Chapter 14 Ocular Prenatal Imaging
Introduction
Ultrasonographic studies are routinely conducted during prenatal care in the United States. As of 2000, nearly two-thirds of pregnant women received at least one prenatal ultrasonogram.1 However, the optimal number and timing of ultrasonographic studies during pregnancy has not been established. Although it has been deemed a cost-effective tool safe for mother and fetus, several limitations, including operator experience variability, fetal position, gestational age, and tissue definition on ultrasonography, may negatively affect this prenatal screening technique.2
Additionally, there is no conclusive evidence that routine ultrasonographic screening of all pregnancies is effective. In 1984, the National Institute of Health organized the Consensus Development Conference on Diagnostic Imaging in Pregnancy.3 This conference concluded that prenatal ultrasonography improves patient management and outcome only when there is an accepted indication.3 The Routine Antenatal Diagnostic Imaging with Ultrasound study (RADIUS) later conducted a randomized trial comparing a group of women who underwent first and second-trimester screening to a group who underwent ultrasonography only for medical indications, and found that screening ultrasonograms did not reduce perinatal morbidity or mortality when compared with the selective use of ultrasonography based on clinical judgment.4,5 In contrast to these findings, the Helsinki Ultrasound Trial identified a lower perinatal mortality rate in the ultrasound-screening group secondary to a higher detection rate of anomalies and subsequent termination of affected pregnancies.6
Current recommendations from the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists do not recommend examination of the globe, orbit, or adnexal structures as part of the routine fetal anatomy screening evaluation.7 However, reports of prenatal ultrasonography for diagnosis of diseases involving the eye and ocular adnexae have been described since the 1980s. Herein, we summarize a literature review of relevant reports to date.
Embryology
The optic sulci are the first recognizable ocular structures, originating as indentations in each neural fold at approximately 22 days gestation. The optic pits develop from continued evagination of the sulci, and deepen to become optic vesicles lateral to the forebrain at 25 days. These vesicles remain attached to the neural tube by optic stalks that later develop into the optic nerves. The optic vesicles approach the outer wall as a focal thickening of cells that forms the lens placode in the surface ectoderm. In the fourth week of gestation, invagination of the lens placode forms the lens vesicle. Simultaneously, the optic vesicle invaginates back upon itself to form the optic cup, evolving into an outer pigment layer and an inner neurosensory layer. An additional invagination occurs that forms a groove from the ventral aspect of the optic cup posteriorly to the forebrain wall. This is the optic fetal fissure through which mesenchyme will eventually migrate to form the primary vitreous and hyaloid artery. This fissure fuses during the fifth and early sixth gestational week, enclosing the initial retinal axons as the optic nerve head.8 During the seventh gestational week, the margins of the optic cup grow around the anterior portion of the lens to form the ciliary body and epithelium of the iris.9 The lens and optic cup induce formation of the cornea, with its epithelium derived from surface ectoderm and its stroma and endothelium derived from mesenchyme.10
Imaging modalities
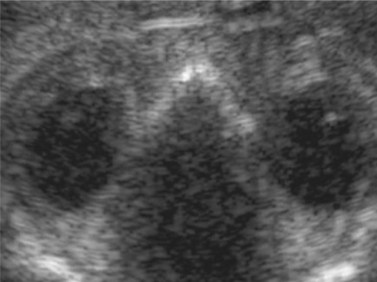
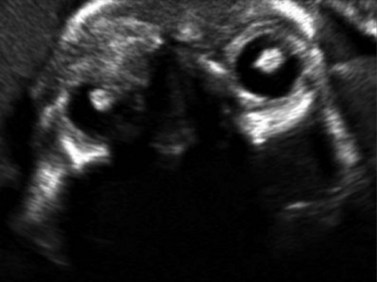
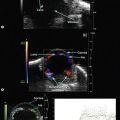
Using transvaginal ultrasonography, the eyes may be detected at 12 weeks gestation as hypoechogenic structures superolateral to the nasal bone. By 14 weeks gestation, the lens may be detected as an oval structure in the center of each orbit. It is characterized by a thin echogenic margin overlying an anechoic center. Additionally, the hyaloid artery can be detected in nearly all fetuses by 14 weeks gestation. This structure should disappear by approximately 29 weeks gestation (Figure 14.1). The eyelids may be identified at the beginning of the second trimester. The earliest reported gestational age at diagnosis of anomalies of the globe, orbit, and ocular adnexae by prenatal ultrasonography are given in Table 14.1.
