Chapter 8 Obesity management
1 INTRODUCTION
Evaluation and management of obesity is an essential step in the treatment of patients with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and snoring based on three important facts. First, 66% of US adults are currently categorized as overweight or obese,1 placing obesity as one of the most common conditions seen among primary care providers and medical and surgical specialists. Second, obesity is a contributor to poor quality of life and increased morbidity and mortality that involves nine organ systems. Obesity, particularly upper body obesity, is a well-documented risk factor for OSA and is reported to be present in 60% to 90% of OSA patients evaluated in sleep clinics.2 Additionally, the severity of OSA is directly related to increasing body weight. Population-based studies have consistently shown an increased incidence of sleep disordered breathing with weight gain and obesity.3–5 Third, weight reduction by dietary and surgical treatment has been shown to improve co-morbid conditions including sleep disordered breathing and sleep quality.6 For these reasons, a thorough evaluation and treatment plan for OSA should specifically address weight loss for patients who are overweight or obese. This chapter will review current evaluation and treatment guidelines for overweight and obesity with a special focus for the otolaryngologist. For a more comprehensive review, readers are referred to the American Medical Association’s Assessment and Management of Adult Obesity: A Primer for Physicians.7
2 EVALUATION OF THE OVERWEIGHT AND OBESE PATIENT
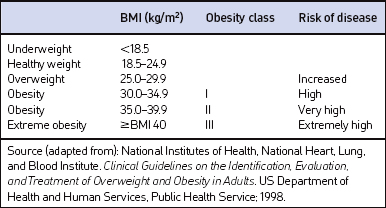
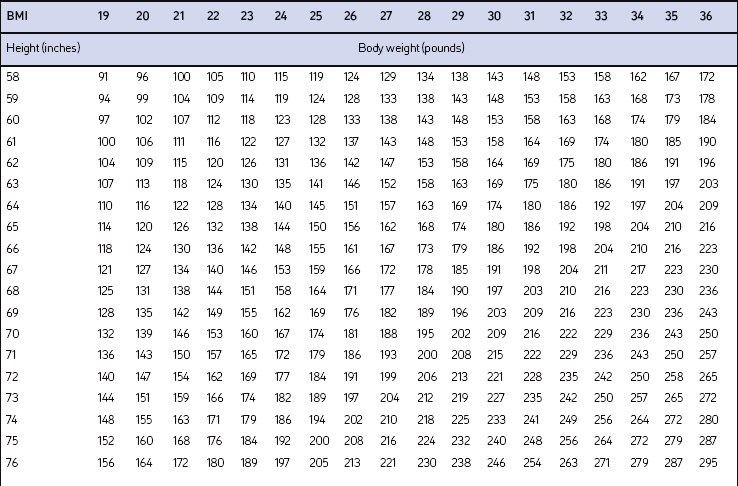
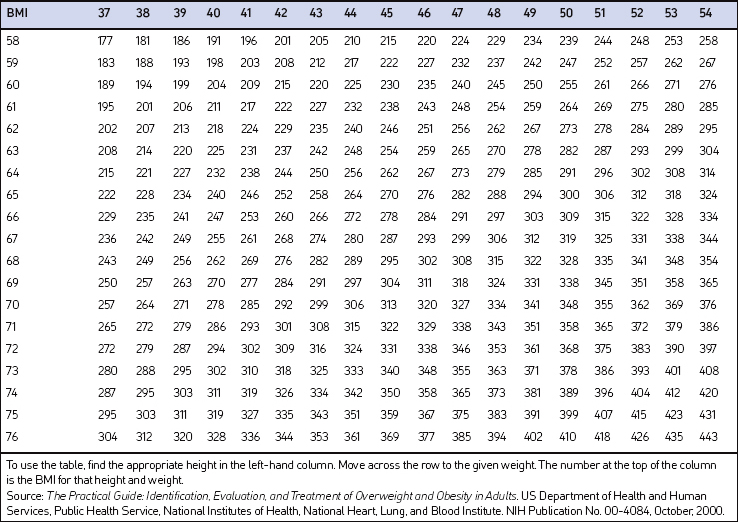
Screening for overweight and obesity should not rely on subjective visual inspection alone. Rather, screening is carried out by performing three simple anthropometric measurements: weight, height and waist circumference. These measurements can be easily obtained by ancillary office personnel. The Body Mass Index (BMI), calculated as weight (kg)/height (m)2, or as weight (pounds)/height (inches)2×703, is used to define classification of weight status and risk of disease (Table 8.1). A BMI table is more conveniently employed for simple reference (Table 8.2). BMI is used since it provides an estimate of body fat and is related to risk of disease.
