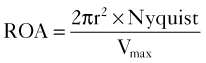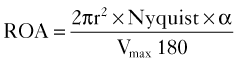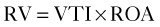2 Mitral Valve Diseases
Introduction: The Role of Intraoperative Transesophageal Echocardiography In Mitral Valve Surgery
Key Points
When used in that fashion, intraoperative TEE has been shown to improve outcome.
Indications
The 2003 ACC/AHA/ASE (American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association/American Society of Echocardiography) Guideline Update for the Clinical Application of Echocardiography lists the various indications for TEE.1 Several of them apply specifically to the MV and they are listed in Table 2-1.
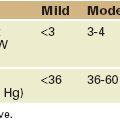
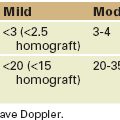
TABLE 2-1 INDICATIONS FOR MITRAL VALVE ASSESSMENT BY TRANSESOPHAGEAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY
| Class I |
Weight of evidence/opinion is in favor of usefulness or efficacy.
Usefulness/efficacy is less well established by evidence or opinion.
LA, left atrium; LA, left atrial; MR, mitral regurgitation.
From the 2003 ACC/AHA/ASE Guideline Update for the Clinical Application of Echocardiography.
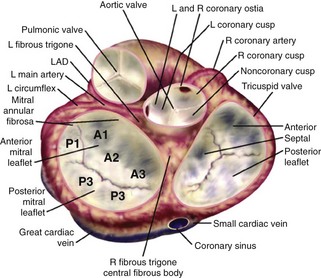
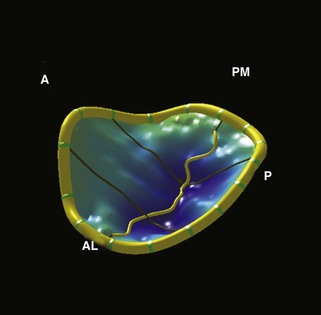
Mitral Valve Anatomy (Figure 2-1)
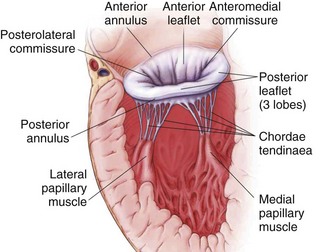
Figure 2-1 MV anatomy.