Table 14.1 Earliest reported diagnoses of ocular anomalies by prenatal ultrasonography.
| Gestational age | Ocular anomaly |
|---|---|
| 11 weeks | Cyclopia42 |
| Microphthalmia31 | |
| 14 weeks | Anophthalmia14 |
| Cataract14,50,51 | |
| 17 weeks | Orbital teratoma78 |
| 19 weeks | Proptosis27,74 |
| 20 weeks | Hypertelorism22 |
| 21 weeks | Retinoblastoma64 |
| 22 weeks | Hypotelorism15 |
| 23 weeks | Orbital cyst75 |
| Persistent hyperplastic primary vitreous46 | |
| 27 weeks | Dacryocystocele81,82 |
| 34 weeks | Retinal detachment68 |
| Orbital rhabdomyosarcoma77 |
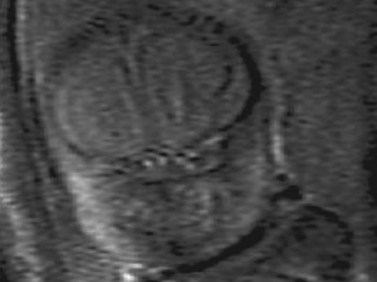
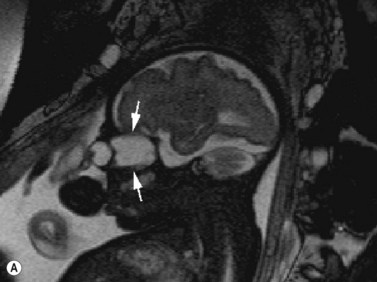
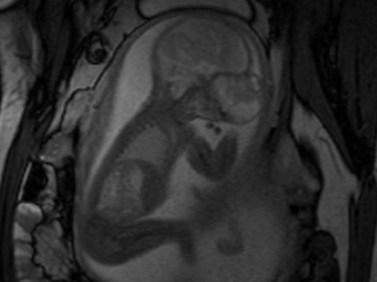
Fetal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is currently accepted as a second line imaging modality in the examination of the normal and pathological fetal central nervous system and is also indicated when there is need to confirm or fully characterize a finding from fetal ultrasonography.11 Current software and hardware for fetal magnetic resonance imaging allow the acquisition of high-quality images of the globe and orbit (Figure 14.2). These images may be acquired in less than 1 second, thus permitting the performance of MRI without maternal or fetal sedation.2 However, while there is no evidence to suggest adverse effects of MRI on the fetus, the safety of MRI during pregnancy has not been proven. Therefore, the use of MRI during the first trimester of pregnancy is best avoided when possible.2

Figure 14.2 Normal fetal globe. Magnetic resonance imaging appearance of fetal globe.
Reproduced with permission from: Paquette L, Miller DA. Retinoblastoma: at risk pregnancies. In: Singh AD, Damato BE, Pe’er J, Murphree AL, Perry JD (eds). Clinical Ophthalmic Oncology. Saunders-Elsevier, Philadelphia, 2007:496–500.
Computed tomography is not routinely used for prenatal diagnosis. Carcinogenesis in the fetus is a major concern, hence this imaging modality should be avoided in all trimesters of pregnancy unless absolutely necessary.12
Globe anomalies
Anophthalmia
True anophthalmia is the complete absence of the globe in the presence of ocular adnexae. However, the term “clinical anophthalmia” is sometimes used to reference extreme microphthalmia in which a small blind eye persists. Primary anophthalmia occurs when the eye never forms during gestation. This diagnosis is oftentimes associated with genetic syndromes or chromosomal anomalies. Secondary anophthalmia, on the other hand, is regression of the globe, usually by an insult during development. Potential etiologies of secondary anophthalmia include infectious, vascular, metabolic, or toxic events. In a review of 58 patients with congenital anophthalmia, Schittkowski and colleagues identified systemic findings in 50% of patients, predominantly Goldenhar’s syndrome, facial clefts, and cerebral anomalies.13 In this review, 18 of the 38 patients with unilateral anophthalmia had anomalies in the fellow eye, for the most part consisting of coloboma, dermoid, sclerocornea, and glaucoma.13
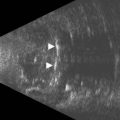
The gestational age at diagnosis in the reports ranged between 14 and 32 weeks (Chapter 19).14–20 Characteristic findings on ultrasonography included an absent or small orbit, an absent globe, and an absent lens (Figure 14.3). Of the three cases that were unilateral,16–18 two were associated with microphthalmia in the fellow eye.16,17 Systemic associations included anophthalmia-plus syndrome,19 Waardenburg-type ophthalmo-acromelic syndrome,20 otocephaly,16 limb body wall complex,17 and holoprosencephaly.15 A family history of anophthalmia was present in two cases14,19 and a maternal history of recurrent miscarriages was present in one case.18 Reported outcomes in pregnancies that were not terminated included stillbirth at 21 weeks gestation in the fetus with limb body wall complex,17 and death shortly after birth in the fetuses with ophthalmo-acromelic syndrome20 and otocephaly.16
Microphthalmia
Microphthalmia refers to an abnormally small eye. Causes of microphthalmia include chromosomal abnormalities, craniofacial disorders, intrauterine infections, teratogens, and syndromic processes.21 It also may be inherited as an autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, or X-linked trait.
