16 Neonatal medicine
Care of the normal baby following delivery
Care on the postnatal ward
Respiratory rate
• Infection – this commonly includes group B β-haemolytic streptococcus, Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Listeria monocytogenes, Klebsiella, Enterobacter and Streptococcus pneumoniae
• Central nervous system depression, especially after birth asphyxia
• Metabolic disease with acidosis
• Transient tachypnoea of the newborn
• Congenital anomalies, including causes of upper airway obstruction like goitre, tracheo-oesophageal fistula, diaphragmatic hernia and pulmonary agenesis.
Feeding
• It contains the maternal factors that reduce infection in babies:
• The water, fat and protein mix varies throughout a feed to give a balanced diet.
• It lessens the risk of cows’ milk intolerance.
• It is associated with a lower risk of sudden infant death syndrome.
• Antibiotics, e.g. chloramphenicol, metronidazole, isoniazid, tetracyclines, trimethoprim
• Antiarrhythmics, e.g. atenolol, amiodarone
• Anti-inflammatories, e.g. indometacin
• Antidepressants, e.g. lithium, doxepin
• Antimalarials, e.g. dapsone preparations
Breastfeeding babies will feed on demand and will self-regulate their intake.
Examination of the newborn
Jaundice
• Shortened lifespan of fetal erythrocytes, resulting in increased breakdown as well as liver enzyme immaturity
Routine investigations include:
• Full blood count, reticulocyte count and blood film
• Maternal and baby blood group
• Full infection screen, depending on status of the baby, may be considered, including blood and cerebrospinal fluid for culture.
If baby fails to respond, then investigate further for rarer causes.
Neonatal resuscitation
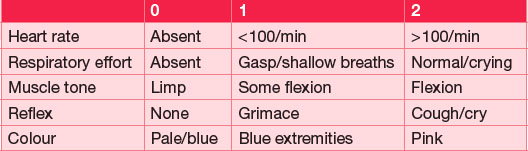
Most babies are born in good condition and do not require any special stimulation or resuscitation. Immediately following delivery, the baby should be gently dried and rapidly assessed. Mucus is only removed from the mouth and then nose if necessary or if meconium is present at delivery. The Apgar score is a system developed for the initial assessment of the newborn at 1 and 5 minutes, and thereafter if indicated. It consists of a score from 0 to 2 for each of five variables, giving a score out of 10 (Table 16.1).
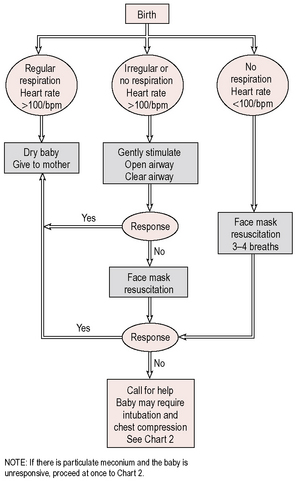
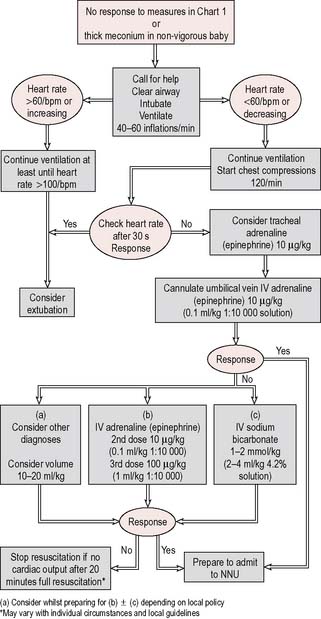
If the baby is vigorous and pink, then the baby can be wrapped to keep warm and passed immediately to the mother. If a baby fails to breathe by 1 minute despite drying off and stimulation of the feet, then immediate paediatric assistance should be called. If the baby is considered ‘flat’ or limp at delivery – impaired breathing or heart rate below 100 bpm – then resuscitate immediately following the guidelines outlined in Figures 16.1 and 16.2.