5 Monitor technology
| Aspect Ratio | The ratio of the width of a display screen to the height, e.g. 4 : 3 |
| Bezel | The plastic or metal frame round a display screen |
| Brightness (Luminance) | The amount of light a LCD monitor produces in candela (cd) per square metre (m2), e.g. 250 to 350 cd/m2 |
| Colour Depth | The number of bits used to give the colour of one pixel, and gives the number of different colours that can be displayed at one time, e.g. |
| Contrast Ratio | The difference in intensity between the black and white on an LCD screen |
| Cursor | A flashing marker on the screen which indicates where the next character is to be inserted |
| Dot Pitch | A measure of the sharpness or resolution of a screen |
| LCD | Liquid Crystal Display monitor |
| Monitor | A device very similar to a television, but which receives video signals directly from the computer |
| Native Resolution | The optimum resolution of a LCD monitor. If this is changed the image quality diminishes Examples of native resolution: |
| Pixel | Picture cell. A pixel is the smallest number of dots which can be used by a character on the display screen |
| Refresh Rate | Number of times the monitor is scanned by the electron beam per second |
| Resolution | The number of ‘dots’ on a monitor screen defines the resolution of a system by describing the number of pixels horizontally and vertically, e.g. 1200 × 1200 gives a resolution of 1200 separate points horizontally and vertically |
| RGB Input | The colour input on a monitor. The signal from the computer is taken by the monitor as a basic Red, Green and Blue input |
| Screen Size | Cathode ray tubes
Liquid Crystal Display screens |
| Scrolling | The movement of text or data on the display screen. Scrolling can be upwards, downwards or sideways |
| Thermionic Emission | The release of electrons when a substance is heated |
| VDU | Visual display unit |
| Viewing Angle | The maximum horizontal and vertical angle that a monitor screen can be viewed at to give a clear image with accurate colours, e.g. |
| Voxel | A three-dimensional pixel |
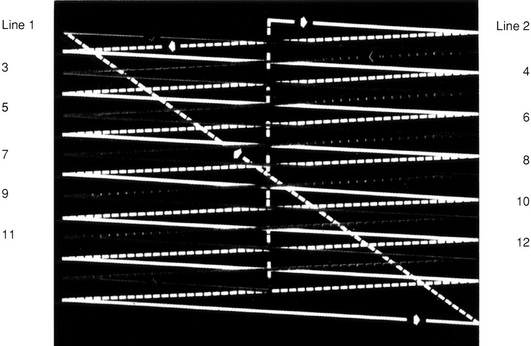
| Interlacing | Consider one still picture on a cathode ray monitor (Figs 5.1, 5.2)
• The picture is constructed by an electron beam scanning the tube phosphor from top left to bottom right in a series of horizontal lines
|
| Principle of Operation |
• The signal is received by the visual display unit in the form of a stream of electrons (on) and gaps (off)
|
| Cathode Ray Tubes | Composed of: |
| In colour monitors: |
| Gas Plasma Monitors | Construction |
| Principles of operation | |
| Liquid Crystal Displays (Active) | Construction |
| Principles of operation | |
| Liquid Crystal Displays (Passive) |