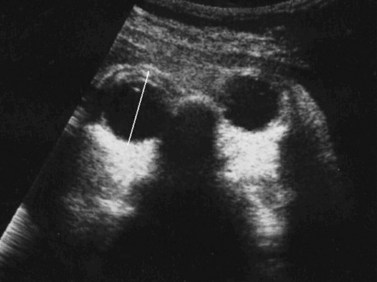
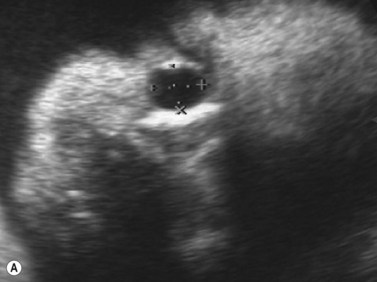
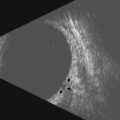
Nomograms for ocular biometric measurements based on ultrasonography have been reported.22–25 Microphthalmia is considered when the ocular diameter is less than the 5th percentile for gestational age (Figure 14.4). However, Blazer has noted that normal ocular biometry in early pregnancy does not preclude the subsequent development of microphthalmia.26
Gestational age at diagnosis has ranged between 11 and 32 weeks. While most of the reported cases were bilateral, several unilateral cases have been reported.26–29 Associated ocular findings include hypotelorism,27 hypertelorism,30 contralateral anophthalmia,31 and colobomatous cyst.28,31 Reported non-ocular associations include Fraser’s syndrome,29,30,32 limb body wall complex,33 trisomy 13,26 trisomy 18,26,34 Dandy Walker malformation,26 holoprosencephaly,26 hydrocephalus with phocomelia,27 and nasal vestibule stenosis.28 Of the 23 cases reporting outcome, 22 pregnancies were terminated.
Optic nerve coloboma
A coloboma of the globe is a congenital anomaly that develops secondary to failure of embryonic fissure closure. Those closure anomalies leading to optic nerve colobomas involve the posterior portion of the embryonic fissure at the optic cup (Chapter 13). Optic nerve colobomas may be isolated, but oftentimes occur with syndromic associations. For this reason, diagnosis of a coloboma may lead to further evaluation for syndromic conditions.28
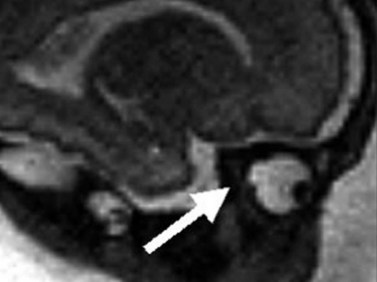
Righini and colleagues reported three cases of optic nerve coloboma initially diagnosed with ultrasonography and confirmed with prenatal MRI (Figure 14.5).28 In this case series, MRI was determined a more effective imaging technique secondary to limitations of ultrasonography to illustrate details of the posterior globe. Ages at initial diagnosis ranged between 30 and 32 weeks. The coloboma was described as a focal bulging of the globe at the insertion of the optic nerve. Reported non-ocular associations included Aicardi’s syndrome, West’s syndrome, and CHARGE syndrome.
Cyclopia
Cyclopia is a rare form of holoprosencephaly in which the embryonic prosencephalon fails to properly divide the orbits into two cavities, resulting in one orbit and eye. Holoprosencephaly ranges from severe alobar holoprosencephaly with cyclopia to ethmocephaly, cebocephaly, premaxillary agenesis, and various microforms. Causes include chromosomal aberrations, single gene mutations, and teratogens.35 An especially severe teratogen associated with this condition is cyclopamine, an alkaloid toxin found in the plant Veratrum californicum.
Several cases of cyclopia diagnosed by prenatal ultrasonography have been reported in the literature, with age at diagnosis ranging between 12 and 35 weeks. The diagnosis at 12 weeks was made by transvaginal ultrasonography in two of the cases.36,37 Characteristic ultrasonographic features include a single median orbit, or absence of one orbit (Figure 14.6). The majority of cases were associated with alobar holoprosencephaly. In the 10 outcomes that were reported, eight pregnancies were terminated,35–41 one suffered intrauterine fetal demise,42 and another case resulted in death shortly postpartem.43
High myopia
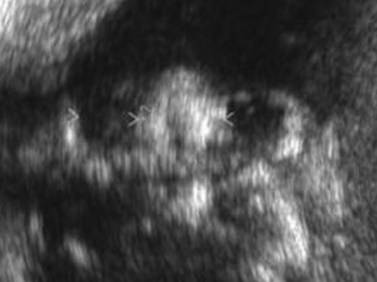
High myopia may be identified on ultrasonography by increased axial length. One case of high myopia diagnosed by prenatal ultrasonography has been reported (Figure 14.7).44 This case, diagnosed at 33 weeks gestation, had an axial length of 24 mm. Normative data suggests the expected axial length at this gestational age to be 15.3 mm. Other reported associated findings included proptosis, hypertelorism, depressed nasal bridge, upslanting palpebral fissures, and lens subluxation.
Delayed regression of the hyaloid artery and persistent hyperplastic primary vitreous
Persistent hyperplastic primary vitreous (PHPV), also known as persistent fetal vasculature, is a congenital anomaly secondary to failed regression of the embryonic primary vitreous and hyaloid vasculature. It may present as an anterior fibrovascular sheath at the posterior lens (persistent tunica vasculosa lentis), as a predominantly posterior process, or as a combination of both. Although bilateral cases have been reported, it is commonly a unilateral finding (Chapter 15).
