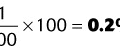CHAPTER 13 NEONATAL AND PEDIATRIC RESPIRATORY CARE
PRETEST QUESTIONS
1. An APGAR score of 5 is determined 5 min after delivery of a term infant. Which of the following should be done at this time?
2. The foramen ovale and ductus arteriosus remain patent in infants with persistent fetal circulation as a direct result of which of the following?
3. Which of the following is not an indication for nasal CPAP in an infant?
4. Which of the following are complications of an umbilical artery catheter (UAC)?
5. Which of the following may occur as a result of cold stress to an infant?
6. An elevation in the levels of chloride in sweat is diagnostic for which of the following lung conditions?
REVIEW
| pH | 7.35 to 7.45 (no less than 7.25 at birth) |
| PaCO2 | 35 to 45 mm Hg |
| PaO2 | 50 to 70 mm Hg |
| HCO3− | 20 to 26 mEq/L |
| BE | −5 to +5 |
II. NEONATAL CARDIOPULMONARY DISORDERS
![]() Exam Note
Exam Note
Any condition that results in increased pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) can cause PPHN.
III. Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO)
ECMO is not specifically mentioned on either exam matrix.
IV. AIRWAY DISORDERS OF THE PEDIATRIC PATIENT
CRT Exam Content Matrix: IA2, IA6, IB1a, IB1c, IB7d, IB8, IC1, IIA12a, IIID5a, IIIE1, IIIF2c-d
RRT Exam Content Matrix: IA2, IA6, IB1a, IB8, IIIE1
POSTCHAPTER STUDY QUESTIONS
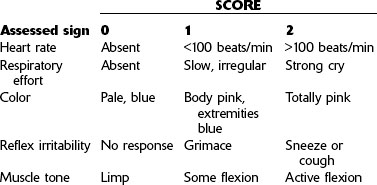
1. What five conditions are assessed in the Apgar score?
2. Describe the appropriate intervention for the following Apgar scores: 0 to 3; 4 to 6; and 7 to 10.
3. What is often the first sign of respiratory distress in the infant?
4. List the normal ABG levels for an infant.
5. List six indications for nasal CPAP.
6. List five complications of CPAP.
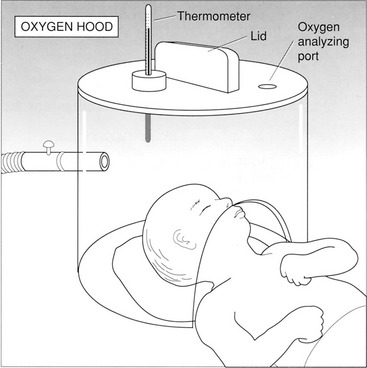
7. List two hazards of O2 therapy in the neonate.
8. Describe where the tip of the UAC should rest when properly positioned.
9. List four advantages of a UAC.
10. List four complications of a UAC.
11. List six clinical manifestations of IRDS.
13. List eight clinical manifestations of BPD.
14. Describe the chest x-ray findings in infants with BPD.
15. List the treatment modalities for BPD.
16. List the causes of meconium aspiration.
17. List eight clinical manifestations of meconium aspiration.
18. List eight conditions that accompany PPHN.
19. List five clinical manifestations of PPHN.
20. List the treatment modalities for PPHN.
21. List the causes of epiglottitis.
22. List 12 clinical manifestations of epiglottitis.
23. Describe the classic x-ray finding for diagnosis of epiglottitis.
24. List the treatment modalities for epiglottitis.
Hess D, Respiratory care principles and practice, ed 1, Philadelphia, Saunders, 2002.
Scanlan C, Spearman C, Sheldon R. Egan’s fundamentals of respiratory care, ed 5. St Louis: Mosby; 1990.
Walsh BK, Czernnske MP, DiBlasi RM. Perinatal and pediatric respiratory care, ed 3. St Louis: Saunders; 2010.
Whitaker K. Comprehensive perinatal and pediatric respiratory care, ed 3. Albany, NY: Delmar; 2001.
Wilkins RL, Stoller JK, Kacmarek R. Egan’s fundamentals of respiratory care, ed 9. St Louis: Mosby; 2009.