Motor System
Arms
BACKGROUND
Upper motor neurone or pyramidal weakness predominantly affects finger extension, elbow extension and shoulder abduction. N.B. Elbow flexion and grip are relatively preserved.
Muscles are usually innervated by more than one nerve root. The exact distribution varies between individuals. The main root innervations and reflexes are shown in simplified form in Table 17.1. More detailed root distribution is given below.
Table 17.1
| Root | Movements | Reflex |
| C5 | Shoulder abduction, elbow flexion | Biceps |
| C6 | Elbow flexion (semi-pronated) | Supinator |
| C7 | Finger extension, elbow extension | Triceps |
| C8 | Finger flexors | Finger |
| T1 | Small muscles of the hand | No reflex |
The three nerves of greatest clinical importance in the arm are the radial, ulnar and median nerves.
• The radial nerve and its branches supply all extensors in the arm.
• The ulnar nerve supplies all intrinsic hand muscles except ‘LOAF’ (see below).
N.B. All intrinsic hand muscles are supplied by T1.
WHAT TO DO
Look at the arms
Basic screening examination
A simple screening procedure is outlined below. Some further muscle power tests are given afterwards. Perform each test on one side, then compare to the other side.
Shoulder abduction
Ask the patient to lift both his elbows out to the side (demonstrate). Ask him to push up (Fig. 17.1).
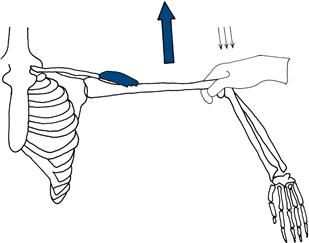
Figure 17.1 Testing shoulder abduction
Elbow flexion
Hold the patient’s elbow and wrist. Ask him to pull his hand towards his face. N.B. Ensure the arm is supinated (Fig. 17.2).
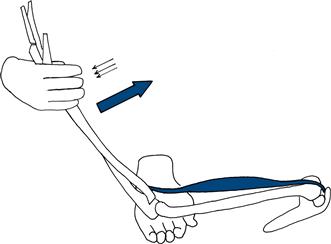
Figure 17.2 Testing elbow flexion
(Trick movement involves pronation of the arm to use brachioradialis—see below.)
Elbow extension
Hold the patient’s elbow and wrist. Ask him to extend the elbow (Fig. 17.3).
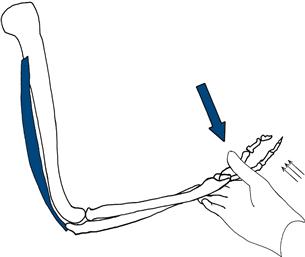
Figure 17.3 Testing elbow extension
Wrist extension
Hold the patient’s forearm. Ask him to make a fist and bend his wrist up (Fig. 17.4).
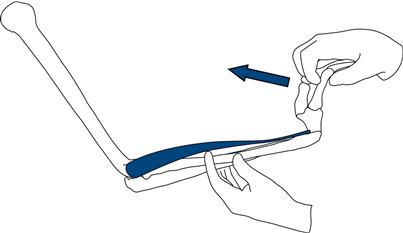
Figure 17.4 Testing wrist extension
Finger extension
Fix the patient’s hand. Ask him to keep his fingers straight. Press against the extended fingers (Fig. 17.5).
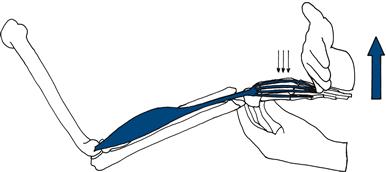
Figure 17.5 Testing finger extension
Finger flexion
Close your fingers on the patient’s fingers palm to palm so that both sets of fingertips are on the other’s metacarpal phalangeal joints. Ask the patient to grip your fingers and then attempt to open the patient’s grip (Fig. 17.6).
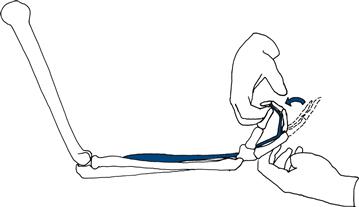
Figure 17.6 Testing finger flexion
Finger abduction
Ask the patient to spread his fingers out (demonstrate). Ensure the palm is in line with the fingers. Hold the middle of the little fingers and attempt to overcome the index finger (Fig. 17.7).
