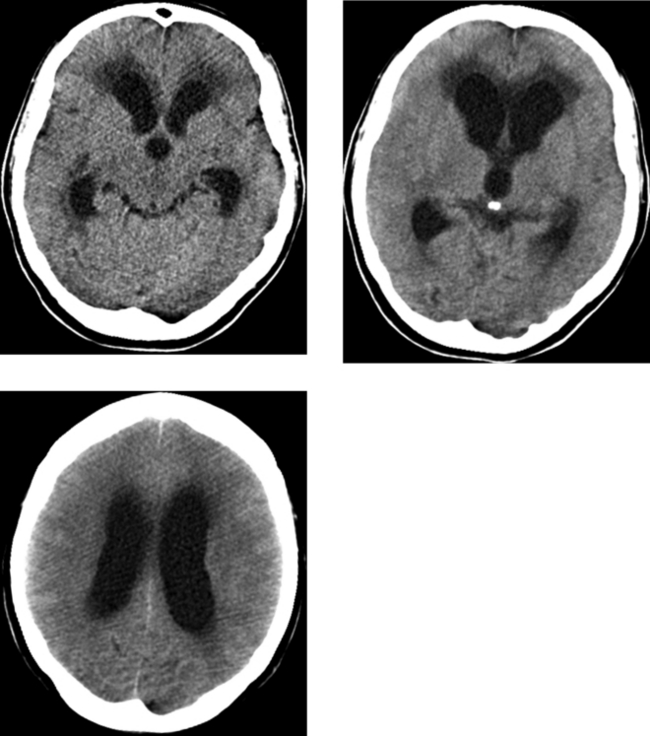
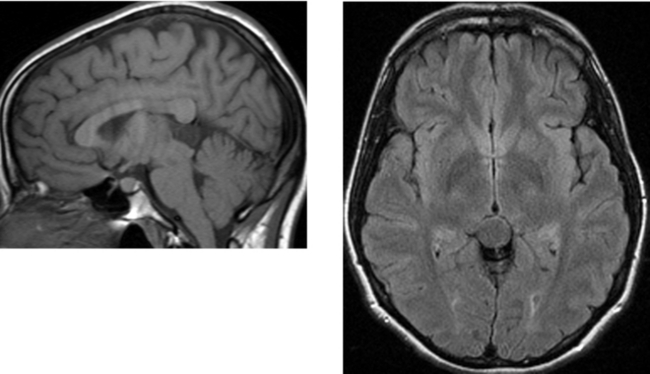
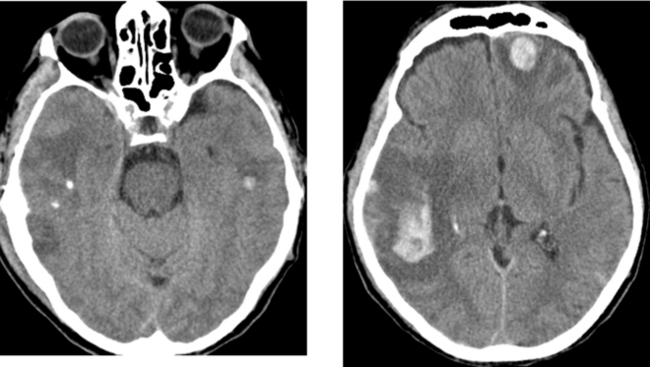
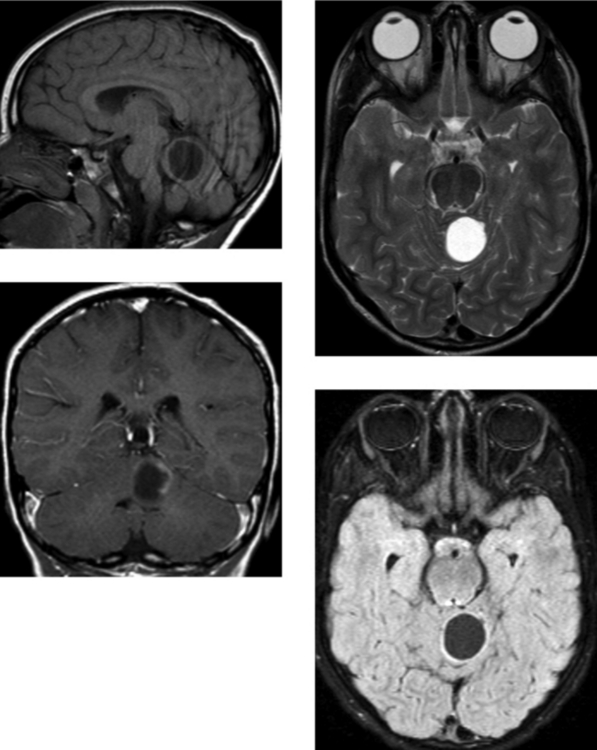
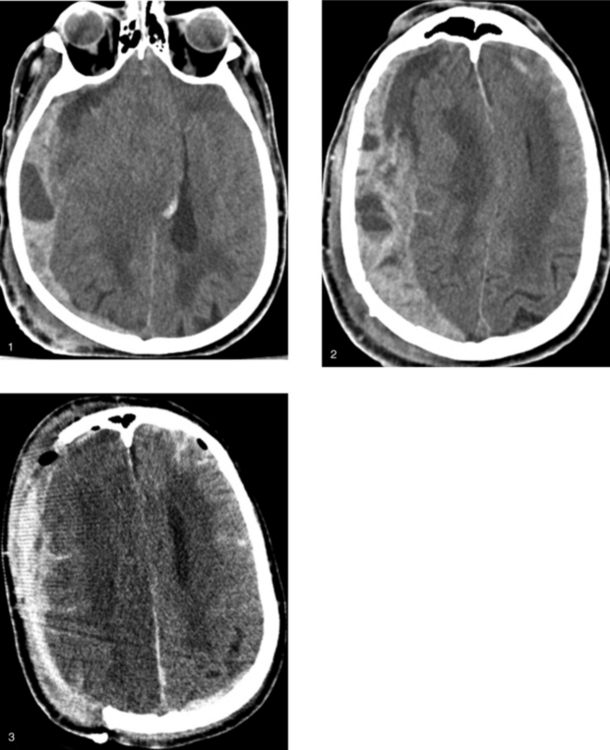
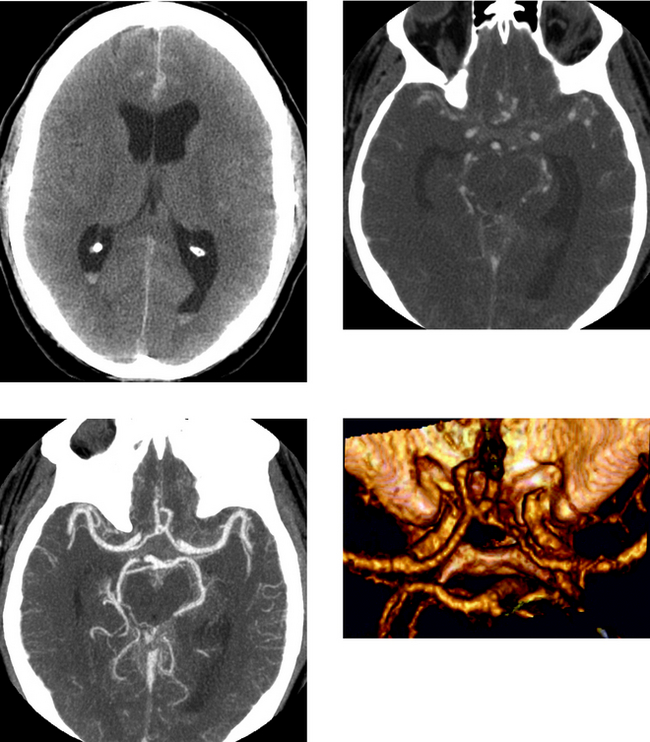
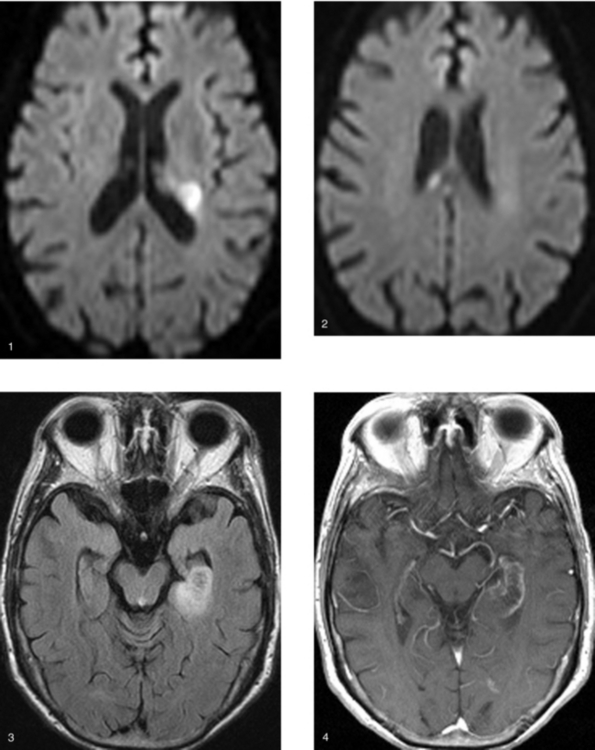
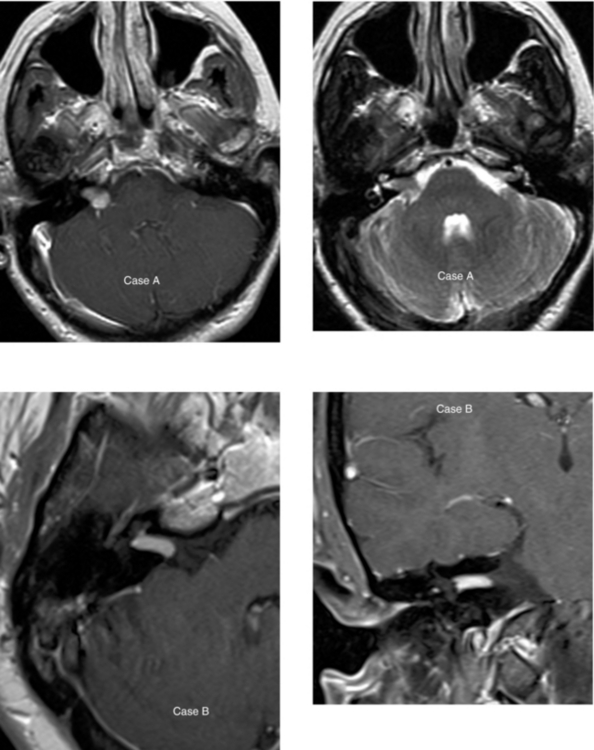
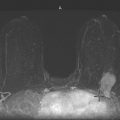
Chapter 1 Opening Round
Kazui S, Sawada T, Naritomi H, Kuriyama Y, Yamaguchi T. Angiographic evaluation of brain infarction limited to the anterior cerebral artery territory. Stroke. 1993;24:549-553.
Naidich TP, Firestone MI, Blum JT, Abrams KJ, Zimmerman RD. Zonal frequency analysis of infarct extent. Part II: anterior and posterior cerebral artery infarctions. Neuroradiology. 2003;45:601-610.
Taoka T, Iwasaki S, Nakagawa H, et al. Distinguishing between anterior cerebral artery and middle cerebral artery perfusion by color-coded perfusion direction mapping with arterial spin labeling. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2004;25:248-251.
CASE 2 Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformation
Nussel F, Wegmuller H, Huber P. Comparison of magnetic resonance angiography, magnetic resonance imaging, and conventional angiography in cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Neuroradiology. 1991;33:56-61.
Suzuki M, Matsui O, Kobayashi K, et al. Contrast enhanced MRI for investigation of cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Neuroradiology. 2003;45:231-235.