Excess abdominal fat, assessed by measurement of waist circumference or waist-to-hip ratio, is independently associated with higher risk for metabolic abnormalities, diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease and OSA.8 Although protocols and guidelines differ among investigators, measurement of waist is most commonly performed in the horizontal plane above the iliac crest or at the narrowest point between the costal margin and iliac crest. Cut points that define higher risk are a waist circumference >102 cm (>40 inches) in men and >88 cm (>35 inches) in women when measured superior to the iliac crest.9 Overweight persons with waist circumferences exceeding these limits should be urged more strongly to pursue weight reduction since it categorically increases disease risk for each BMI class. Measurement of waist circumference should be obtained in those individuals with a BMI ≤35 kg/m2.
Although not specified in the clinical guidelines, it may be useful to measure neck circumference in obese patients presenting with signs and symptoms of OSA. Large neck girth in both men and women who snore is highly predictive of sleep apnea.10 Some studies suggest that neck circumference is a more useful predictor of sleep apnea than BMI11 or waist circumference.12 In general, a neck circumference of 17 inches in men or 16 inches in women indicates a higher risk for sleep apnea.
3 TAKING AN OBESITY-FOCUSED HISTORY
3.1 ASSESSING RISK
The medical history, physical examination and laboratory evaluation should be focused on assessing obesity co-morbid diseases. There is no single laboratory test or diagnostic evaluation that is indicated for all patients with obesity. The specific evaluation performed should be based on presentation of symptoms, risk factors and index of suspicion. However, based on several other screening guideline recommendations, all patients should have a fasting lipid panel (total, LDL and HDL cholesterol and triglyceride levels) and blood glucose measured at presentation along with blood pressure determination. Symptoms and diseases that are directly or indirectly related to obesity are listed in Table 8.3. Although individuals will vary, the number and severity of organ specific co-morbid conditions usually rise with increasing levels of obesity.
| Cardiovascular | Respiratory |
| Hypertension Congestive heart failure Cor pulmonale Varicose veins Pulmonary embolism Coronary artery disease |
Dyspnea Obstructive sleep apnea Hypoventilation syndrome Pickwickian syndrome Asthma |
| Endocrine | Gastrointestinal |
| Metabolic syndrome Type 2 diabetes Dyslipidemia Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS)/angrogenicity Amenorrhea/infertility/menstrual disorders |
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) Cholelithiasis Hernias Colon cancer |
| Musculoskeletal | Genitourinary |
| Hyperuricemia and gout Immobility Osteoarthritis (knees and hips) Low back pain Carpal tunnel syndrome |
Urinary stress incontinence Obesity-related glomerulopathy End-stage renal disease Hypogonadism (male) Breast and uterine cancer Pregnancy complications |
| Psychological | Neurologic |
| Depression/low self-esteem Body image disturbance Social stigmatization |
Stroke Idiopathic intracranial hypertension Meralgia paresthetica Dementia |
| Integument | |
| Striae distensae (stretch marks) Stasis pigmentation of legs Lymphedema Cellulitis Intertrigo, carbuncles Acanthosis nigricans Acrochordon (skin tags) Hidradenitis suppurativa |
An increased waist circumference has been found to be predictive of a constellation of metabolic risk factors termed the metabolic syndrome that includes elevated blood pressure, impaired fasting glucose or glucose intolerance, hypertriglyceridemia, and low HDL cholesterol.6 Although the components and cutoff values selected to define the metabolic syndrome are useful for clinical practice, the constellation of abnormalities associated with insulin resistance is much broader. These ‘non-traditional risk factors’ include increased biomarkers of chronic inflammation (C-reactive protein, tumor necrosis factor-a, interleukin-6), a prothrombotic state (increased plasma plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI)-1 and fibrinogen), endothelial dysfunction (decreased endothelium-dependent vasodilatation), hemodynamic changes (increased sympathetic nervous activity and renal sodium retention), hyper-uricemia, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). OSA often co-exists with these traditional and non-traditional cardiovascular risk factors, leading one author to coin the term ‘Syndrome Z’.13
