70 Neurofibromatosis
Salient features
History
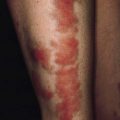
• Presents in childhood with cutaneous features including café-au-lait spots, axillary freckles and neurofibromas
• Obtain history of learning disabilities (about half the patients with neurofibroma 1 are affected; Nature 2000;403:846–7)
• Childhood leukaemia: the risk of malignant myeloid disorders, particularly juvenile myelomonocytic leukaemia and the monosomy 7 syndrome (a childhood variant of myeloid dysplasia) is 200 to 500 times the normal risk (N Engl J Med 1997;336:1713–20).
Examination
• Multiple neurofibroma and café-au-lait spots (brown macules, >2.5 cm diameter and >5 lesions)
• Examine the axilla for freckles
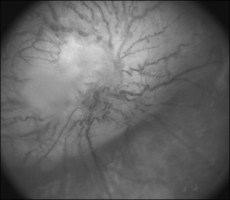
• Check visual acuity and fundus for optic glioma (Fig. 70.1)
• Hearing and corneal sensation for acoustic neuroma
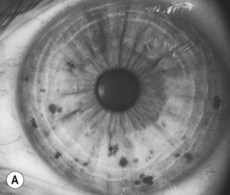
• The iris for Lisch nodules (often apparent only by slit-lamp examination). The incidence of Lisch nodules in type 1 increases with age (at the age of 5 years only 22% have Lisch nodules, whereas at the age of 20 years 100% have them). Therefore, older individuals who do not have Lisch nodules are unlikely to have type 1 neurofibromatosis (Fig. 70.2)
• The spine for kyphoscoliosis
• Tell the examiner that you would like to check the BP (for renal artery stenosis or phaeochromocytoma).
Advanced-level questions
What are the criteria for neurofibromatosis type 1 (von Recklinghausen’s disease)?
Neurofibromatosis type 1 may be diagnosed when two or more of the following are present:
• Six or more café-au-lait spots, the greatest diameter of which is >5 mm in prepubertal patients and >15 mm in postpubertal patients
• Two or more neurofibromas or one plexiform neurofibroma. Plexiform neurofibroma is considered by some to be a defining lesion of neurofibroma type 1
• Freckling in the axilla or inguinal region (Crowe’s sign)
• Two or more Lisch nodules (iris hamartoma)
• A distinctive osseous lesion such as sphenoid dysplasia or thinning of long bone cortex with or without pseudoarthroses
• A parent, sibling or child with neurofibromatosis according to the above criteria.
What are the criteria for neurofibromatosis type 2?
• Bilateral eighth nerve palsy confirmed by CT or MRI
• A parent, sibling or child with neurofibromatosis type 2 and either unilateral eighth nerve mass or any two of the following: neurofibroma, meningioma, glioma, schwannoma or juvenile posterior subcapsular lenticular opacity (N Engl J Med 1988;318:685).
What is the histology of the skin tumours?
The peripheral nerve tumours are of two types:
• Schwannomas: arise in cranial and spinal nerve roots and also in peripheral nerve trunks.
• Neurofibromas: composed of a proliferation of all elements of the peripheral nerve including neuritis, Schwann cells and fibroblasts. In sensory nerve twigs, they appear as subcutaneous nodules, while in peripheral nerve trunks they may appear as a fusiform enlargement or a plexiform neurofibroma.
Is a biopsy of the neurofibromas required to make a diagnosis?
No, as the diagnosis is usually evident on clinical grounds.