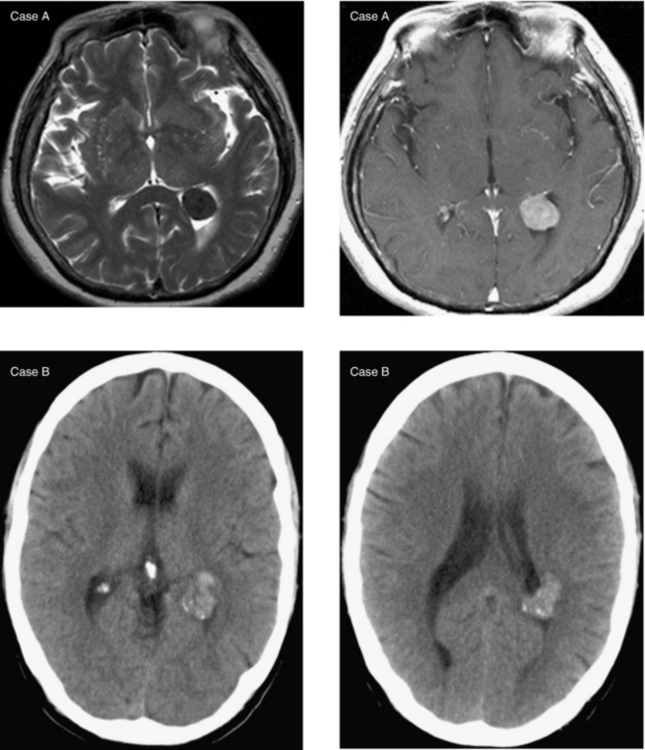
CASE 3 Hemorrhagic Metastases—Melanoma
CASE 4 Penetrating Brain Injury—Bow and Arrow Injury
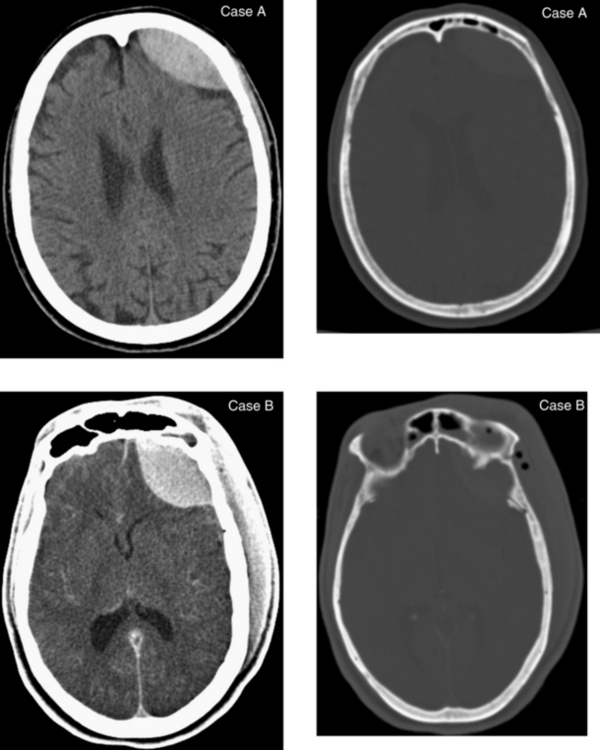
CASE 6 Acute Epidural Hematoma and Associated Linear Fracture of the Frontal Bone
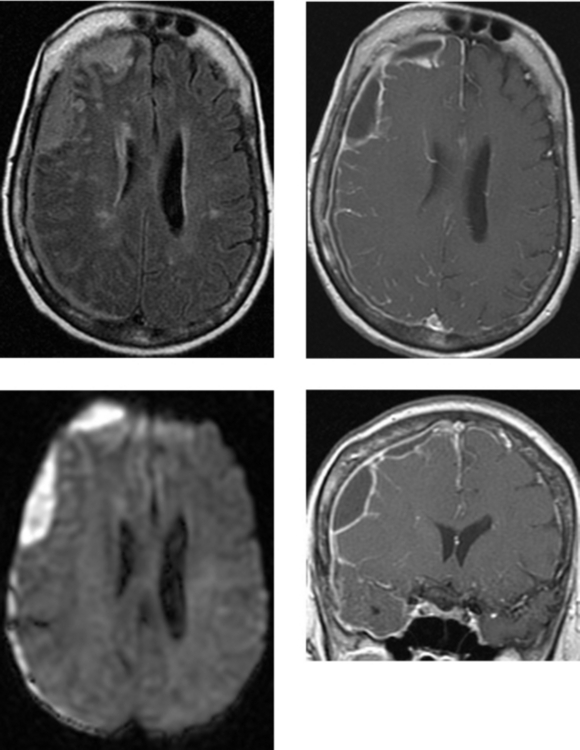
CASE 7 Pyogenic Brain Abscess
CASE 8 Chiari II Malformation with Associated Anomalies
Naidich TP, McLone DG, Fulling KH. The Chiari II malformation: part IV. The hindbrain deformity. Neuroradiology. 1983;25:179-197.
Royal SA, Tubbs RS, D’Antonio MG, Rauzzino MJ, Oakes WJ. Investigations into the association between cervicomedullary neuroschisis and mirror movements in patients with Klippel-Feil syndrome. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2002;23:724-729.