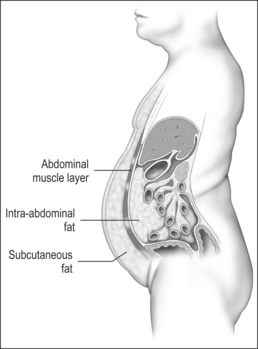
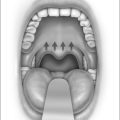
Measurement of waist circumference is a surrogate marker for visceral adipose tissue (VAT) which refers to adipose tissue located within the abdominal cavity, below abdominal muscles, and comprising omental and mesenteric adipose tissue, as well as adipose tissue of the retroperitoneal and perinephric regions (Fig. 8.1). Visceral fat accumulation has also been shown to have a significant negative impact on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes. Recent studies have linked the metabolic and inflammatory abnormalities seen in abdominal obesity to the secretion of adipocyte and adipose connective tissue products called adipokines. Secreted factors include leptin, IL-6, TNF-α, angiotensinogen, PAI-1, transforming growth factor (TGF)-β, and adiponectin among many others.14 Secretion of these products results in altered endocrine, paracrine and autocrine functions. The metabolic dysregulation and systemic inflammation seen in OSA is likely related, in part, to VAT- derived secretory products.15–17
4 TREATMENT OF THE OVERWEIGHT AND OBESE PATIENT
Guidance for weight loss should be part of the non-surgical treatment for all obese patients with OSA.18 The evidence that treatment of obesity improves OSA is reasonably well established. Both medical and surgical approaches to weight loss have been associated with a consistent but variable reduction in number of respiratory events, as well as improvement in oxygenation.10 A critical review of the literature by Strobel and Rosen6 concluded that obesity treatments have shown varying degrees of improvement in sleep disordered breathing, oxygen hemogloblin saturation, sleep fragmentation, and daytime performance. Dietary weight losses of 9–18% body weight have been associated with reductions in AHI ranging from 30% to 75%. The authors note, however, that it is presently unclear how much weight loss is necessary to achieve significant improvements in sleep disordered breathing and which patients are most likely to benefit from weight loss. In a population-based study, a 10% weight loss was associated with a 26% decrease in the AHI.5 In general, surgical weight loss interventions have shown greater improvements in the AHI compared to dietary treatments. A recent systematic literature review of bariatric gastric banding surgery noted improvement in OSA in a number of studies.19 This was consistent with another bariatric surgical meta-analysis that showed striking results with over 85% of patients having complete resolution of the disorder.20 The authors also report data from a sub-analysis of four studies (92 subjects) that showed a mean decrease of 33.85 apneas or hypopneas per hour after bariatric surgery.
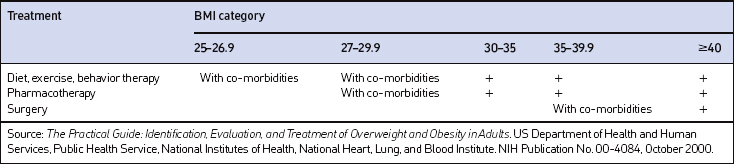
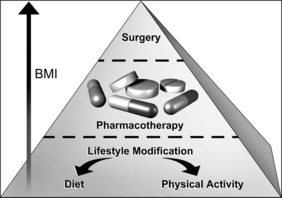
The decision of how aggressively to treat patients and which modalities to use is determined by the patient’s risk status, their abilities and desires, and by what resources are available. Table 8.4 provides a guide to selecting adjunctive treatments based on the BMI category. Equally important in choosing a treatment approach is the patient’s interest and ability to comply with the regimen and their perceptions of its effectiveness and safety. Therapy for obesity always includes lifestyle management and may include pharmacotherapy or surgery (Fig. 8.2). Since the otolaryngologist is unlikely to manage obesity by him or herself, it is essential to identify resources, e.g. registered dietitian, physician specialist, commercial or internet program, that can provide the needed assistance, monitoring and accountability for successful obesity care. The primary role of the otolaryngologist is to recognize the importance of weight loss, to incorporate weight loss into the treatment plan, and be supportive of the patient’s initiatives.
