Mushroom Toxicity
There are four major types of mushroom toxins:
If a toxic mushroom ingestion is suspected, follow this guide to mushroom identification:
1. Collect any specimens left at home—preferably uncooked.
2. Collect fresh specimens from gathering site(s).
3. Transport and store mushrooms in paper bags.
4. Spores can be recovered from gastrointestinal fluid.
5. Note initial toxicity and time since ingestion. Note symptoms or lack of symptoms among others ingesting mushrooms.
6. Contact a regional poison information center for assistance in locating an expert in identification.
7. When symptoms are not consistent with the identified species, consider that the person might have ingested another type of mushroom.
Disorders Caused by Gastrointestinal Toxins (Table 41-1)
Signs and Symptoms
Table 41-1
Gastrointestinal Disorders: Causative Mushrooms and Identification
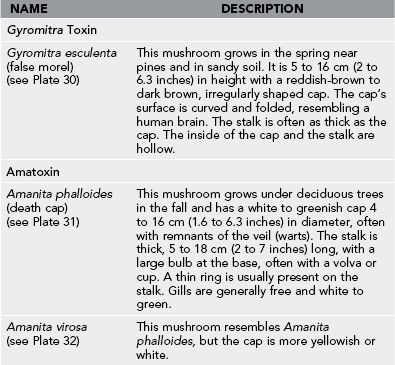
| NAME | DESCRIPTION |
| Chlorophyllum molybdites (green-spored parasol) (see Plate 23) | This summer mushroom has a large, whitish cap (often 10 to 40 cm [3.9 to 15.7 inches] in diameter) that is initially smooth and becomes convex with maturity. Tan or brown warts may be present. The gills are free from the stalk, initially white to yellow and becoming green with maturity. The stalk is 5 to 25 cm (2 to 9.8 inches) long, smooth, and white. The ring is generally brown on the underside. |
| Omphalotus olearius (jack-o’-lantern) (see Plate 24) | This bright orange to yellow mushroom has sharp-edged gills. It often grows in clusters at the base of stumps or on buried roots of deciduous trees. The cap is 4 to 16 cm (1.6 to 6.3 inches) in diameter on a stalk that is 4 to 20 cm (1.6 to 7.9 inches) long. Gills are olive to orange, with white to yellow spores. |
| Amanita flavorubescens and Amanita brunnescens | Both have broad caps (3 to 15 cm [1.2 to 5.9 inches] in diameter) with loosely attached warts. The caps are yellowish to brown. The stalks are 3 to 18 cm (1.2 to 7.1 inches) long, enlarging toward the base with a superior ring. |
Treatment
1. Initiate supportive treatment, including intravenous or oral fluid and electrolyte replacement.
2. For a severe case, administer an antiemetic such as prochlorperazine (Compazine), 2.5 to 10 mg IV or a 25-mg suppository, or ondansetron 4 to 8 mg oral disintegrating tablet or IV.
3. Treat diarrhea with loperamide 4 mg initially, followed by 2 mg after each loose stool, up to 16 mg/day.
Disorders Caused by Disulfiram-Like Toxins (Table 41-2)
Signs and Symptoms
Table 41-2
Disulfiram-like Disorders: Causative Mushroom and Identification
| NAME | DESCRIPTION |
| Coprinus atramentarius (inky cap) (see Plate 25) | This mushroom has a 2- to 8-cm (0.8- to 3.1-inch) cylindric cap on a 4- to 5-cm (1.6- to 2-inch) thin stalk. The cap is white, occasionally orange or yellow at the top, with a surface that is characteristically shaggy. The mature cap often develops cracks at its margins, which turn up. The cap blackens as it matures and then liquefies. |
1. If a person ingests these mushrooms and subsequently ingests alcohol, symptoms similar to those of an alcohol-disulfiram (Antabuse) reaction
a. Severe headache, flushing, and tachycardia within 15 to 30 minutes of alcohol ingestion
b. Hyperventilation, shortness of breath, palpitations
c. Chest pain and orthostatic hypotension in severe cases; may be confused with an allergic reaction or acute myocardial infarction
2. Sensitivity to alcohol ingestion 2 to 6 hours after ingestion and lasting for up to 72 hours
Treatment
1. Generally requires only supportive care.
2. Hypotension responds to fluid or, if necessary, norepinephrine (2 to 4 mcg/min IV or 0.05 to 0.1 mcg/kg/min in children, increasing as needed every 5 to 10 minutes).