CASE 9 Acute Hydrocephalus Secondary to Meningitis
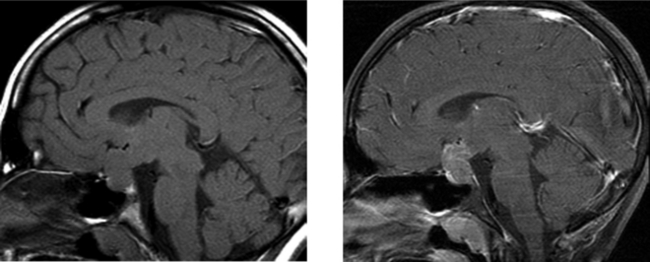
CASE 10 Pineal Cyst
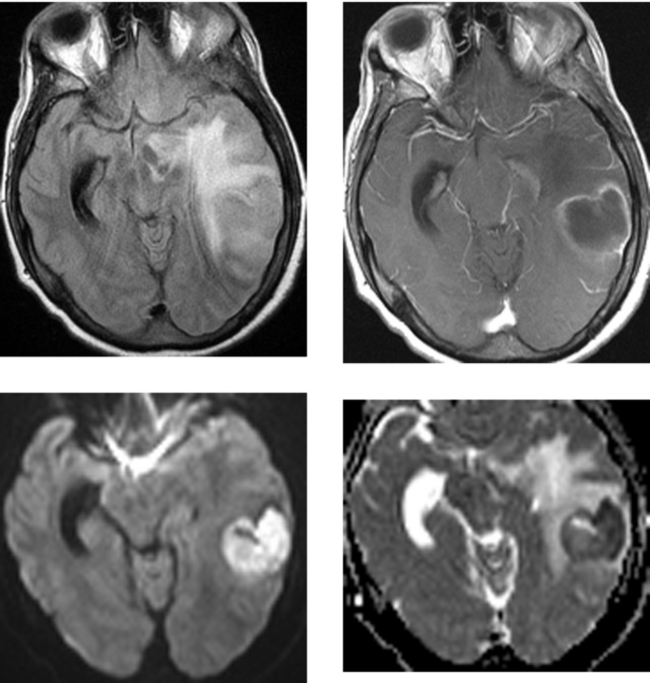
CASE 11 Hemorrhagic Contusion—Closed Head Injury
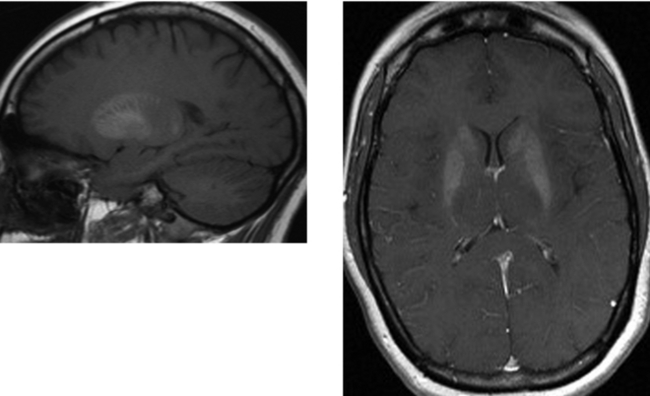
CASE 12 Juvenile Pilocytic Astrocytoma of the Cerebellum
CASE 13 Fibrous Dysplasia
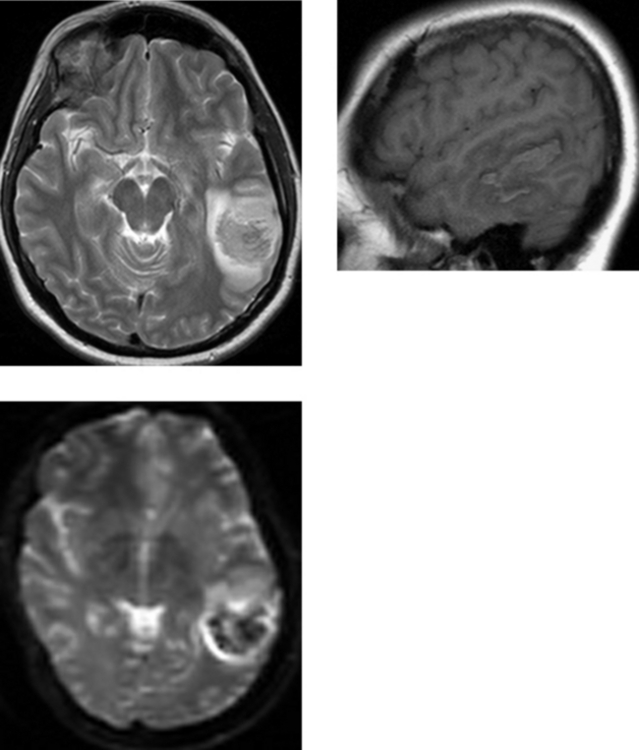
CASE 14 Acute Middle Cerebral Artery Stroke: “Hyperdense” Middle Cerebral Artery and Insular Ribbon Sign
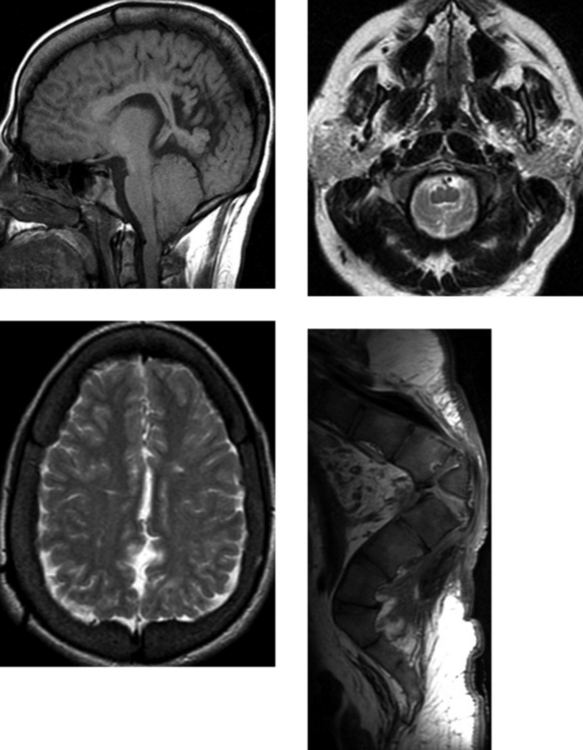
CASE 15 Multiple Sclerosis
Loevner LA, Grossman RI, McGowan JC, Ramer KN, Cohen JA. Characterization of multiple sclerosis plaques with T1-weighted MR and quantitative magnetization transfer. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1995;16:1473-1479.
Rovaris M, Comi G, Ladkani D, Wolinsky JS, Filippi M, European/Canadian Glatiramer Acetate Study Group. short-term correlations between clinical and MR imaging findings in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003;24:75-81.
CASE 16 Meningioma
Alvernia JE, Sindou MP. Preoperative neuroimaging findings as a predictor of the surgical plane of cleavage: prospective study of 100 consecutive cases of intracranial meningioma. J Neurosurg. 2004;100:422-430.
Sheporaitis LA, Osborn AG, Smirniotopoulos JG, et al. Intracranial meningioma. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1992;13:29-37.
