Chapter 183 Nocardia
Epidemiology
Once thought to be a rare cause of human disease, nocardiosis is being recognized more frequently, and has been diagnosed in persons from 4 wk to 82 yr of age. Almost all patients have compromised cellular immunity from an underlying disease such as organ transplantation, malignancy, corticosteroids, diabetes, HIV infection, or primary immunodeficiency, especially chronic granulomatous disease (Chapter 124). Nocardia infections among stem cell transplant recipients are associated with a high rate of concomitant invasive fungal infection and a notable lack of protection with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole prophylaxis. An evaluation of opportunistic infections in 547 organ transplant recipients receiving Alemtuzumab (humanized monoclonal CD52 antibody) revealed that 62 opportunistic infections developed in 56 patients (10%), Nocardia being found in 4 patients.
Clinical Manifestations
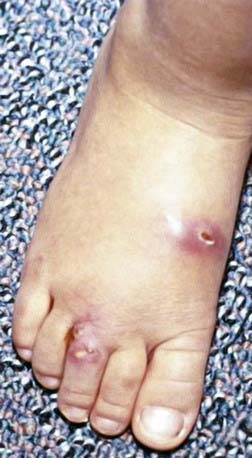
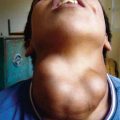
The skin is the third most commonly involved organ, and its infection may be manifested by sporotrichoid nocardiosis or superficial ulcers (Fig. 183-1). Mycetoma is a chronic, progressive infection developing days to months after inoculation, usually on a distal location on the limbs. Renal nocardiosis, the 4th most common type, typically manifests as dysuria, hematuria, or pyuria. Lesions may extend from the cortex into the medulla. Gastrointestinal involvement may also be associated with nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal distention, and melena. Infection may spread to skin, pericardium, myocardium, spleen, liver, or adrenal glands. Bone involvement is rare. Almost all of the involved organs have several abscesses, but in contrast to actinomycosis, granules are rarely found in nocardiosis. Keratitis caused by N. farcinica has been associated with the use of semipermeable rigid contact lenses.
Barton LL. Lymphocutaneous Nocardia brasiliensis infection in children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2001;20:232-233.
Bonifaz A, Gonzalez-Silva A, Albrandt-Salmeron A, et al. Utility of helical computed tomography to evaluate the invasion of actinomycetoma; a report of 21 cases. Br J Dermatol. 2008;158:698-704.
Dorman SE, Guide SV, Conville PS, et al. Nocardia infection in chronic granulomatous disease. Clin Infect Dis. 2002;35:390-394.
Fergie JE, Purcell K. Nocardiosis in south Texas children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2001;20:711-714.
Peleg AY, Husain S, Kwak EJ, et al. Opportunistic infections in 547 organ transplant recipients receiving Alemtuzumab, a humanized monoclonal CD-52 antibody. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;44:204-212.
Torres OH, Domingo P, Pericas R, et al. Infection caused by Nocardia farcinica: case report and review. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2000;19:205-212.