Gestational age at diagnosis ranged between 28 and 36 weeks for cases diagnosed on prenatal ultrasonography.45–48 The characteristic findings on ultrasonography were high acoustic contrast against the anechoic vitreous,45 oftentimes taking a conical shape with the base lying at the lens and the apex pointing towards the posterior pole (Figure 14.8),47,48 as well as an increased thickness of the hyaloid artery-lens junction.46 Systemic associations included trisomy 13,45 trisomy 18,45 trisomy 21,45 Walker–Warburg syndrome,47,48 hydrocephalus,48 cerebellar hypoplasia,48 buphthalmia,48 corpus callosum agenesis,48 microcephaly without chromosomal anomaly,45 bilateral cataracts,46 fetal alcohol syndrome,45 and fetal exposure to hydantoin.45
Cataract
The etiologies for congenital cataract include metabolic disorders, infectious diseases, toxins, faciocraniostenosis, polymalformation and complex craniofacial malformation syndromes, musculoskeletal conditions, aneuploidism and chromosomal anomalies, cutaneodental disorders, and idiopathic etiology.49 While autosomal dominant inheritance patterns are more common, autosomal recessive modes of inheritance have been reported.14 Leonard and colleagues conducted a literature review of prenatally diagnosed cataracts and established a management algorithm for further evaluation.49
Gestational age at diagnosis has ranged between 14 weeks14,50,51 and 34 weeks.52 Characteristic appearance on ultrasonography is hyperechogenicity of the lens (Figure 14.9). Reported associated ocular findings have included microphthalmia,53,54 hypertelorism,51 macroglobus,51 malformation of the anterior segment,53 retinal dysplasia,53 microphthalmia,49 and anophthalmia.50 Reported non-ocular associations have included hydrocephalus with midline cleft,27 Lowe syndrome’s,55 Neu–Laxova syndrome,51 Walker–Warburg syndrome,52,56 multiple pterygium syndrome,14 Nance–Horan syndrome,57 toxoplasmosis,58 rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctata type I,59 Micro syndrome,49 trisomy 13,51 trisomy 21,60 and a supernumerary chromosome from chromosome 21.61
Retinoblastoma
Retinoblastoma is a rare intraocular tumor developing from photoreceptor cells. While worldwide incidence varies, it affects approximately 1 in 15 000 live births.62 In the developed world, it has a very high cure rate, although secondary cancers are common and sometimes fatal. There are two forms of retinoblastoma; a genetic, heritable form secondary to germline mutations, and a non-genetic, non-heritable form secondary to sporadic nongermline mutations. Approximately two-thirds of cases are unilateral.63 In trilateral retinoblastoma, the pineal gland is affected. Ultrasonographic findings of retinoblastoma are well known in the postnatal period, and are characterized by an echogenic intraocular mass, oftentimes associated with calcium deposits identified by hyperechogenicity (Chapter 11).
Only two cases of retinoblastoma diagnosed on prenatal ultrasonography have been reported.64,65 One case was detected at 21 weeks gestation as an irregular, echogenic mass, surrounded by a sonolucent area and protruding from the right side of the face.64 This pregnancy was terminated. The second case, which was detected at 38 weeks gestation, was described as a solid mass occupying the left orbit and spreading towards the left facial and cerebral frontotemporoparietal regions.65 This baby died two hours after birth secondary to respiratory insufficiency.
Retinal detachment
Three cases of prenatally diagnosed retinal detachment have been described, with detection occurring between 34 and 37 weeks gestation.66–68 The characteristic feature on ultrasonography is a conical echogenic structure with its base towards the lens and its apex towards the posterior pole, specifically at the optic nerve. These findings are more evident in the presence of total retinal detachment. Of the three reported cases, two were associated with Walker–Warburg syndrome,66,67 and one was associated with Norrie’s disease.68 Of the two outcomes reported, one of the fetuses with Walker–Warburg syndrome was stillborn at 38 weeks,67 and the fetus with Norrie’s disease had a normal term delivery.68
Orbit and adnexae
Hypertelorism and hypotelorism
Hypertelorism refers to an abnormally enlarged interpupillary distance, and results in increased distance between the orbits. Primary hypertelorism results from undermigration of the paired nasal swellings, which results in an increased distance between the two halves of the face. Various chromosomal abnormalities and systemic syndromes may manifest with hypertelorism. Secondary hypertelorism is associated with abnormalities of the skull, specifically anterior cephaloceles and craniosynostoses.69 Nomograms for ocular measurements on ultrasonography have been established.22–2570 Sukonpan et al reviewed 595 measurements of normal pregnancies to develop normative data regarding a linear growth model for fetal interocular and binocular distance to allow prenatal identification of hypotelorism and hypertelorism.70
Gestational age at prenatal diagnosis of hypertelorism has ranged between 20 and 33 weeks.22,71 Non-ocular associations include median cleft face syndrome, hydrocephalus,71 polyhydramnios, frontal encephalocele, omphalocele, and imperforate anus.22
In contrast, hypotelorism refers to an abnormally decreased interpupillary distance (Figure 14.10). Primary hypotelorism may occur secondary to overmigration of the paired nasal swellings, thereby resulting in the two facial halves lying too close together. It is usually associated with a variant of holoprosencephaly. Secondary hypotelorism is commonly caused by bony skull abnormalities, specifically microcephaly and plagiocephaly.69 Sixteen cases of prenatally-diagnosed hypotelorism have been reported, with age at diagnosis ranging between 22 and 38 weeks gestation.15,22,72,73 Variants of holoprosencephaly were observed in 14 cases.