CASE 17 Acute Actively Bleeding Subdural Hematoma—Subfalcine Herniation and Stroke
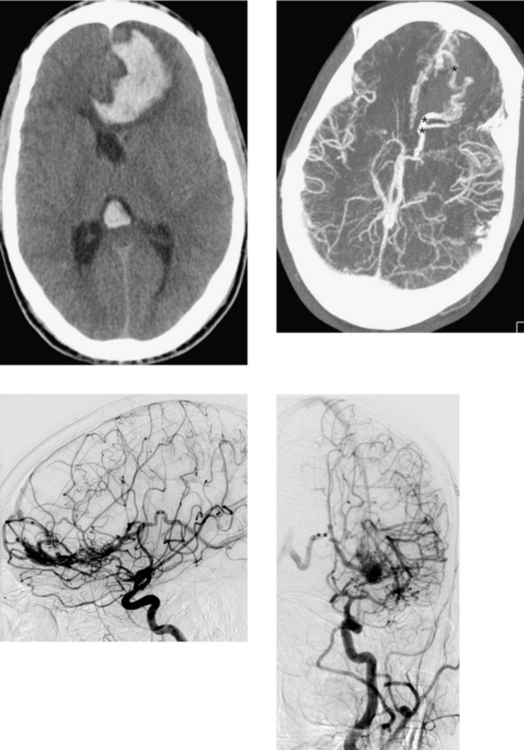
CASE 18 Acute Subarachnoid Hemorrhage—Rupture of an Anterior Communicating Artery Aneurysm
Jayaraman MV, Mayo-Smith WW, Tung GA, et al. Detection of intracranial aneurysms: multi-detector row CT angiography compared with DSA. Radiology. 2004;230:510-518.
Klisch J, Weyerbrock A, Spetzger U, Schumacher M. Active bleeding from ruptured aneurysms during diagnostic angiography: emergency treatment. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003;24:2062-2065.
CASE 19 Embolic Infarcts (Acute and Subacute)—Atrial Fibrillation
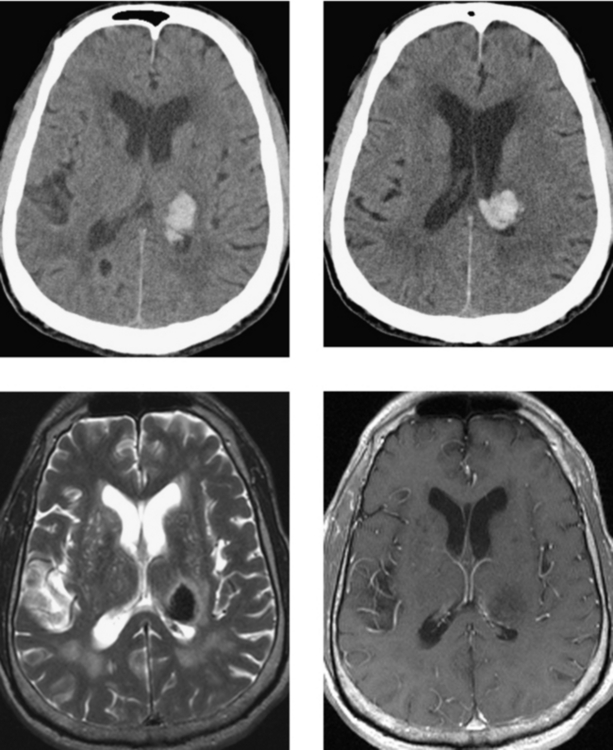
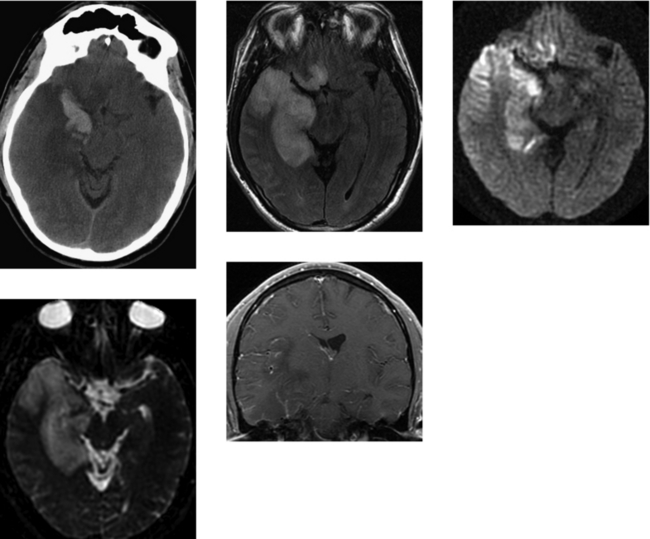
CASE 22 Acute Hypertensive Thalamic Hemorrhage
Chan S, Kartha K, Yoon SS, Desmond DW, Hilal SK. Multifocal hypointense cerebral lesions on gradient-echo MR are associated with chronic hypertension. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1996;17:1821-1827.
Tanaka A, Ueno Y, Nakayama Y, Takano K, Takebayashi S. Small chronic hemorrhages and ischemic lesions in association with spontaneous intracerebral hematomas. Stroke. 1999;30:1637-1642.
CASE 23 Infiltrating Astrocytoma—Low Grade
Bagley LJ, Grossman RI, Judy KD, et al. Gliomas: correlation of magnetic susceptibility artifact with histologic grade. Radiology. 1997;202:511-516.
Preul C, Kuhn B, Lang EW, Mehdorn HM, Heller M, Link J. Differentiation of cerebral tumors using multi-section echo planar MR perfusion imaging. Eur J Radiol. 2003;48:244-251.
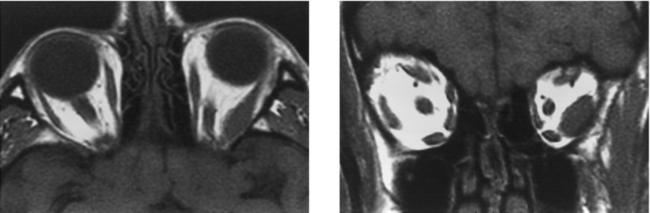
CASE 25 Retinoblastoma
Brisse HJ, Lumbroso L, Freneaux PC, et al. Sonographic, CT, and MR imaging findings in diffuse infiltrative retinoblastoma: report of two cases with histological comparison. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001;22:499-504.
Tateishi U, Hasegawa T, Miyakawa K, Sumi M, Moriyama N. CT and MRI features of recurrent tumors and second primary neoplasms in pediatric patients with retinoblastoma. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003;181:879-884.