4.1 LIFESTYLE MANAGEMENT
Lifestyle management incorporates three essential components of obesity care: dietary therapy, physical activity and behavior therapy. Since obesity is fundamentally a disease of energy imbalance, all patients must learn how and when energy is consumed (diet), how and when energy is expended (physical activity) and how to incorporate this information into their daily life (behavior therapy). Lifestyle management has been shown to result in a modest (typically 3–5 kg) weight loss compared to no treatment or usual care.
The primary focus of diet therapy is on reducing overall consumption of calories. The NHLBI guidelines recommend initiating treatment with a diet producing a calorie deficit of 500–1000 kcal/day from the patient’s habitual diet with the goal of losing approximately 1–2 lb per week.21,22 This can be accomplished by suggesting substitutions or alternatives to the diet to achieve the desired calorie deficit. Examples include choosing smaller portion sizes, eating more fruits and vegetables, consuming more whole grain cereals, selecting leaner cuts of meat and skimmed dairy products, reducing fried foods and other added fats and oils, and drinking water instead of caloric beverages. Since portion control is one of the most difficult strategies for patients to manage, use of pre-prepared products, called meal replacements, is a simple and convenient suggestion. Examples include frozen entrees, canned beverages and bars. Use of meal replacements in the diet has been shown to result in a 7–8% weight loss. It is important that the dietary counseling remains patient centered and consistent with his or her cultural preferences.
Although exercise alone is only moderately effective for weight loss, the combination of dietary modification and exercise is the most effective behavioral approach for treatment of obesity. Focusing on simple ways to add physical activity into the normal daily routine through leisure activities, travel and domestic work should be suggested. Examples include walking, using the stairs, doing home and garden work, and engaging in sport activities. Asking the patient to wear a pedometer to monitor total accumulation of steps as part of the activities of daily living, or ADLs, is a useful strategy. Step counts are highly correlated with inactivity (low number of steps) as well as with activity (high number of steps). Studies have demonstrated that lifestyle activities are as effective as structured exercise programs in improving cardiorespiratory fitness and weight loss. The American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM) recommends that overweight and obese individuals progressively increase to a minimum of 150 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity per week as a first goal.23 However, for long-term weight loss, higher amounts of exercise (200–300 minutes per week or ≥2000 kcal/week) are needed. The Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2005 found compelling evidence that at least 60–90 minutes of daily moderate-intensity physical activity (420–630 minutes per week) are needed to sustain weight loss.24 The ACSM also recommends that resistance exercise supplement the endurance exercise program. These recommendations will feel daunting to most patients and need to be implemented gradually. Many patients would benefit from consultation with an exercise physiologist or personal trainer.
4.2 PHARMACOTHERAPY
Adjuvant pharmacological treatments should be considered for patients with a BMI of 30 kg/m2 or with a BMI of 27 kg/m2 who also have concomitant obesity-related risk factors or diseases and for whom dietary and physical activity therapy has not been successful. When prescribing an anti-obesity medication, patients should be actively engaged in a lifestyle program that provides the strategies and skills needed to effectively use the drug since this support increases total weight loss. There are several potential targets of pharmacological therapy for obesity, all based on the concept of producing a sustained negative energy (calorie) balance.25,26
4.5 THE ENDOCANNABINOID SYSTEM
Cannabinoid receptors and their endogenous ligands have been implicated in a variety of physiological functions, including feeding, modulation of pain, emotional behavior, and peripheral lipid metabolism.27 The cannabinoid receptors, the endocannabinoids and the enzymes catalyzing their biosynthesis and degradation constitute the endocannabinoid system or ECS. Cannabis and its main ingredient, Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), is an exogenous cannabinoid compound. Two endocannabinoids have been identified: anandamide and 2-arachidonyl glyceride (2-AG). Two cannabinoid receptors have been cloned termed CB1 (abundant in the brain) and CB2 (present in immune cells). The brain ECS is thought to control food intake through reinforcing motivation to find and consume foods with high incentive value and regulate actions of other mediators of appetite. The first selective cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist, called rimonabant, was discovered in 1994. The medication is effective in antagonizing the appetite-stimulating effect of THC and suppressing appetite when given alone in animal models.
