Chapter 68 Nail disorders
Table 68-1. Nail Disorders in Systemic Disease
| NAIL ABNORMALITY | AREA INVOLVED | ASSOCIATED DISEASE |
|---|---|---|
| Splinter hemorrhages | Bed | Bacterial endocarditis |
| Mees’ lines | Plate | Arsenic exposure |
| Muehrcke’s lines | Bed | Nephrotic syndrome |
| Terry’s nails | Bed | Cirrhosis |
| Half-and-half nails | Bed | Chronic renal failure |
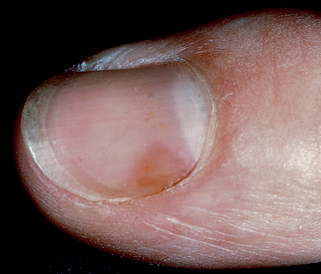
| Blue lunulae | Matrix | Wilson’s disease |
| Red lunulae | Matrix | Rheumatoid arthritis |
| Clubbing | Plate/matrix | Pulmonary disorders |
| Spoon nails | Plate/matrix | Iron deficiency |
| Nail fold telangiectasias | Nailfold | Scleroderma, systemic lupus |
| Yellow nails | Plate | Pulmonary disorders, sinusitis |
Scher RK, Daniel CR: Nails: therapy, diagnosis, surgery, ed 3: Philadelphia, 2005, WB Saunders.
Muehrcke RC: The finger-nails in chronic hypoalbuminaemia, Br Med J 9:1327–1328, 1956.
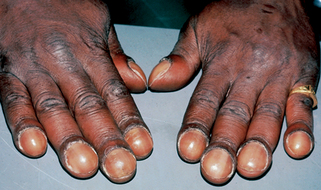
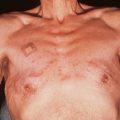
Figure 68-1. Half-and-half nails in a patient with chronic renal disease.
(Courtesy of the Fitzsimons Army Medical Center teaching files.)
Tosti A: The nail apparatus in collagen disorders, Semin Dermatol 10:71–76, 1991.
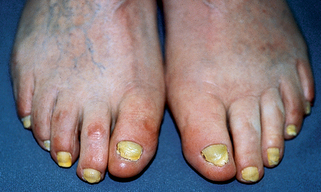
Figure 68-3. Yellow nail syndrome, demonstrating typical thick, yellow, and curved nails.
(Courtesy of James E. Fitzpatrick, MD.)
Table 68-2. Dermatologic Disorders with Nail Changes
| DISEASE | INCIDENCE | FINDINGS |
|---|---|---|
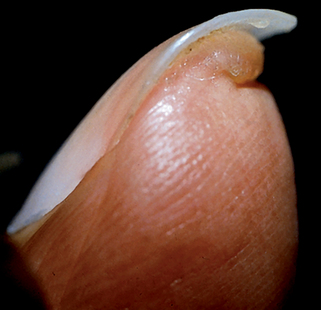
| Psoriasis | 10%–50% | Pits, “oil spots” |
| Alopecia areata | 20%–50% | Pits |
| Lichen planus | 10% | Pterygium |
| Scleroderma | Frequent | Pterygium inversus unguium |
| Darier’s disease | High | Wedge shaped, hyperkeratosis |
| Pityriasis rubra pilaris | Majority | Yellow-brown, hyperkeratotic |
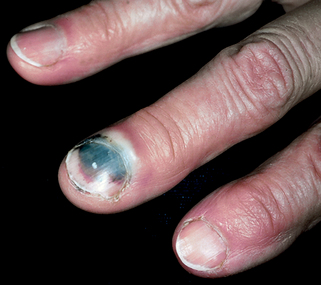
Pterygium inversus unguium occurs when the nail plate distally does not separate from the underlying digital bed skin. The fingertip ulcerations and scarring also seen in scleroderma contribute to the inability of the nail to separate (Fig. 68-5).
Jebson PJL: Infections of the fingertip: paronychias and felons, Hand Clin 14:547–555, 1998.
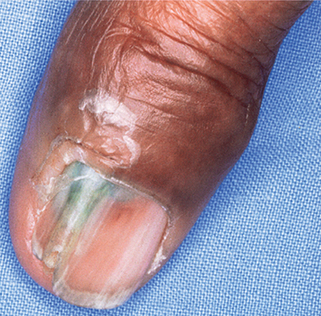
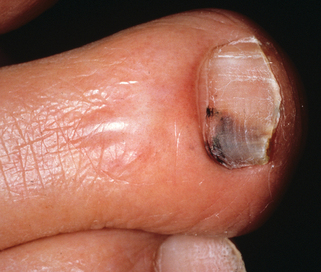
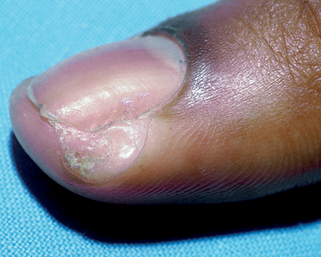
Figure 68-8. Green nail with onycholysis secondary to Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection.
(Courtesy of the Fitzsimons Army Medical Center teaching files.)
Table 68-3. Antifungal Medications for Treatment of Toenail Onychomycosis
| DRUG | BRAND NAME | DOSE |
|---|---|---|
| Itraconazole | Sporanox | Continuous: 200 mg qd for 12 weeks Pulse: 200 mg bid 1 week per month for 12 weeks |
| Terbinafine | Lamisil | Continuous: 250 mg qd for 12 weeks Pulse: 250 mg qd 1 week per q 3 months for 6–12 months |
| Fluconazole | Diflucan | 150–200 mg every week for 12 months or until nails clear |
Adapted from Zaias N, Rebell G: The successful treatment of Trichophyton rubrum nail bed (distal subungual) onychomycosis with intermittent pulse-dosed terbinafine, Arch Dermatol 140:691–695, 2004.
Wolverton S: Comprehensive dermatologic drug therapy, Philadelphia, 2001, WB Saunders.