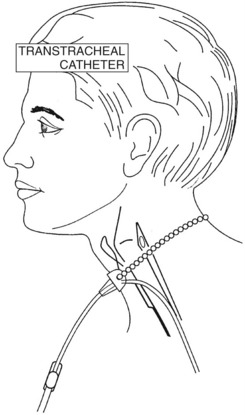
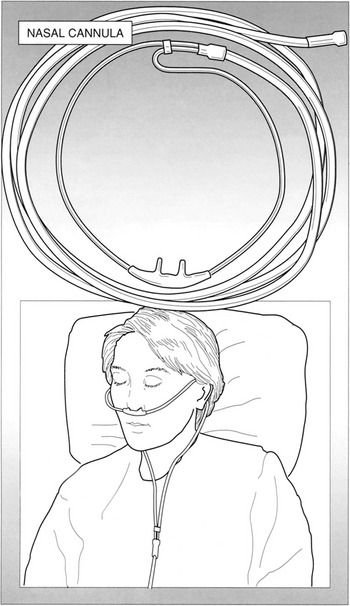
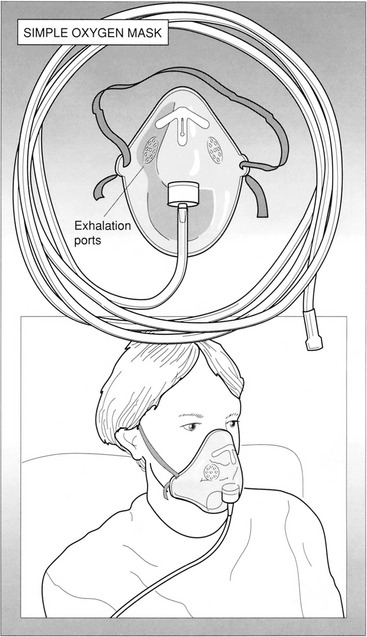
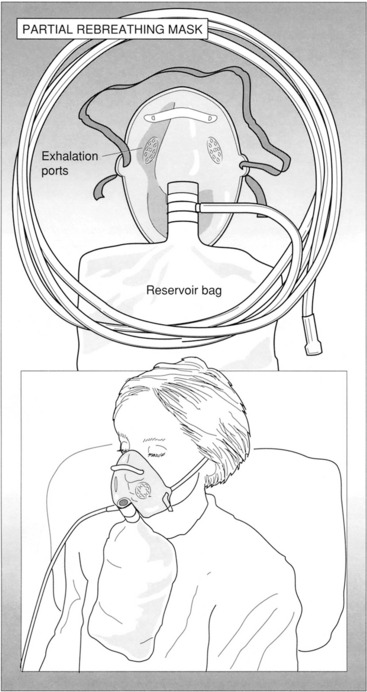
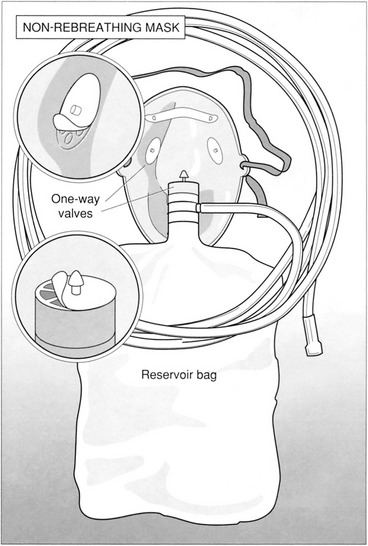
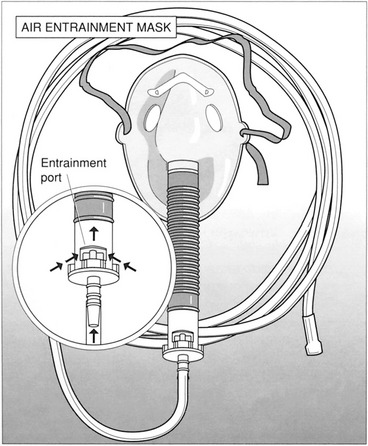
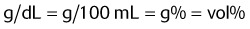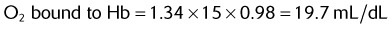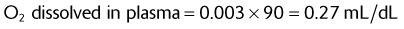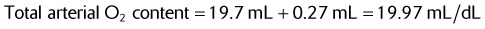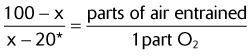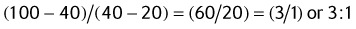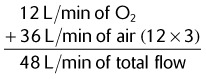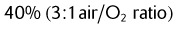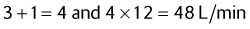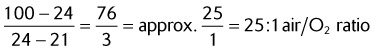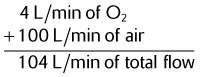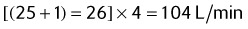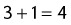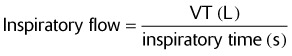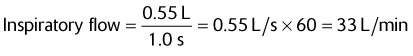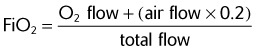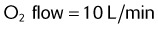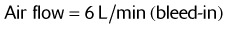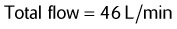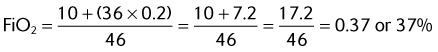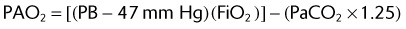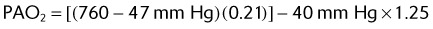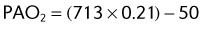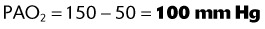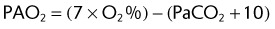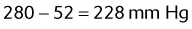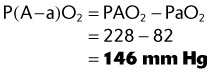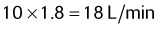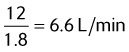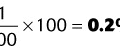CHAPTER 1 OXYGEN AND MEDICAL GAS THERAPY
PRETEST QUESTIONS
1. A patient is receiving oxygen from an “E” cylinder at 4 L/min through a nasal cannula. The cylinder pressure is 1900 psig. How long will the cylinder run until it is empty?