CASE 26 Subdural Empyema—Complicated by Cerebritis
CASE 27 Glioblastoma Multiforme of the Corpus Callosum—”Butterfly Glioma”
CASE 28 Virchow-Robin Perivascular Spaces
CASE 29 Agenesis of the Corpus Callosum
Lee SK, Mori S, Kim DJ, Kim SY, Kim SY, Kim DI. Diffusion tensor MR imaging visualizes the altered hemispheric fiber connection in callosal dysgenesis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2004;25:25-28.
Quigley M, Cordes D, Turske P, Moritz C, Haughton V, Seth R. Role of the corpus callosum in functional connectivity. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003;24:208-212.
CASE 30 Nonaccidental Trauma—Child Abuse
CASE 31 Dermoid Cysts
CASE 32 Calvarial Metastases—Breast Carcinoma
Loevner LA, Tobey JD, Yousem DM, Sonners AI, Hsu WC. MR imaging characteristics of cranial bone marrow in adults with underlying systemic disorders compared with healthy controls. Am J Neuroradiol. 2002;23:248-254.
West MS, Russel EJ, Breit R, Sze G, Kim IKS. Calvarial and skull base metastases: comparison of nonenhanced and Gd-DTPA-enhanced MR images. Radiology. 1990;174:85-91.
CASE 33 Chronic Anemia—Diffuse Replacement of Fat in the Calvarial Marrow
Loevner LA, Tobey JD, Yousem DM, Sonners AI, Hsu WC. MR imaging characteristics of cranial bone marrow in adults with underlying systemic disorders compared with healthy controls. Am J Neuroradiol. 2002;23:248-254.
Ricci C, Cova M, Kang YS, et al. Normal age-related patterns of cellular and fatty bone marrow distribution in the axial skeleton: MR imaging study. Radiology. 1990;177:83-88.
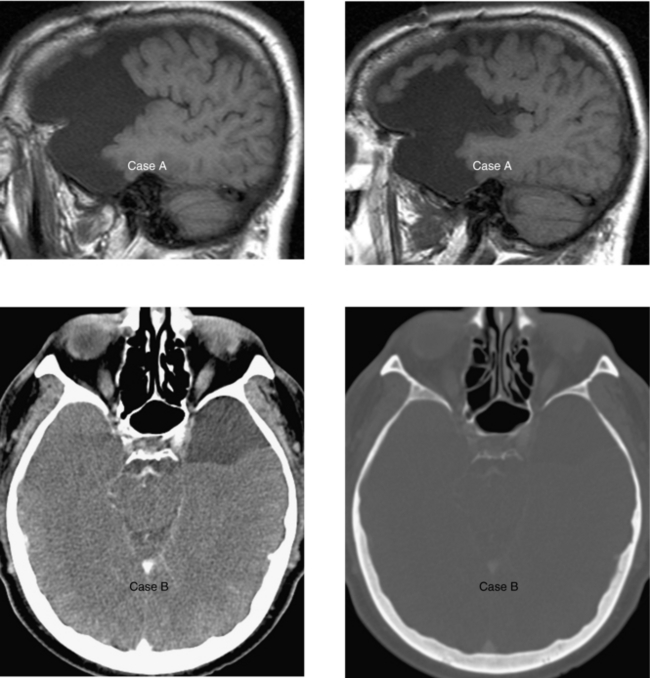
CASE 34 Giant Aneurysm—Middle Cerebral Artery
CASE 35 Bilateral Subacute Subdural Hematomas
CASE 36 Parafalcine Meningioma Invading the Superior Sagittal Sinus
Takeguchi T, Miki H, Shimizu T, et al. The dural tail of intracranial meningiomas on fluid-attenuated inversion-recovery images. Neuroradiology. 2004;46:130-135.
Tsuchiya K, Katase S, Yoshino A, Hachiay J. MR digital subtraction angiography in the diagnosis of meningiomas. Eur J Radiol. 2003;46:130-138.
CASE 37 Hemorrhagic Venous Infarction
Tong KA, Ashwal S, Obenaus A, Nickerson JP, Kido D, Haacke EM. Susceptibility-weighted MR imaging: a review of clinical applications. Am J Neuroradiol. 2008;29:9-17.
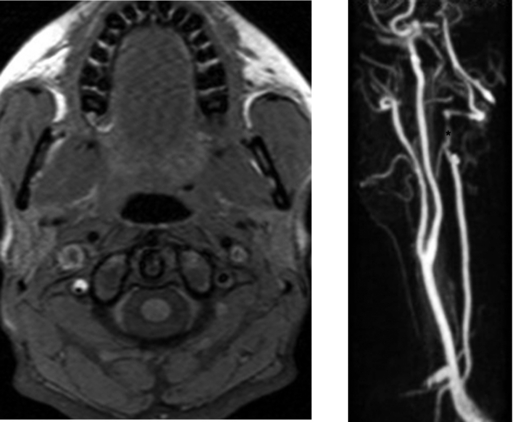
CASE 38 Vertebral Artery Dissection—Spontaneous
CASE 39 Spontaneous Cerebral Hematoma—Ruptured Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformation
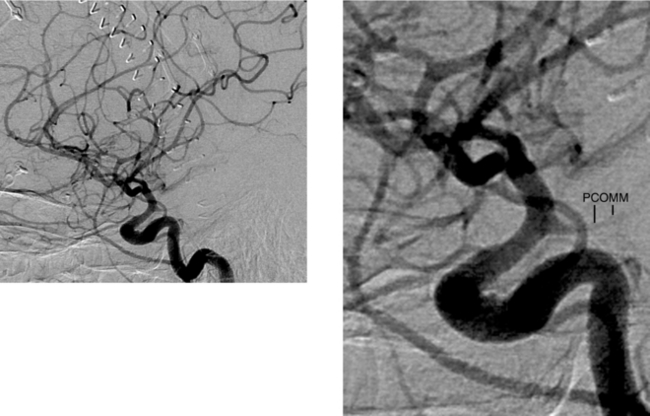
CASE 40 Vascular Infundibulum—Posterior Communicating Artery
Marshman LA, Ward PJ, Walter PH, Dossetor RS. The progression of an infundibulum to aneurysm formation and rupture: case report and literature review. Neurosurgery. 1998;43:1445-1448.