Thus far, several large prospective, randomized controlled trials have demonstrated the effectiveness of rimo-nabant as a weight loss agent.28 Taken as a 20 mg dose, subjects lost an average of approximately 6.5 kg compared to approximately 1.5 kg for placebo at 1 year. Concomi-tant improvements were seen in waist circumference and cardiovascular risk factors. The most common reported side effects include depression, anxiety and nausea. Rimonabant is approved for use in Europe and other countries outside the US.
4.6 WEIGHT LOSS SURGERY
Bariatric surgery can be considered for patients with severe obesity (BMI=40 kg/m2) or those with moderate obesity (BMI=35 kg/m2) associated with a serious medical condition such as OSA.29 Surgical weight loss functions by reducing caloric intake and, depending on the procedure, macronutrient absorption. The improvement in co-morbid conditions is the result of multiple factors including weight and body fat loss, change in diet, and for the malabsorptive procedures, anatomical changes of the gastrointestinal tract that effect altered responses of several gut hormones involved in glucose regulation and appetite control.
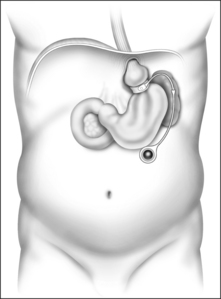
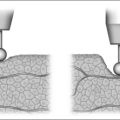
Weight loss surgeries fall into one of two categories: restrictive and restrictive malabsorptive. Restrictive surgeries limit the amount of food the stomach can hold and slow the rate of gastric emptying. The laparoscopic adjustable silicone gastric banding (LASGB) is the most commonly performed restrictive operation. The first banding device, the LAP-BAND, was approved for use in the United States in 2001. In contrast to previous devices, the diameter of this band is adjustable by way of its connection to a reservoir that is implanted under the skin (Fig. 8.3). Injection or removal of saline into the reservoir tightens or loosens the band’s internal diameter, respectively, thus changing the size of the gastric opening. Since there is no rerouting of the intestine with LASGB, the risk for developing micronutrient deficiencies is entirely dependent on the patient’s diet and eating habits.
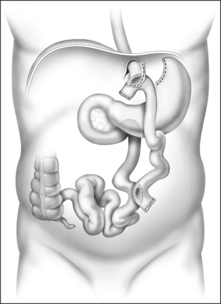
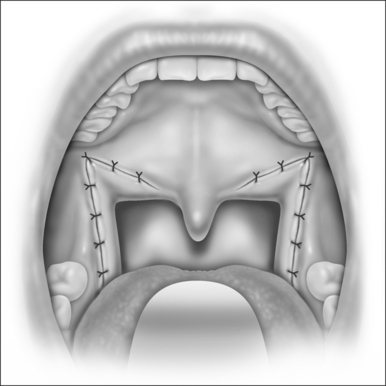
The Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) is the most commonly performed and accepted of the restrictive-malabsorptive bypass procedures. It involves formation of a 10–30 ml proximal gastric pouch by either surgically separating or stapling the stomach across the fundus (Fig. 8.4). Outflow from the pouch is created by performing a narrow (10 mm) gastrojejunostomy. The distal end of jejunum is then anastomosed 50–150 cm below the gastrojejunostomy. ‘Roux-en-Y’ refers to the Y-shaped section of small intestine created by the surgery; the Y is created at the point where the pancreo-biliary conduit (afferent limb) and the Roux (efferent) limb are connected. ‘Bypass’ refers to the exclusion or bypassing of the distal stomach, duodenum and proximal jejunum. RYGB may be performed with an open incision or laparoscopically.
1. Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Curtin LR. Prevalence of overweight and obesity in the United States, 1999–2004. JAMA. 2006;295:1549-1555.
2. Strohl KP, Redline S. Recognition of obstructive sleep apnea. Am J Crit Care Med. 1996;154:279-289.
3. Newman AB, Foster G, Givelber R, et al. Progression and regression of sleep-disordered breathing with changes in weight. The Sleep Heart Health Study. Arch Intern Med. 2005;165:2408-2413.
4. Young T, Shahar E, Nieto FJ, et al. Predictors of sleep-disordered breathing in community-dwelling adults: the Sleep Heart Health Study. Arch Intern Med. 2002;162:893-900.