2. After setting up a partial rebreathing mask on a patient at a flow of 8 L/min, the reservoir bag collapses before the patient finishes inspiring. The respiratory care practitioner should do which of the following?
3. A patient with carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning can best be treated with which of the following therapies?
4. The following blood gas levels have been obtained from a patient using a 60% aerosol mask.
What should the respiratory care practitioner recommend at this time?
5. Given the following data, what is the patient’s total arterial O2 content?
6. A patient is using a 30% Venturi mask at an O2 flow of 5 L/min. The total flow delivered by this device is which of the following?
See answers and rationales at the back of the text.
REVIEW
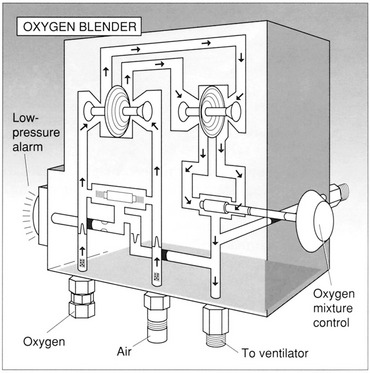
I. STORAGE AND CONTROL OF MEDICAL GASES
CRT Exam Content Matrix: IIA9a
| Gas | Color of Cylinder |
|---|---|
| Oxygen | Green; white (internationally) |
| Helium | Brown |
| Carbon dioxide | Gray |
| Nitrous oxide | Light blue |
| Cyclopropane | Orange |
| Ethylene | Red |
| Air | Yellow |
| CO2/O2 | Gray and green |
| He/O2 | Brown and green |
Air is drawn into the compressor, where it travels to a reservoir tank. From this tank, the air passes through a dryer to remove moisture and on to a pressure-reducing valve, which reduces the pressure to 50 psig to power a compressed-air wall outlet. As the piston drops, gas is drawn in through a one-way intake valve. On the upstroke, the intake valve closes and gas exits through a one-way outflow valve. Piston air compressors are seen most commonly on large medical air piping systems.
A diaphragm is used instead of a piston. On the downstroke, the flexible diaphragm bends downward, drawing air through a one-way intake valve. On the upstroke, air is forced out the one-way outflow valve. Diaphragm air compressors are commonly used on O2 concentrators and portable air compressors.
CRT Exam Content Matrix: IIA1a-c, IIA9a-b, IIA12a-b, IIID2d, IIID6, IIIE10, IIIF2d1-2, IIIG2c
RRT Exam Content Matrix: IIA4b
| Age (yr) | Normal PaO2 |
|---|---|
| ≤60 | 80 mm Hg |
| 70 | 70 mm Hg |
| 80 | 60 mm Hg |
EXAMPLE:
Given the following information, calculate the patient’s total arterial O2 content.
| Arterial Blood Gas Study Results | |
|---|---|
| pH | 7.42 |
| PCO2 | 41 mm Hg |
| PO2 | 90 mm Hg |
| SaO2 | 98% |
| Hb | 15 g/dL |
*
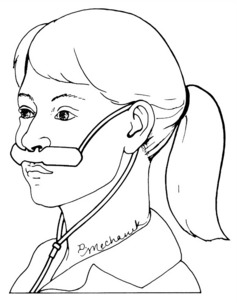
FIGURE 1-11 Nasal reservoir cannula.
From Scanlan C, Wilkins R, Stoller J: Egan’s fundamentals of respiratory care, ed 8, St Louis, 2003, Mosby.
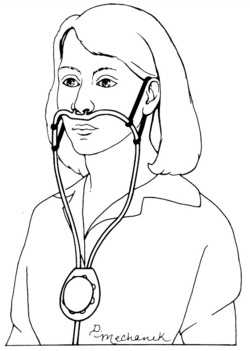
FIGURE 1-12 Pendant reservoir cannula.
From Scanlan C, Wilkins R, Stoller J: Egan’s fundamentals of respiratory care, ed 8, St Louis, 2003, Mosby.
| O2 Percentage | Air/O2 Entrainment Ratio |
|---|---|
| 24% | 25 : 1 |
| 28% | 10 : 1 |
| 30% | 8 : 1 |
| 35% | 5 : 1 |
| 40% | 3 : 1 |
| 45% | 2 : 1 |
| 50% | 1 : 7 : 1 |
| 60% | 1 : 1 |
| These ratios may be calculated by the following formula: | |
*Use 21 with percentages less than 40%.