Proptosis
Proptosis refers to forward displacement of the globe. Two cases of proptosis diagnosed in the prenatal period have been reported in the literature, both of which were diagnosed at 19 weeks gestational age.27,74 Modes of diagnosis between these two cases differed by transvaginal or transabdominal ultrasound. One case was associated with holoprosencephaly,27 and the other was associated with Apert’s syndrome.74 Both pregnancies were terminated.
Strabismus
Strabismus, or ocular misalignment, may be identified on ultrasonography by divergence of the fetal lens indicating exotropia. Two cases of strabismus have been reported by Bronshtein et al.27 Both of these cases were diagnosed by transvaginal ultrasound at 12 and 15 weeks gestational age. One of these cases, associated with an enlarged urinary bladder and choroid plexus dysmorphism, resulted in intrauterine fetal death at 14 weeks. The other case, associated with microphthalmia, hydrocephalus, ventricular septal defect, pericardial effusion, and omphalocele, was terminated.
Orbital cyst
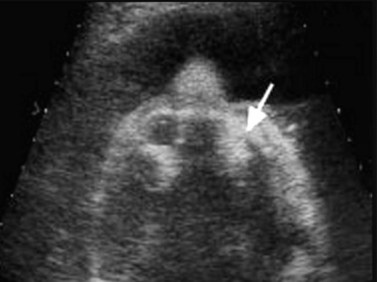
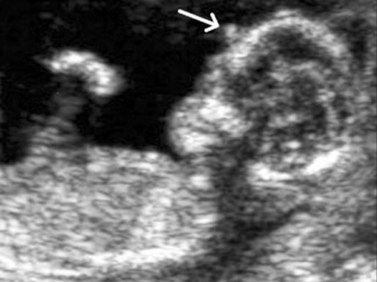
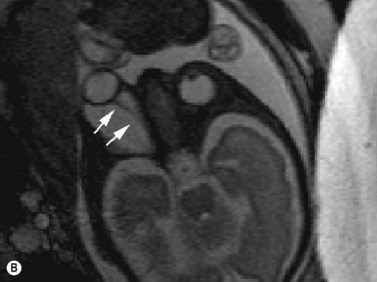
Two cases of prenatally diagnosed orbital cysts have been reported, at 23 and 27 weeks.75,76 The first of these was diagnosed by transabdominal and transvaginal ultrasonography.75 At birth, this cyst was associated with proptosis, ectropic upper and lower eyelids, and central corneal exposure keratopathy. Singh later reported a cyst diagnosed by ultrasonography and confirmed by fetal MRI.76 MRI studies revealed a large cystic lesion, with no solid component or calcification, associated with proptosis and elongation of the optic nerve (Figure 14.11). A planned Caesarean delivery was performed at 38 weeks. Immediately at birth, a tarsorrhaphy to prevent exposure was performed. Shortly after, the baby underwent orbitotomy with aspiration and partial excision of the lesion.
Rhabdomyosarcoma
Rhabdomyosarcoma is a rapidly growing tumor, often involving the orbit. One case of orbital rhabdomyosarcoma diagnosed on prenatal ultrasonography has been described.77 The reported findings of an irregular, echo-dense structure originating from the orbit, were observed at 34 weeks gestation. This patient died 5 days after birth from sepsis.
Teratoma
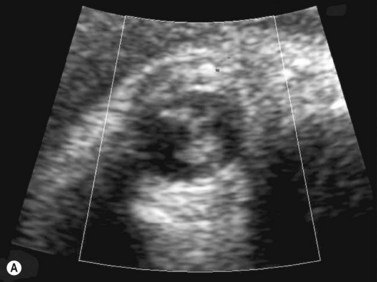
A teratoma is an encapsulated tumor made up of tissues from all three germ layers. Orbital teratomas usually coexist with a normal globe and grow rapidly following birth to cause severe proptosis and exposure keratopathy. One case of teratoma diagnosed on prenatal ultrasonography has been reported.78 This was identified at 17 weeks gestation, and described as a solid, cystic mass with internal complex echogenicity in the infratentorial region of the eyeball (Figure 14.12). PHPV was additionally noted on this ultrasound. The pregnancy was terminated.
Dacryocystocele
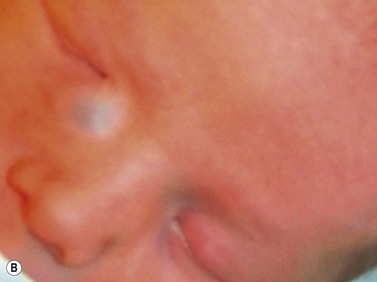
A dacryocystocele, or distended lacrimal sac, is caused by failed canalization of the nasolacrimal system during development. Usually, the valve of Hasner persists as a thin mucosal membrane causing fluid to accumulate in the sac. Newborns usually present with a bluish-gray mass inferior to the medial canthal tendon with associated epiphora, discharge, dacryocystitis, conjunctivitis, and facial cellulitis. Rarely, serious complications such as orbital cellulitis or upper airway obstruction occur. The differential diagnosis for this type of mass when observed on prenatal ultrasound or after birth includes encephalocele, nasal glioma, rhabdomyosarcoma, dermoid cyst, and hemangioma.79,80
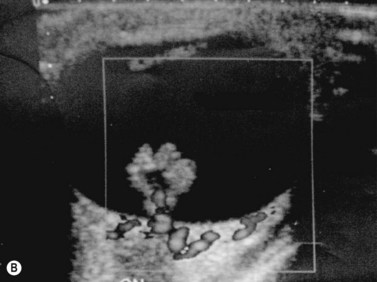
Prenatal diagnosis of dacryocystocele has been widely reported with age at diagnosis ranging between 27 and 38 weeks gestation. Characteristic findings of dacryocystocele on ultrasonography include a hypoechoic mass inferomedial to the eye with no blood flow on color Doppler (Figure 14.13). Although non-ocular associations have been reported, including polyhydramnios,80 Canavan’s disease,81 microcystic kidney disease with dysplastic kidney,81 pyelectasis,81 mildly pervious duct of Botallo,79 and unilateral ventriculomegaly,79 it is commonly a solitary finding.
