Breast Pain
Pain in the breast is a common symptom in general surgical practice. Most cases are benign and due to cyclical mastalgia, but occasionally pain may be the presenting symptom of carcinoma.
History
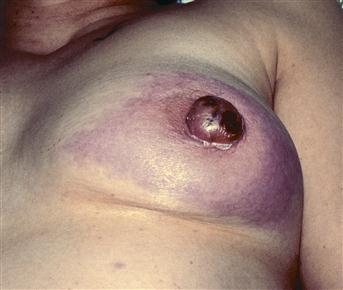
Cyclical mastalgia causes soreness, frequently in the upper and outer quadrants of the breast in the week preceding a period. The pain usually disappears after the period and there is freedom from soreness or pain for two weeks, when it recommences. Symptoms are common in the 20–45-year age group. Non-cyclical mastalgia may occur and is more common in the fourth and fifth decades. Duct ectasia occurs in the fifth decade. The pain is usually behind the nipple and associated with subareolar erythema and a thick, creamy nipple discharge. Fat necrosis will be suggested by a history of trauma, which occasionally the patient will be embarrassed to admit (often the partner’s teeth!). Breast abscess or mastitis will be obvious. It usually occurs during pregnancy or lactation but it may occur in a retroareolar position in a patient with duct ectasia. Breast fullness and soreness is a symptom of early pregnancy. Patients may indicate breast pain where the condition is not actively in the breast but behind it. Tietze’s disease (costochondritis of the costal cartilages) will present with pain related to the breast. Mondor’s disease (superficial thrombophlebitis of the subcutaneous veins of the chest wall) also presents with pain in the breast. It may be associated with an underlying carcinoma. Rib secondaries may also present with pain behind the breast. Herpes zoster may present with pain radiating round into the breast and precedes the development of a vesicular eruption by 2–3 days.
Examination
A hard, irregular lump is suggestive of carcinoma (this is discussed in the section on Breast lumps). Tenderness and lumpiness, occasionally with a smooth, mobile swelling (cyst), is suggestive of cyclical mastalgia. The tenderness and lumpiness is most often palpated in the upper and outer quadrants of the breast. In the early stages of fat necrosis, there may be bruising over the breast and the lump is tender. In the later stages, it becomes hard and irregular and may be tethered to the skin. Breast abscess will present with redness, swelling, heat and pain in the breast during pregnancy or, more commonly, lactation. The swelling will be fluctuant and usually there is associated fever. Duct ectasia presents with subareolar erythema, tenderness and occasionally a subareolar lump. Nipple retraction may be present in longstanding cases and there may be a thick, creamy discharge that can be expressed from the nipple. Pregnancy will present with fullness of the breast and increased circumareolar pigmentation. In Tietze’s disease, there will be tenderness, and occasionally swelling over the second, third and fourth costal cartilages. In Mondor’s disease, the veins of the chest wall are felt as red, tender cords, often extending onto the anterior axillary fold. The breast should be carefully checked for an underlying mass, as the condition may be associated with carcinoma of the breast. Herpes zoster will usually present with a characteristic vesicular eruption a few days after the pain.
General Investigations
■ FBC, ESR
WCC ↑ mastitis and breast abscess. ESR ↑ widespread carcinoma.
■ LFTs
Alkaline phosphatase may be raised with liver or bony secondaries.
■ Serum calcium
May be raised with bone secondaries.
■ Swab
C&S if there is any discharge from an abscess or from the nipple.
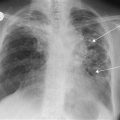
■ CXR
Secondaries in lung or ribs. Pleural effusion in carcinoma.