Adapted from Otto CM. Evaluation and management of chronic mitral regurgitation. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:740-746. Reproduced with permission.
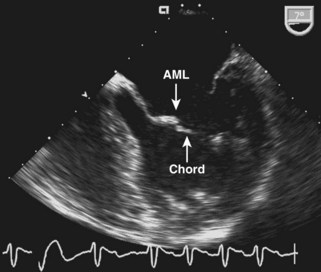
Mitral Valve Nomenclature
Systematic Examination of the Mitral Valve
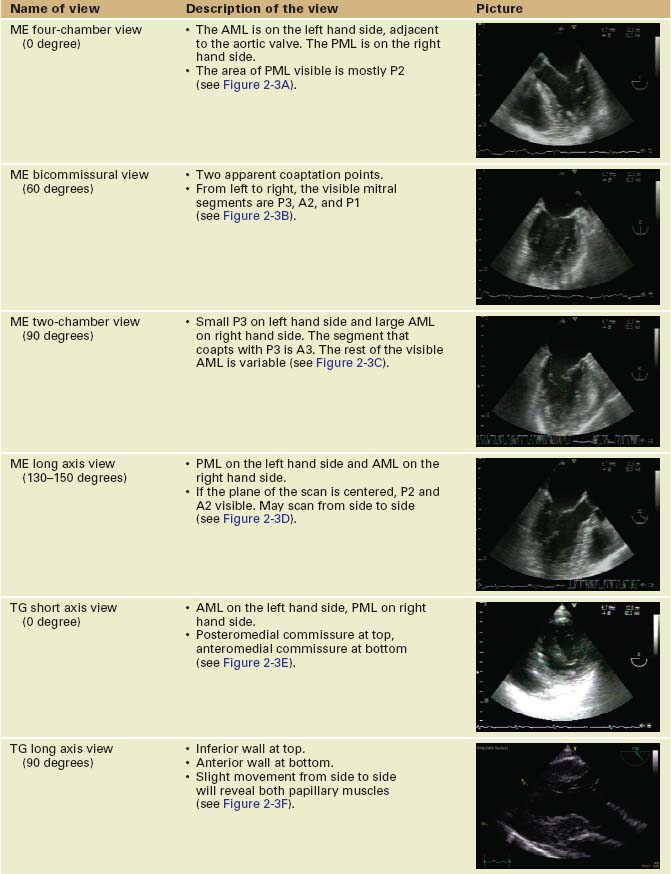
Sequence of Views (Table 2-2 and Figure 2-3)
TABLE 2-2 The Systematic Mitral Valve Examination

Key Points
Three-Dimensional Echocardiography
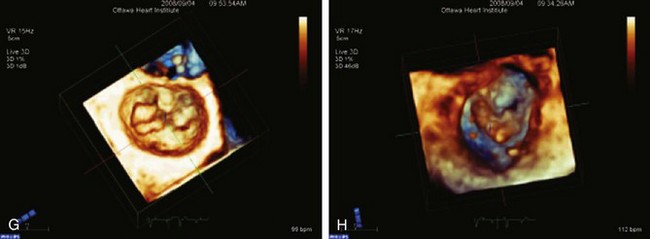
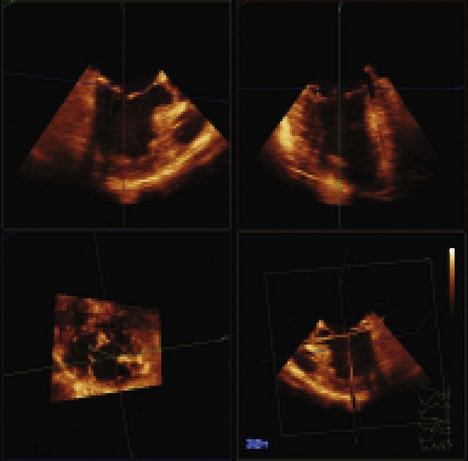
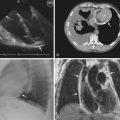
Three-dimensional (3D) TEE provides exceptional images of the heart. Instead of a plane of information, the computer acquires a volume of data, which can then be reconstructed and viewed from any angle (Figure 2-4). Moreover, the data set can be sliced in any desired plane, much like a computed tomography (CT) scan, in order to re-create 2D images sometimes impossible to obtain by standard 2D echocardiography (Figure 2-5).
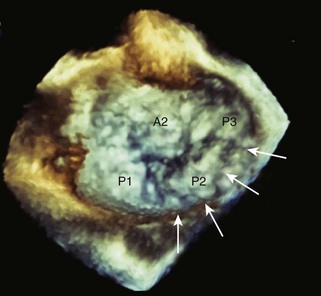
The mechanism of MR is usually readily apparent on 3D imaging. Furthermore, off-line MV analysis software packages allow detailed quantification of MV disease, including dimensions, prolapses, and restriction (Figure 2-6). This is very useful in planning the surgical management of MR and may help to identify patients who require specialized surgical care. Moreover, the development of leaflet stress analysis packages opens the door to the possibility of predicting, in the immediate post-bypass stage, the durability of some MV repairs.
