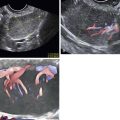
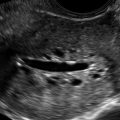
Fibroma (Ovarian), Thecoma, and Fibrothecoma
Synonyms/Description
Etiology
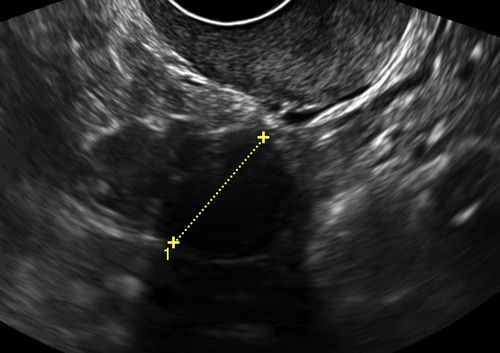
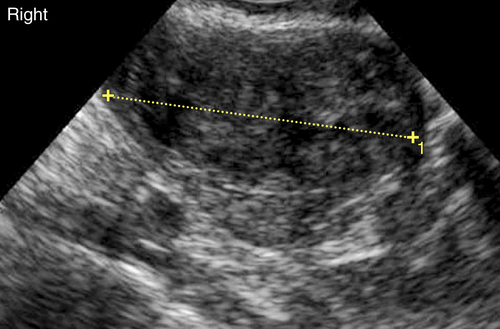
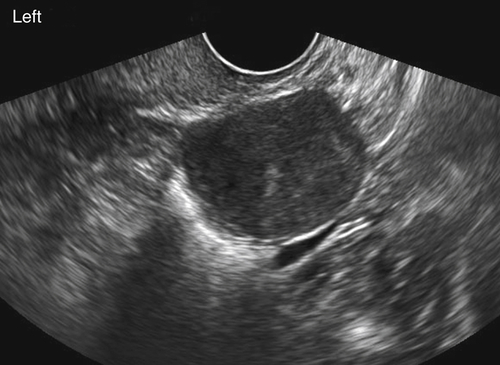
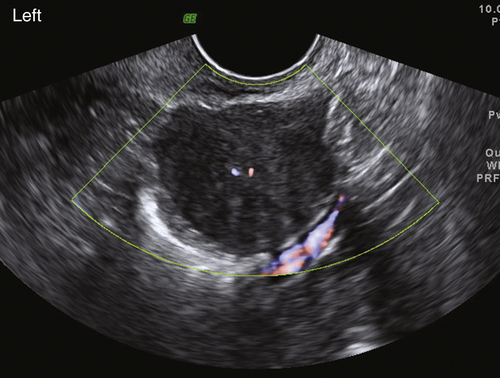
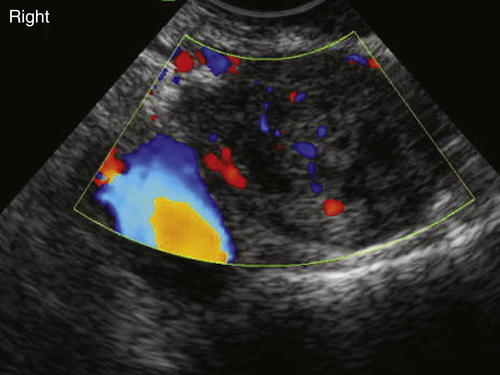
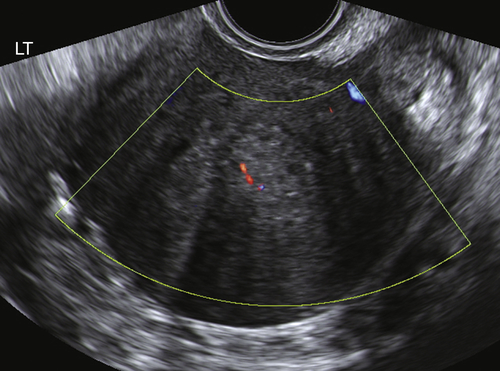
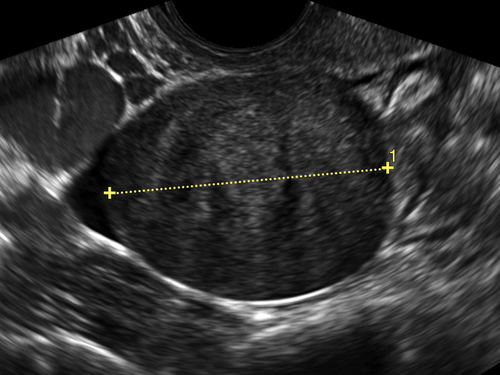
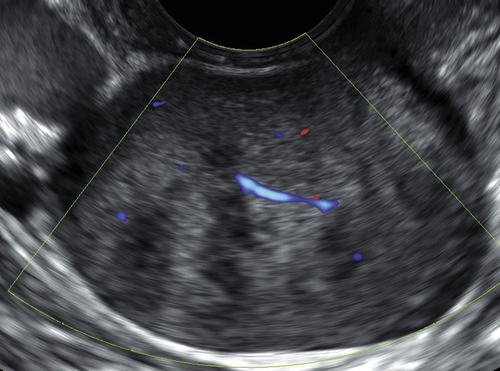
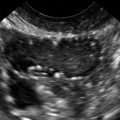
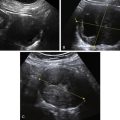
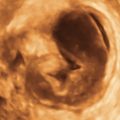
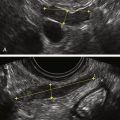
Ultrasound Findings
Differential Diagnosis
Clinical Aspects and Recommendations
Figures
Suggested Reading
Chechia A., Attia L., Temime R.B., Makhlouf T., Koubaa A. Incidence, clinical analysis, and management of ovarian fibromas and fibrothecomas. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2008;199 473.e1-4.
Conte M., Guariglia L., Benedetti Panici P., Scambia G., Rabitti C., Capelli A., Mancuso S. Ovarian fibrothecoma: sonographic and histologic findings. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 1991;32:51–54.
Paladini D., Testa A., Van Holsbeke C., Mancari R., Timmerman D., Valentin L. Imaging in gynecological disease (5): clinical and ultrasound characteristics in fibroma and fibrothecoma of the ovary. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2009;34:188–195.
Yaghoobian J., Pinck R.L. Ultrasound findings in thecoma of the ovary. J Clin Ultrasound. 1983;11:91–93.
Yen P., Khong K., Lamba R., Corwin M.T., Gerscovich E.O. Ovarian fibromas and fibrothecomas. J Ultrasound Med. 2013;32:13–18.