3. Severe symptomatic supraventricular tachycardia can be controlled with propranolol (0.5 to 3 mg IV in adults, or in children 0.01 to 0.02 mg/kg up to a maximum of 1 mg per dose, repeated after 5 to 10 minutes as needed).
4. Note that symptoms may resolve spontaneously within 3 to 6 hours.
Disorders Caused by Neurologic Toxins (Muscarine) (Table 41-3)
Signs and Symptoms
Table 41-3
Muscarine Disorders: Causative Mushrooms and Identification
| NAME | DESCRIPTION |
| Amanita muscaria (see Plate 26) | This mushroom has a cap 5 to 30 cm (2 to 11.9 inches) in diameter that is scarlet red with white warts. The stalk is white, often hollow, and grows 15 to 20 cm (5.9 to 7.9 inches) long, tapering upward. It has a prominent cup and volva and numerous rings. Gills are free and white. |
| Inocybe cookei (see Plate 27) | The Inocybe family contains small brown mushrooms with conical caps up to 6 cm (2.4 inches) in diameter. Stalks are 2 to 10 cm (0.8 to 3.9 inches) long, covered with fine brown to white hairs. Gills are brown and notched. |
| Clitocybe dealbata | Clitocybe mushrooms are whitish tan to gray, with 15- to 33-mm (0.6- to 1.3-inch) caps on hairless stalks 1 to 5 cm (0.4 to 2 inches) long. Gills run down the stalk. |
1. Symptoms developing within 15 to 30 minutes of ingesting muscarine-containing mushrooms
2. Salivation, lacrimation, urination, diarrhea, diaphoresis, gastrointestinal upset, and emesis (SLUDGE)
3. Bradycardia and bronchospasm
5. Copious bronchial secretions that may cause respiratory failure, requiring mechanical ventilation
Treatment
1. Supportive care with oxygen, suctioning, and endotracheal intubation as needed
2. Fluid and electrolyte replacement
3. Atropine (if symptoms are life threatening) 0.01 mg/kg IV every 5 to 10 minutes until secretions are controlled. There is no upper limit to the dose if secretions are excessive. Atropine may worsen central nervous system effects of some mushrooms, such as Amanita muscaria
Isoxazole Reactions (Table 41-4)
Signs and Symptoms
Table 41-4
Isoxazole Reactions: Causative Mushrooms and Identification
| NAME | DESCRIPTION |
| Amanita muscaria | See Table 41-3. |
| Amanita pantherina (see Plate 28) | This mushroom is 5 to 15 cm (2 to 5.9 inches) long with a cap 5 to 15 cm in diameter. The cap is white to pink early and becomes reddish-brown or brown with maturity. The stalk has a distinct ring, with a volva or cup at the bottom. When the flesh is cut or injured, it develops a pinkish tinge. Gills are free and produce white spores. |
Disorders Caused by Hallucinogenic Mushrooms (Table 41-5)
Signs and Symptoms
Table 41-5
Hallucinogenic Disorders: Causative Mushrooms and Identification
| NAME | DESCRIPTION |
| Species of Psilocybe (see Plate 29) | These are little brown mushrooms with 0.5- to 4-cm (0.2- to 1.6-inch) broad caps that are smooth and become sticky or slippery when wet. The stalks are slender and 4 to 15 cm (1.6 to 5.9 inches) long. Gills are gray to purple-gray. The flesh of these mushrooms turns blue or greenish when bruised or cut. |
| Species of Panaeolus | These little brown mushrooms are about the same size as Psilocybe. Gills are dark gray or black with black spores. Unlike Psilocybe, the caps are not sticky or slippery when wet. |
Disorders Caused by Protoplasmic Poisons (Table 41-6)
Signs and Symptoms
Treatment
1. Activated charcoal if the patient presents within 1 hour of ingestion. Note that most of these patients will be asymptomatic
2. Fluid and electrolyte replacement as needed
3. Glucose replacement. Treat hypoglycemia with glucose infusion
4. Pyridoxine 25 mg/kg up to 20 g/day IV to control seizures or coma
5. If significant hepatic failure occurs, transfer to transplant facility.