1 Martin JA, Hamilton BE, Ventura SJ, et al. Births: final data for 2000. Nat Vital Stat Rep. 2002;50(5):1-101.
2 Reddy UM, Filly RA, Copel JA. Prenatal imaging: ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging. Obstet Gynecol. 2008;112:145-157.
3 National Institutes of Health. Diagnostic ultrasound imaging in pregnancy. National Institutes of Health Consensus Development Conference Statement. 1984, Feb 6–8;5(1):1-16.
4 Ewigman BG, Crane JP, Frigoletto FD, et al. Effect of prenatal ultrasound screening on perinatal outcome. RADIUS Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1993;329:821-827.
5 Crane JP, LeFevre ML, Winborn RC, et al. A randomized trial of prenatal ultrasonographic screening: impact on the detection, management, and outcome of anomalous fetuses. The RADIUS Study Group. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1994;171:392-399.
6 Saari-Kemppainen A, Karjalainen O, Ylostalo P, et al. Ultrasound screening and perinatal mortality: controlled trial of systematic one-stage screening in pregnancy. The Helsinki Ultrasound Trial. Lancet. 1990;336:387-391.
7 ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 101: Ultrasonography in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 2009;113:451-461.
8 Tripathi BJ, Tripathi RC. Development of the human eye. In Bron AJ, Tripathi RC, Tripathi BJ, editors: Wolff’s Anatomy of the Eye and Orbit, 8th ed, London: Chapman & Hall, 1997.
9 Barkovich AJ. Pediatric Neuroimaging, 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2005. p. 932
10 Som PM, Curtin HD. Head and Neck Imaging, 4th ed. St. Louis, MO: Mosby; 2003. p. 57
11 Huisman TA. Fetal magnetic resonance imaging. Semin Roentgenol. 2008;43:314-336.
12 Chen MM, Coakley FV, Kaimal A, et al. Guidelines for computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging use during pregnancy and lactation. Obstet Gynecol. 2008;112:333-340.
13 Schittkowski MP, Guthoff RF. Systemic and ophthalmological anomalies in congenital anophthalmic or microphthalmic patients. Br J Ophthalmol. 2010;94(4):487-493.
14 Mashiach R, Vardimon D, Kaplan B, et al. Early sonographic detection of recurrent fetal eye anomalies. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2004;24:640-643.
15 Pilu G, Reece EA, Romero R, et al. Prenatal diagnosis of craniofacial malformations with ultrasonography. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1986;155:45-50.
16 Chen CP, Wang KG, Huang JK, et al. Prenatal diagnosis of otocephaly with microphthalmia/anophthalmia using ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2003;22:214-215.
17 Wu YC, Yang ML, Yuan CC. Prenatal diagnosis of anophthalmos with limb-body wall complex. Prenat Diagn. 2000;20:769-770.
18 Wong HS, Parker S, Tait J, et al. Antenatal diagnosis of anophthalmia by three-dimensional ultrasound: a novel application of the reverse face view. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2008;32(1):103-105.
19 Fryns JP, Legius E, Moerman P, et al. Apparently new “anophthalmia-plus” syndrome in sibs. Am J Med Genet. 1995;58:113-114.
20 Kara F, Yesildaglar N, Tuncer RA, et al. A case report of prenatally diagnosed ophthalmo-acromelic syndrome type Waardenburg. Prenat Diagn. 2002;22:395-397.
21 Paquette L, Randolph L, Incerpi M, et al. Fetal microphthalmia diagnosed by magnetic resonance imaging. Fetal Diagn Ther. 2008;24:182-185.
22 Trout T, Budorick NE, Pretorius DH, et al. Significance of orbital measurements in the fetus. J Ultrasound Med. 1994;13:937-943.
23 Jeanty P, Dramaix-Wilmet M, Van Gansbeke D, et al. Fetal ocular biometry by ultrasound. Radiology. 1982;143:513-516.
24 Mayden KL, Tortora M, Berkowitz RL, et al. Orbital diameters: a new parameter for prenatal diagnosis and dating. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1982;144:289-297.
25 Rosati P, Bartolozzi F, Guariglia L. Reference values of fetal orbital measurements by transvaginal scan in early pregnancy. Prenat Diagn. 2002;22:851-855.
