysmal tachyarrhythmias)?
• How frequent are the palpitations?
• Do you have palpitations at work? (More likely to be a cardiac arrhythmia.)
• Do the palpitations start on sleeping or on termination of exercise? (Both these are states of increased vagal tone suggesting vagally mediated atrial fibrillation or certain subtypes of long-QT syndrome.)
• What is the duration of each episode? (palpitations lasting <5 min makes the diagnosis of cardiac arrhythmia slightly less likely) (JAMA 2009;302:2135–43).
• Is there accompanying pounding sensation in the neck? (The presence of regular rapid pounding sensation in the neck or visible neck pulsations increases the likelihood of atrioventricular nodal re-entry tachycardia when contraction of the atria against closed atrioventricular valves produces increased right atrial pressures and reflux of blood into the inferior vena cava.)
• Is each episode followed by polyuria? (Seen in supraventricular tachycardia.)
• Is there any relation to exercise? (For example, polymorphic VT in long-QT syndrome.)
• What happens on standing? (Postural hypotension, atrioventricular nodal tachycardia.)
• Are there any precipitating factors such as coffee, tea, alcohol or medications such as thyroid extract, ephedrine, aminophylline, monoamino oxidase inhibitors?
• Are there any associated symptoms such as chest pain or shortness of breath?
• Associated shirt flapping, which is defined as visible movements of patients’ clothes during the episode (described with both atrioventricular node re-entry tachycardia and atrioventricular re-entry tachycardia).
• Is there associated syncope? (Dizziness, or syncope accompanying palpitations should prompt a search for ventricular tachycardia.)
• Are the palpitations associated with anxiety or panic attacks? (Anxiety or panic can result in palpitations; a known history of panic disorder makes diagnosis of cardiac arrhythmia slightly less likely.)
• Is there a family history of palpitations, especially history of atrial fibrillation or a diagnosis of arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy?
Examination
• Check the pulse for arrhythmia.
• JVP is distended in heart failure and ‘frog’ sign in atrioventricular node re-entry tachycardia (Lancet 1993;341:1254–8). The presence of cannon A waves suggests associated atrioventricular dissociation such as VT.
• Auscultate the heart for murmurs (mitral valve prolapse, valvular heart disease, harsh systolic murmur of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy), split second heart sound (atrial fibrillation).
• Look for signs of atrial fibrillation.
• Although palpitations may not be present at rest, when the ventricular response is slow, a brisk walk down the corridor may result in palpitations.
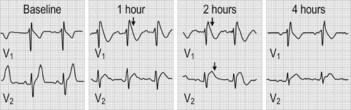
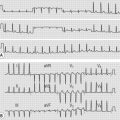
• Tell the examiner that you would like to examine the ECG for:
Questions
How would you investigate a patient suspected of having a disorder of cardiac rhythm?
• 12-lead ECG (look for evidence of a rhythm disturbance and pre-excitation syndrome)
• Continuous ambulatory (Holter) echocardiography (many patients with palpitations may have stable sinus rhythm)
• Exercise ECG particularly in those whose palpitations occur on exercise or are provoked by cardiac ischaemia
• Loop monitors have the highest diagnostic yield (34–84%) for diagnosing arrhythmia.