Borderline Ovarian Tumor
Synonyms/Description
Etiology
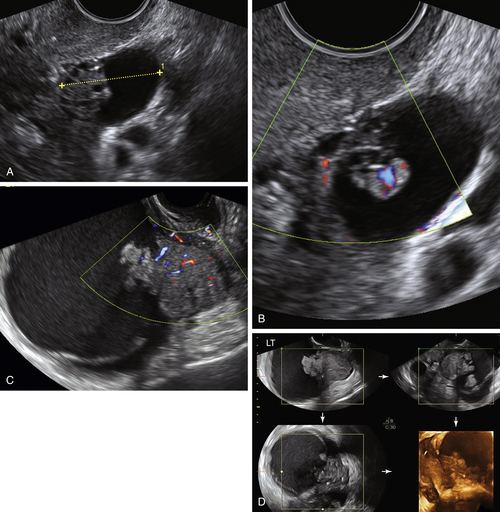
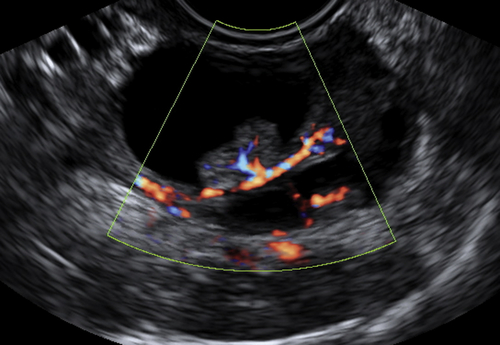
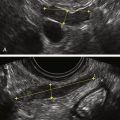
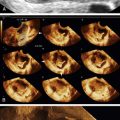
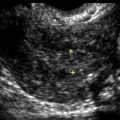
Ultrasound Findings
Differential Diagnosis
Clinical Aspects and Recommendations
Figures
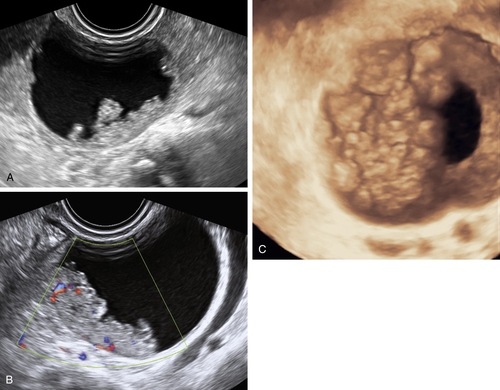
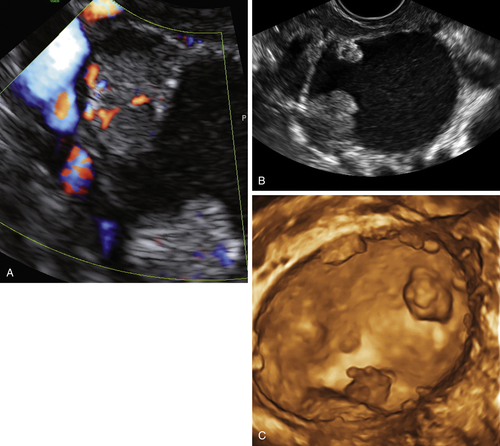
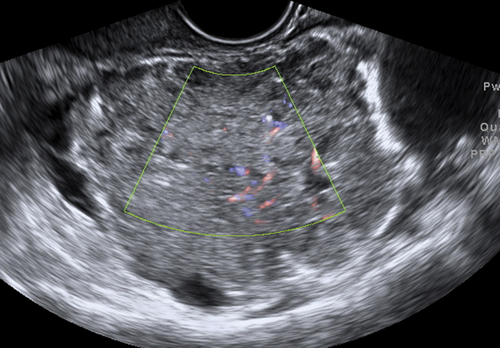
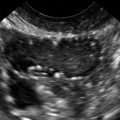
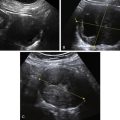
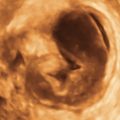
Figure B2-1 A papillary serous cystadenoma with irregular nodularity. A, The lateral side of the mass. B, The medial side with thicker nodularity. Note the modest blood flow in the solid areas, less than would be expected in a more aggressive tumor. C, A 3-D image of the surface texture of the inner aspect of the tumor.
Suggested Reading
Behtash N., Modares M., Abolhasani M., Ghaemmaghami F., Mousavi M., Yarandi F., Hanjani P. Borderline ovarian tumours: clinical analysis of 38 cases. J Obstet Gynaecol.. 2004;24:157–160.
Fruscella E., Testa A.C., Ferrandina G., De Smet F., Van Holsbeke C., Scambia G., Zannoni F.G., Ludovisi M. Ultrasound features of different histopathological subtypes of borderline ovarian tumors. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2005;26:644–650.
Morice P., Uzan C., Fauvet R., Gouy S., Duvillard P., Darai E. Borderline ovarian tumour: pathological diagnostic dilemma and risk factors for invasive or lethal recurrence. Lancet Oncol.. 2012;13:103–115.
Tropé C.G., Kaern J., Davidson B. Borderline ovarian tumours. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2012;26:325–336.