26 Blazer S, Zimmer EZ, Mezer E, et al. Early and late onset fetal microphthalmia. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2006;194:1354-1359.
27 Bronshtein M, Zimmer E, Gershoni-Baruch R, et al. First- and second-trimester diagnosis of fetal ocular defects and associated anomalies: report of eight cases. Obstet Gynecol. 1991;77:443-449.
28 Righini A, Avagliano L, Doneda C, et al. Prenatal magnetic resonance imaging of optic nerve head coloboma. Prenat Diagn. 2008;28:242-246.
29 Vijayaraghavan SB, Suma N, Lata S, et al. Prenatal sonographic appearance of cryptophthalmos in Fraser syndrome. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2005;25:629-630.
30 Schauer GM, Dunn LK, Godmilow L, et al. Prenatal diagnosis of Fraser syndrome at 18.5 weeks gestation, with autopsy findings at 19 weeks. Am J Med Genet. 1990;37:583-591.
31 Porges Y, Gershoni-Baruch R, Leibu R, et al. Hereditary microphthalmia with colobomatous cyst. Am J Ophthalmol. 1992;114:30-34.
32 Feldman E, Shalev E, Weiner E, et al. Microphthalmia – prenatal ultrasonic diagnosis: a case report. Prenat Diagn. 1985;5:205-207.
33 Chen CP. Prenatal diagnosis of limb-body wall complex with craniofacial defects, amniotic bands, adhesions and upper limb deficiency. Prenat Diagn. 2001;21:418-419.
34 de Elejalde MM, Elejalde BR. Ultrasonographic visualization of the fetal eye. J Craniofac Genet Dev Biol. 1985;5:319-326.
35 Chen CP, Devriendt K, Lee CC, et al. Prenatal diagnosis of partial trisomy 3p(3p23→pter) and monosomy 7q(7q36→qter) in a fetus with microcephaly alobar holoprosencephaly and cyclopia. Prenat Diagn. 1999;19:986-989.
36 van Zalen-Sprock R, van Vugt JM, van der Harten HJ, et al. First trimester diagnosis of cyclopia and holoprosencephaly. J Ultrasound Med. 1995;14:631-633.
37 Dane B, Dane C, Aksoy F, et al. Semilobar holoprosencephaly with associated cyclopia and radial aplasia: first trimester diagnosis by means of integrating 2D-3D ultrasound. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2009;280:647-651.
38 Lee YY, Lin MT, Lee MS, et al. Holoprosencephaly and cyclopia visualized by two- and three-dimensional prenatal ultrasound. Chang Gung Med J. 2002;25:207-210.
39 Elejalde BR, de Elejalde MM, Hamilton PR, et al. Prenatal diagnosis of cyclopia. Am J Med Genet. 1983;14:15-19.
40 Toth Z, Csecsei K, Szeifert G, et al. Early prenatal diagnosis of cyclopia associated with holoprosencephaly. J Clin Ultrasound. 1986;14:550-553.
41 Cho FN, Kan YY, Chen SN, et al. Prenatal diagnosis of cyclopia and proboscis in a fetus with normal chromosome at 13 weeks of gestation by three-dimensional transabdominal sonography. Prenat Diagn. 2005;25:1059-1060.
42 Hsu TY, Chang SY, Ou CY, et al. First trimester diagnosis of holoprosencephaly and cyclopia with triploidy by transvaginal three-dimensional ultrasonography. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2001;96:235-237.
43 Lev-Gur M, Maklad NF, Patel S. Ultrasonic findings in fetal cyclopia. A case report. J Reprod Med. 1983;28:554-557.
44 Kim MJ, Lee JH, Lee DW, et al. Congenital axial high myopia detected by prenatal ultrasound. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 2009;46:50-53.
45 Birnholz JC, Farrell EE. Fetal hyaloid artery: timing of regression with US. Radiology. 1988;166:781-783.
46 Katorza E, Rosner M, Zalel Y, et al. Prenatal ultrasonographic diagnosis of persistent hyperplastic primary vitreous. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2008;32:226-228.
47 Vohra N, Ghidini A, Alvarez M, et al. Walker–Warburg syndrome: prenatal ultrasound findings. Prenat Diagn. 1993;13:575-579.
48 Yazicioglu HF, Ocak Z. Walker–Warburg syndrome with persistent hyperplastic primary vitreous detected by prenatal ultrasonography. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2010;35:246-249.
49 Leonard A, Bernard P, Hiel AL, et al. Prenatal diagnosis of fetal cataract: case report and review of the literature. Fetal Diagn Ther. 2009;26:61-67.
50 Monteagudo A, Timor-Tritsch IE, Friedman AH, et al. Autosomal dominant cataracts of the fetus: early detection by transvaginal ultrasound. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 1996;8:104-108.
51 Zimmer EZ, Bronshtein M, Ophir E, et al. Sonographic diagnosis of fetal congenital cataracts. Prenat Diagn. 1993;13:503-511.
52 Monteagudo A, Alayon A, Mayberry P. Walker–Warburg syndrome: case report and review of the literature. J Ultrasound Med. 2001;20:419-426.
53 Rosner M, Bronshtein M, Leikomovitz P, et al. Transvaginal sonographic diagnosis of cataract in a fetus. Eur J Ophthalmol. 1996;6:90-93.