5. Peppard PE, Young T, Palta M, et al. Longitudinal study of moderate weight change and sleep-disordered breathing. JAMA. 2000;284:3015-3021.
6. Strobel RJ, Rosen RC. Obesity and weight loss in obstructive sleep apnea: a critical review. Sleep. 1996;19:104-115.
7. Kushner RF. Roadmaps for Clinical Practice. Case Studies in Disease Prevention and Health Promotion – Assessment and Management of Adult Obesity. A Primer for Physicians. Chicago, Illinois: American Medical Association; 2003. Available at: www.ama-assn.org/ama/pub/category/10931.html
8. Tishler PV, Larkin EK, Schluchter MD, Redline S. Incidence of sleep-disordered breathing in an urban adult population. The relative importance of risk factors in the development of sleep-disordered breathing. JAMA. 2003;289:2230-2237.
9. National Institutes of Health. Third Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). Bethesda, MD: National Institutes of Health; 2001. NIH Publication No. 01-3670.
10. National Institutes of Health and National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Sleep Apnea: Is Your Patient at risk? NIH Publication No. 95-3803, September 1995.
11. Davies RJO, Ali NJ, Stradling JR. Neck circumference and other clinical features in the diagnosis of the obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome. Thorax. 1992;47:101-105.
12. Resta O, Foschino-Barbaro MP, Legari G, et al. Sleep-related breathing disorders, loud snoring and excessive daytime sleepiness in obese subjects. Int J Obesity. 2001;25:669-675.
13. Wilcox I, McNamara SG, Collins FL, et al. ‘Syndrome Z’: the interaction of sleep apnoea, vascular risk factors and heart disease. Thorax. 1998;53(Suppl 3):S25-S28.
14. Greenberg AS, Obin MS. Obesity and the role of adipose tissue in inflammation and metabolism. Am J Clin Nutr. 2006;83:461S-465S.
15. Brown LK. A waist is a terrible thing to mind. Central obesity, the metabolic syndrome, and sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome. Chest. 2002;122:774-778.
16. Coughlin S, Calverley P, Wilding J. Sleep disordered breathing – a new component of syndrome X? Obes Rev. 2001;2:267-274.
17. Wolk R, Shamsuzzaman ASM, Somers VK. Obesity, sleep apnea, and hypertension. Hypertension. 2003;42:1067-1074.
18. Capies SM, Gami AS, Somers VK. Obstructive sleep apnea. Ann Intern Med. 2005;142:187-197.
19. Chapman AE, Kiroff G, Game P. Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding in the treatment of obesity: a systematic literature review. Surgery. 2004;135:326-351.
20. Buchwald H, Avidor Y, Braunwald E. Bariatric surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2004;292:1724-1737.
21. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) Obesity Education Initiative Expert Panel. Identification, Evaluation, and Treatment of Overweight and Obesity in Adults: Evidence Report. NIH Publication NO. 4083, June 1998.
22. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) and North American Association for the Study of Obesity (NAASO). The Practical Guide. Identification, Evaluation, and treatment of Overweight and Obesity in Adults. NIH Publication NO. 00-4084, October 2000.
23. Jakicic JM, et al. Appropriate intervention strategies for weight loss and prevention of Weight Regain for Adults. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2001;33:2145-2156.
24. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services and U.S. Department of Agriculture. Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2005, 6th edn. Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office, January 2005. Available at: www.health.gov/dietaryguidelines/dga2005/document/html
25. Yanovski S, Yanovski JA. Obesity. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:591-602.
26. Padwal R, Li SK, Lau DCW. Long-term pharmacotherapy for overweight and obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int J Obesity. 2003;27:1437-1446.
27. Cota D, Woods SC. The role of the endocannabinoid system in the regulation of energy homeostasis. Curr Opin Endo Diab. 2005;12:338-351.
28. Pi-Sunyer FX, Aronne LJ, Heshmati HM, et al. Effect of rimonabant, a cannabinoid-1 receptor blocker, on weight and cardiometabolic risk factors in overweight or obese patients. RIO-North America: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2006;295:761-775.
29. Consensus Development Conference Panel. Gastrointestinal surgery for severe obesity. Ann Intern Med. 1991;115:956-961.