EXAMPLE:
| 20 | 60 | |
| 40 | ||
| 100 | 20 |
EXAMPLE:
![]() Exam Note
Exam Note
To determine a patient’s inspiratory flow, use the following equation:
The flow will be in L/s, so multiply by 60 to change to L/min.
CRT Exam Content Matrix: IB9k, IB10k
RRT Exam Content Matrix: IB10l
(47 mm Hg is the level of water vapor pressure at body temperature)
![]() Exam Note
Exam Note
A patient using a 40% air entrainment mask has the following arterial blood gas (ABG) levels:
What is this patient’s A−a gradient? (PB = 747 mm Hg)
CRT Exam Content Matrix: IIIF2e1-2
RRT Exam Content Matrix: IB9k, IB10k, IIA8, IIIF2c1-2
CRT Exam Content Matrix: IIA2,4, IIC2, IIIE10
RRT Exam Content Matrix: IIA10, IIC2
VII. OXYGEN SATURATION MONITORING (PULSE OXIMETRY)
CRT Exam Content Matrix: IA7e, IB9c, o, IB10c, o, r, IC7, IIA20, IIIA1b5, IIIE3b, IIIE4d
RRT Exam Content Matrix: IA7e, IB9c, p, IB10c, q, IC8, IIIA1b5
VIII. CO-OXIMETRY (HEMOXIMETRY)
CRT Exam Content Matrix: IB10j, IIA24, IIC2, IIIE3c, IIIE4b
RRT Exam Content Matrix: IB9j, IB10j, IIA10, IIC2, IIIE3b
Transcutaneous oxygen monitoring is covered in Chapter 13 on neonatal and pediatric respiratory care.
POSTCHAPTER STUDY QUESTIONS
1. List the air/O2 ratios for 60% O2, 40% O2, 35% O2, 30% O2, and 24% O2.
2. Give four examples of high-flow O2 delivery devices.
3. What is the primary benefit of using a reservoir cannula?
4. Calculate total O2 content, given the following ABG test results:
5. What is the total flow delivered by an aerosol mask on 60% O2, running at 12 L/min?
6. List the three ventilatory criteria that should be met by patients receiving O2 from a low-flow device.
7. An 80 : 20 mixture of helium/O2 running through an O2 flowmeter at 6 L/min is delivering how much flow to the patient?
8. Calculate how long an “E” cylinder with 1900 psig will run at 5 L/min.
9. Give examples of three low-flow O2 delivery devices.
10. List five conditions that affect the accuracy of pulse oximeters.
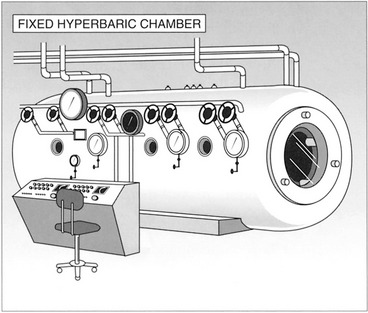
11. List five indications for the use of hyperbaric O2 therapy.
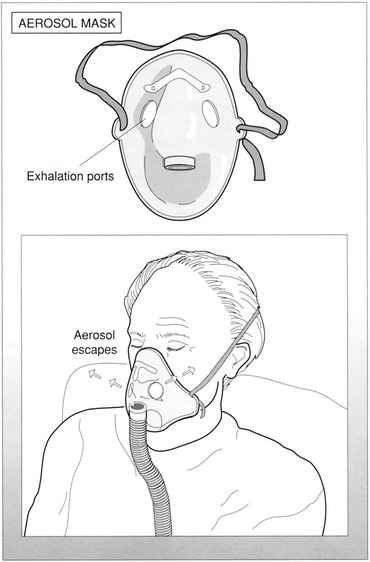
12. How does water in the aerosol tubing of a mask affect the delivered FiO2?
13. The physician orders O2 therapy for a patient with a VT of 400 mL and an inspiratory time of 0.5 s. What flow must the mask deliver to meet this patient’s inspiratory flow demands?
Cairo J, Pilbeam S. Mosby’s respiratory care equipment, ed 8. St Louis: Mosby; 2009.
Fink J, Hunt G. Clinical practice in respiratory care. Philadelphia: JB Lippincott; 1999.
Hess D, Respiratory care principles and practice, ed 1, Philadelphia, Saunders, 2002.
Malley W. Clinical blood gases: assessment and intervention, ed 2. St Louis: Saunders; 2005.
Scanlan C, Wilkins R, Stoller J. Egan’s fundamentals of respiratory care, ed 8. St Louis: Mosby; 2003.
Wilkins RL, Stoller JK, Kacmarek R. Egan’s fundamentals of respiratory care, ed 9. St Louis: Mosby; 2009.
Wilkins RL, Stoller JK, Scanlan C. Egan’s fundamentals of respiratory care, ed 8. St Louis: Mosby; 2003.