Ng SH, Wong HF, Ko SF, Lee CM, Yen PS, Wai YY. CT angiography of intracranial aneurysms: advantages and pitfalls. Eur J Radiol. 1997;25:14-19.
CASE 41 Closed Head Injury—Diffuse Axonal Injury
Scheid R, Preul C, Gruber O, Wiggins C, von Cramon DY. Diffuse axonal injury associated with chronic traumatic brain injury: evidence from T2-weighted gradient-echo imaging at 3T. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003;24:1049-1056.
Tong KA, Ashwal S, Holshouser BA, et al. Hemorrhagic shearing lesions in children and adolescents with posttraumatic diffuse axonal injury: improved detection and initial results. Radiology. 2003;227:332-339.
CASE 42 Glioblastoma Multiforme—Subependymal Spread
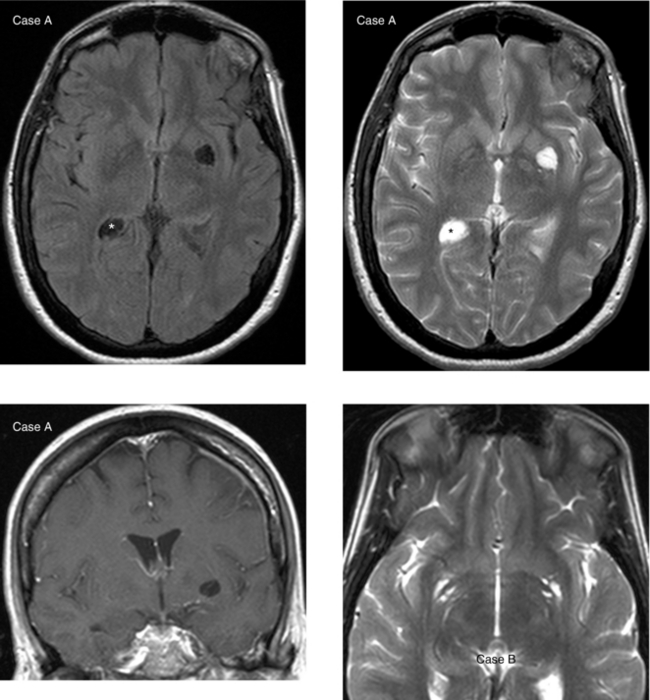
CASE 43 Amyloid Angiopathy
CASE 44 Mesial Temporal Sclerosis
Briellman RS, Syngeniotis A, Fleming S, et al. Increased anterior temporal lobe T2 times in cases of hippocampal sclerosis: a multi-echo T2 relaxometry study at 3T. Am J Neuroradiol. 2004;25:389-394.
Hogan RE, Wang L, Bertrand ME, et al. MRI-based high dimensional hippocampal mapping in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain. 2004;127:1731-1740.
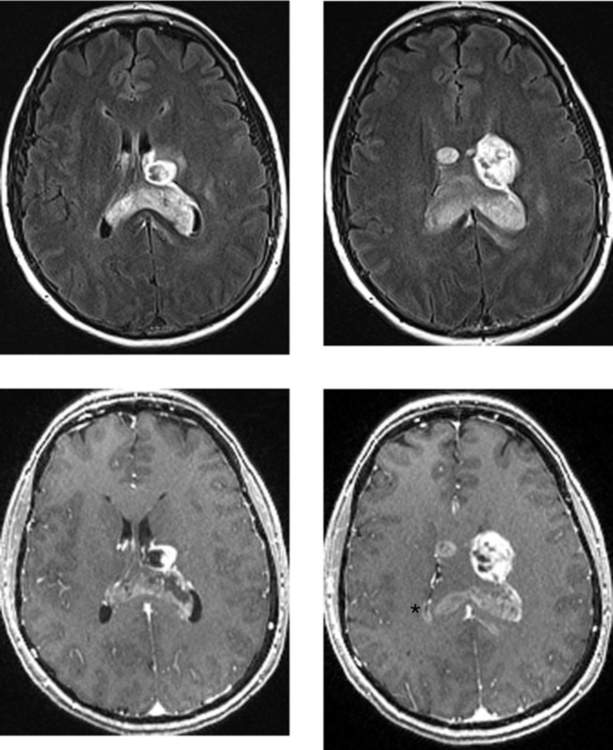
CASE 45 Intraventricular Meningioma
Jelinek J, Smirniotopoulos JG, Parisi JE, Kanzer M. Lateral ventricular neoplasms of the brain: differential diagnosis based on clinical, CT, and MR findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1990;155:365-372.
Majos C, Cucurella G, Aguilera C, Coll S, Pons LC. Intraventricular meningiomas: MR imaging and MR spectroscopic findings in two cases. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1999;20:882-885.
CASE 46 Suprasellar Germinoma
CASE 47 Mineral Deposition in the Basal Ganglia on T1W Imaging—Abnormal Calcium and Phosphate Metabolism
Baba Y, Ohkubo K, Hamada K, Hokotate H, Nakajo M. Hyperintense basal ganglia lesions on T1-weighted images in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia with hepatic involvement. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1998;22:976-979.
Komiyama M, Nakajima H, Nishikawa M, Yasui T. Chronological changes in nonhaemorrhagic brain infarcts with short T1 in the cerebellum and basal ganglia. Neuroradiology. 2000;42:492-498.