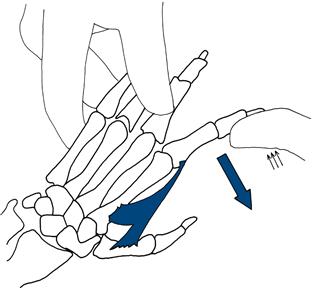
Figure 17.7 Testing finger abduction
Finger adduction
Ask the patient to bring his fingers together. Make sure the fingers are straight. Fix the middle, ring and little fingers. Attempt to abduct the index finger (Fig. 17.8).
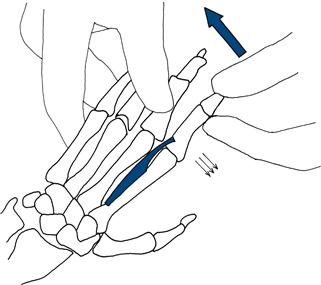
Figure 17.8 Testing finger adduction
Thumb abduction
Ask the patient to place his palm flat with a supinated arm. Ask him then to bring his thumb towards his nose. Fix the palm and, pressing at the end of the proximal phalanx joint, attempt to overcome the resistance (Fig. 17.9).
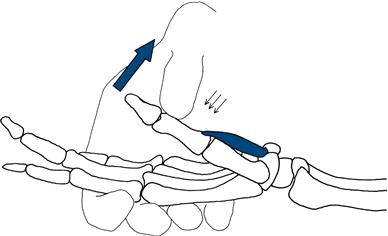
Figure 17.9 Testing thumb abduction
FURTHER TESTS OF ARM POWER
These tests are performed in the light of the clinical abnormality.
Serratus anterior
Stand behind the patient in front of a wall. Ask him to push against the wall with his arms straight and his hands at shoulder level. Look at the position of the scapula. If the muscle is weak, the scapula lifts off the chest wall: ‘winging’ (Fig. 17.10).
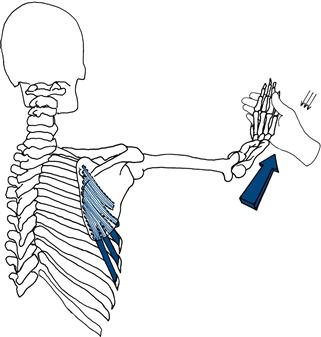
Figure 17.10 Testing strength of serratus anterior
Rhomboids
Ask the patient to put his hands on his hips. Hold his elbow and ask him to bring his elbow backwards (Fig. 17.11).
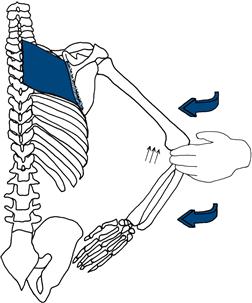
Figure 17.11 Testing strength of rhomboids
Supraspinatus
Stand behind the patient. Ask the patient to lift his arm from the side against resistance (Fig. 17.12).
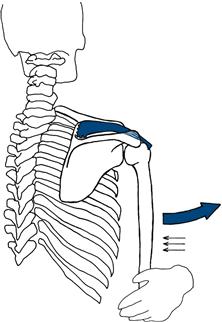
Figure 17.12 Testing strength of supraspinatus
Infraspinatus
Stand behind the patient, hold his elbow against his side with the elbow flexed, asking him to keep his elbow in and move his hand out to the side. Resist this with your hand at his wrist (Fig. 17.13).
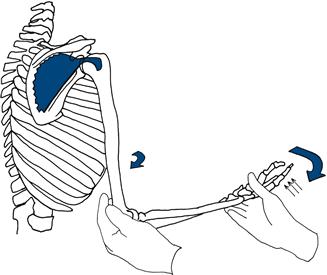
Figure 17.13 Testing strength of infraspinatus
Brachioradialis
Hold the patient’s forearm and wrist with the forearm semi-pronated (as if shaking hands). Ask the patient to pull his hand towards his face (Fig. 17.14).
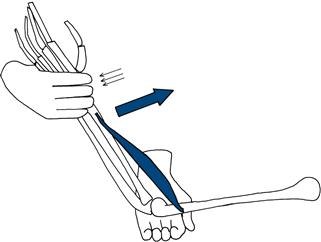
Figure 17.14 Testing strength of brachioradialis
Long flexors of little and ring finger
Ask the patient to grip your fingers. Attempt to extend the distal interphalangeal joint of the little and ring fingers.
WHAT YOU FIND
This will be considered in Chapter 20.