54 Drysdale K, Kyle PM, Sepulveda W. Prenatal detection of congenital inherited cataracts. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 1997;9:62-63.
55 Gaary EA, Rawnsley E, Marin-Padilla JM, et al. In utero detection of fetal cataracts. J Ultrasound Med. 1993;12:234-236.
56 Beinder EJ, Pfeiffer RA, Bornemann A, et al. Second-trimester diagnosis of fetal cataract in a fetus with Walker-Warburg syndrome. Fetal Diagn Ther. 1997;12:197-199.
57 Reches A, Yaron Y, Burdon K, et al. Prenatal detection of congenital bilateral cataract leading to the diagnosis of Nance-Horan syndrome in the extended family. Prenat Diagn. 2007;27:662-664.
58 Pedreira DA, Diniz EM, Schultz R, et al. Fetal cataract in congenital toxoplasmosis. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 1999;13:266-267.
59 Basbug M, Serin IS, Ozcelik B, et al. Prenatal ultrasonographic diagnosis of rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctata by detection of rhizomelic shortening and bilateral cataracts. Fetal Diagn Ther. 2005;20:171-174.
60 Romain M, Awoust J, Dugauquier C, et al. Prenatal ultrasound detection of congenital cataract in trisomy 21. Prenat Diagn. 1999;19:780-782.
61 Roberts F, Wisdom S, Howatson AG, et al. Clinicopathological study of bilateral developmental cataracts diagnosed in utero. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2006;244:237-242.
62 Mastrangelo D, De Francesco S, Di Leonardo A, et al. Does the evidence matter in medicine? The retinoblastoma paradigm. Int J Cancer. 2007;121(11):2501-2505.
63 MacCarthy A, Birch JM, Draper GJ, et al. Retinoblastoma in Great Britain 1963–2002. Br J Ophthalmol. 2006;93(1):33-37.
64 Maat-Kievit JA, Oepkes D, Hartwig NG, et al. A large retinoblastoma detected in a fetus at 21 weeks of gestation. Prenat Diagn. 1993;13:377-384.
65 Salim A, Wiknjosastro GH, Danukusumo D, et al. Fetal retinoblastoma. J Ultrasound Med. 1998;17:717-720.
66 Chitayat D, Toi A, Babul R, et al. Prenatal diagnosis of retinal nonattachment in the Walker-Warburg syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1995;56:351-358.
67 Farrell SA, Toi A, Leadman ML, et al. Prenatal diagnosis of retinal detachment in Walker-Warburg syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1987;28:619-624.
68 Redmond RM, Vaughan JI, Jay M, et al. In-utero diagnosis of Norrie disease by ultrasonography. Ophthalmic Paediatr Genet. 1993;14:1-3.
69 Robinson AJ, Blaser S, Toi A, et al. MRI of the fetal eyes: morphologic and biometric assessment for abnormal development with ultrasonographic and clinicopathologic correlation. Pediatr Radiol. 2008;38:971-981.
70 Sukonpan K, Phupong V. Fetal ocular distance in normal pregnancies. J Med Assoc Thai. 2008;91(9):1318-1322.
71 Chervenak FA, Tortora M, Mayden K, et al. Antenatal diagnosis of median cleft face syndrome: sonographic demonstration of cleft lip and hypertelorism. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1984;149:94-97.
72 Araujo Junior E, Filho HA, Pires CR, et al. Prenatal diagnosis of the 13q-syndrome through three-dimensional ultrasonography: a case report. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2006;274:243-245.
73 Kuo HC, Chang FM, Wu CH, et al. Antenatal ultrasonographic diagnosis of hypotelorism. J Formos Med Assoc. 1990;89:803-805.
74 Skidmore DL, Pai AP, Toi A, et al. Prenatal diagnosis of Apert syndrome: report of two cases. Prenat Diagn. 2003;23:1009-1013.
75 Yen MT, Tse DT. Congenital orbital cyst detected and monitored by prenatal ultrasonography. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2001;17:443-446.
76 Singh AD, Traboulsi EI, Reid J, et al. Orbital cyst: prenatal diagnosis. Ophthalmology. 116, 2009. 2042-2042, e2
77 Sueters M, Peek AM, Ball LM, et al. Prenatal detection of orbital rhabdomyosarcoma. Arch Ophthalmol. 2005;123:276-279.
78 Moon YJ, Hwang HS, Kim YR, et al. Prenatally detected congenital orbital teratoma. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2008;31:107-109.
79 Bianchini E, Zirpoli S, Righini A, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging in prenatal diagnosis of dacryocystocele: report of 3 cases. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2004;28:422-427.
80 Davis WK, Mahony BS, Carroll BA, et al. Antenatal sonographic detection of benign dacrocystoceles (lacrimal duct cysts). J Ultrasound Med. 1987;6:461-465.
81 Sharony R, Raz J, Aviram R, et al. Prenatal diagnosis of dacryocystocele: a possible marker for syndromes. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 1999;14:71-73.
82 Sepulveda W, Wojakowski AB, Elias D, et al. Congenital dacryocystocele: prenatal 2- and 3-dimensional sonographic findings. J Ultrasound Med. 2005;24:225-230.