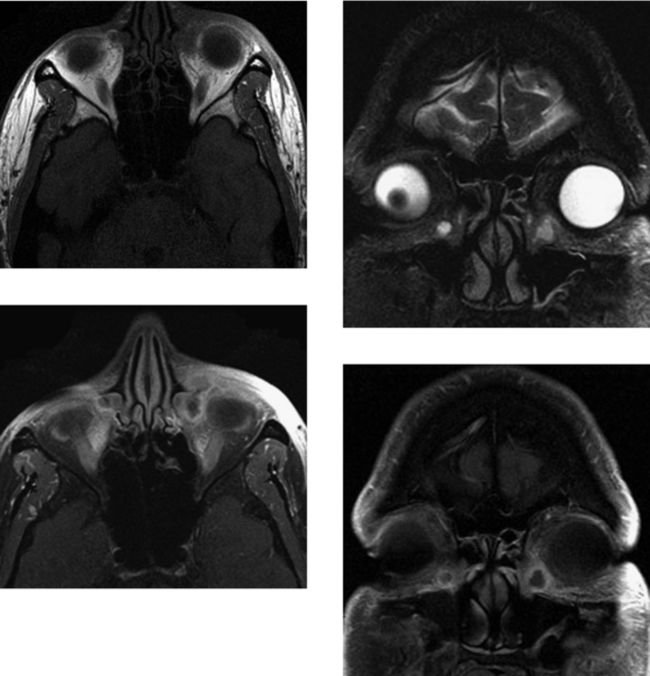
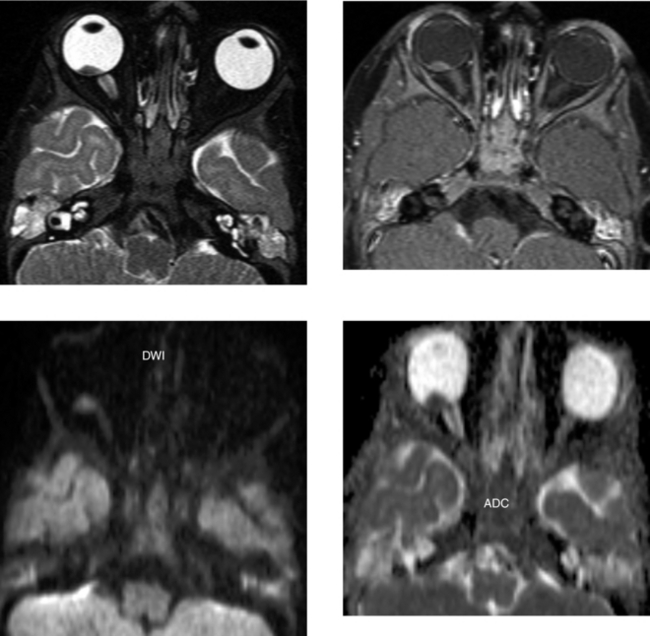
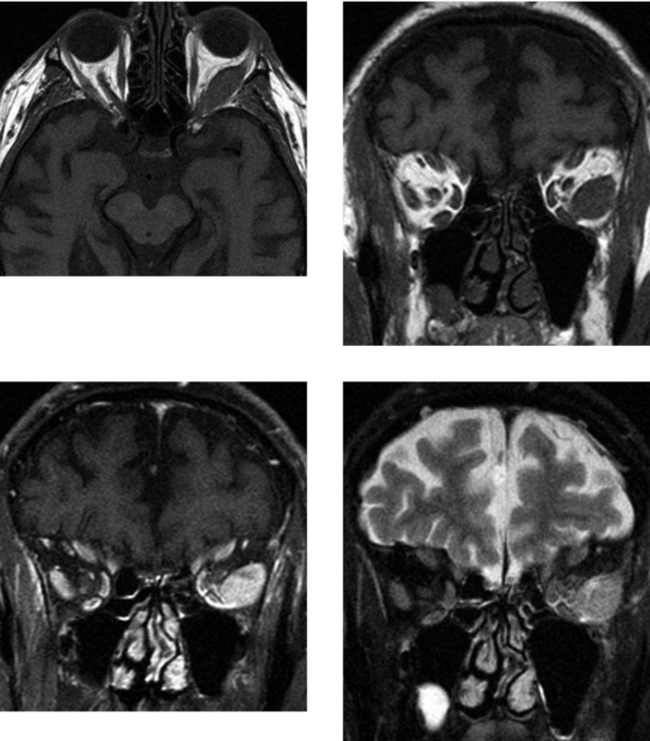
CASE 49 Primary Orbital Lymphoma
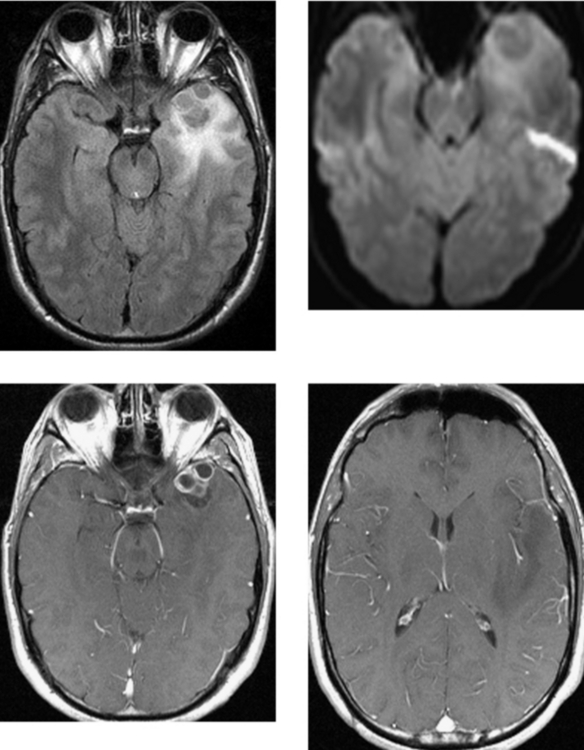
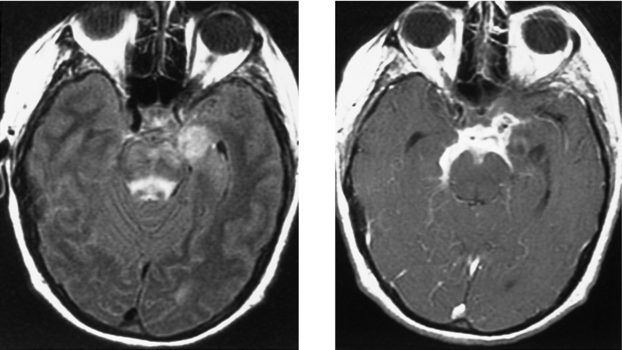
CASE 50 Basilar Meningitis and Encephalitis—Tuberculosis
Bernaerts A, Vanhoenacker FM, Parizel PM, et al. Tuberculosis of the central nervous system: overview of neuroradiological findings. Eur Radiol. 2003;13:1876-1890.
Gupta RK, Vatsal DK, Husain N, Chawla S, Prasad KN, Roy R. Differentiation of tuberculous from pyogenic brain abscesses with in vivo proton MR spectroscopy and magnetization transfer MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001;22:1503-1509.