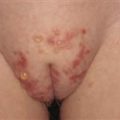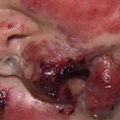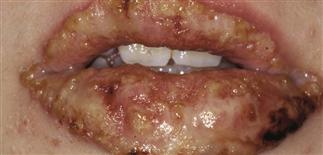
Childhood pemphigus vulgaris with severe erosions in oral mucosa and on the lips.
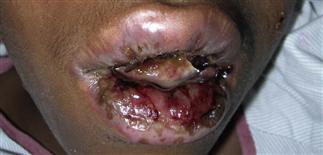
Lip and mucosal erosions in child with pemphigus vulgaris.
CLINICAL FEATURES
Oral erosions are also seen in immunobullous diseases and are particularly characteristic of pemphigus vulgaris and paraneoplastic pemphigus. They are rarely seen in dermatitis herpetiformis and not at all in children with linear IgA disease, bullous pemphigoid or pemphigus foliaceous.
Of the hereditary mechanobullous diseases, mucosal erosions are prominent in the oral cavity of newborns with recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa, and with junctional epidermolysis bullosa. In those two conditions, mucosal lesions, particularly oral lesions, become progressively worse. In most forms of epidermolysis bullosa simplex, newborns do not have mucosal involvement except in the Koebner type and Dowling–Meara type. Oral involvement in EB simplex improves with age.