Mitral Regurgitation
MR can be due to a structural problem in the valve itself or it may be due to distortion of the valve by external factors, described in Table 2-3.
| Structural MR |
HOCM, hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy; LV, left ventricle; LVOT, left ventricular outflow tract; MR, mitral regurgitation.
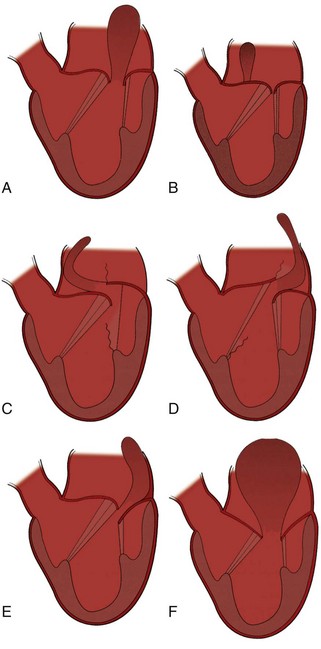
Classification of Mitral Regurgitation
Key Points
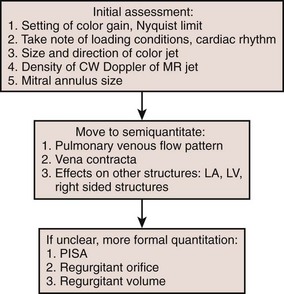
Evaluation of Mitral Regurgitation
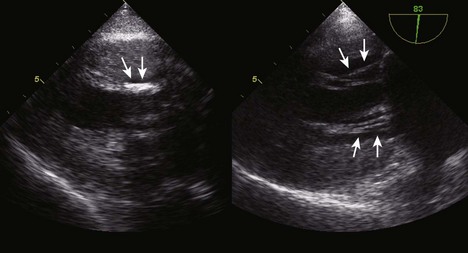
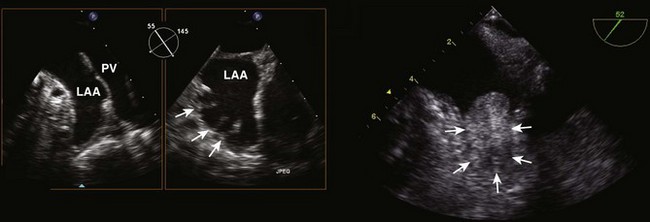
Step 1: Determine the Mechanism and Localization of Lesions and Etiology
Key Points
Examination of the Mitral Annulus
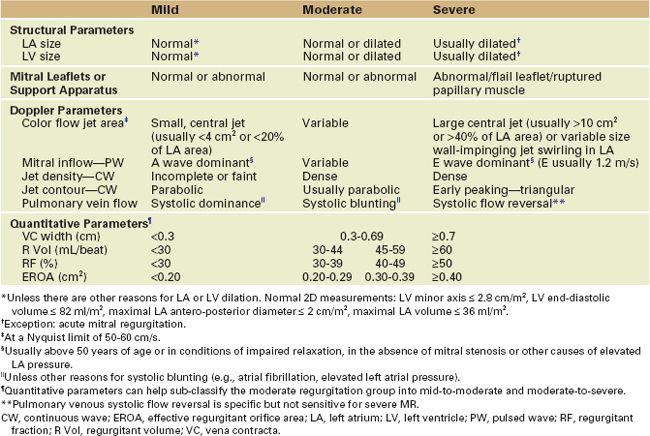
Severity of Mitral Regurgitation
Step 2: Qualitative Assessment
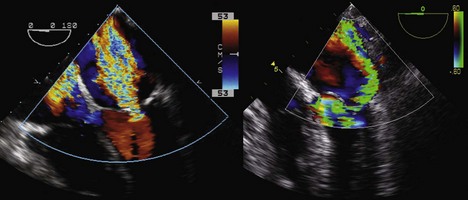
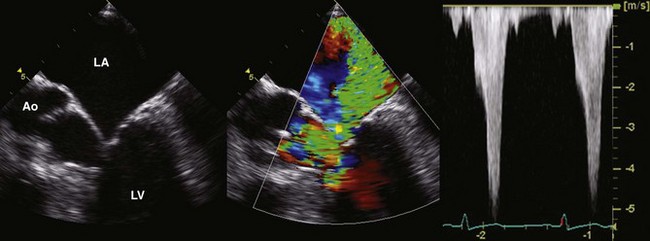
Color Flow Doppler
Spectral Doppler
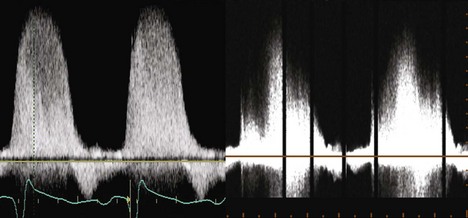
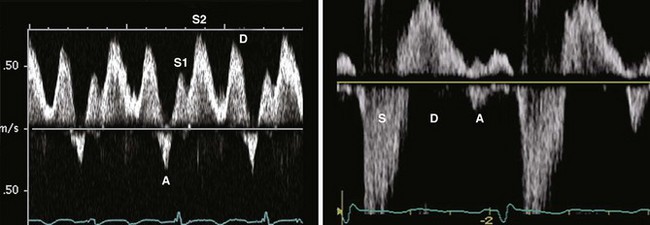
Spectral Doppler provides additional qualitative signs of the severity of MR
Step 3: Quantitative Assessment
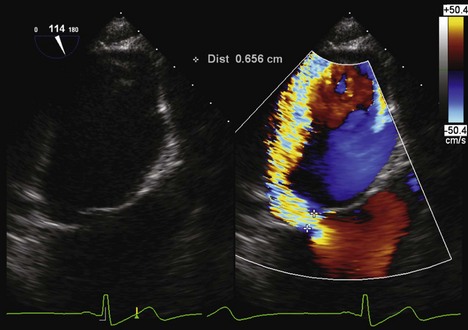
Vena Contracta (Figure 2-13)
Key Points
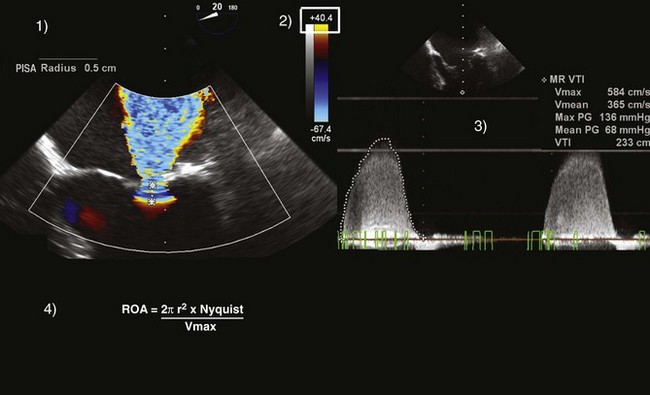
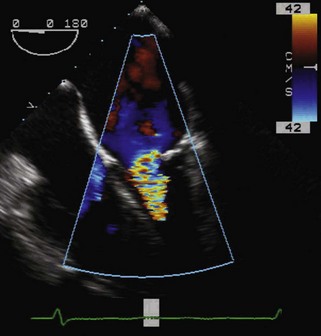
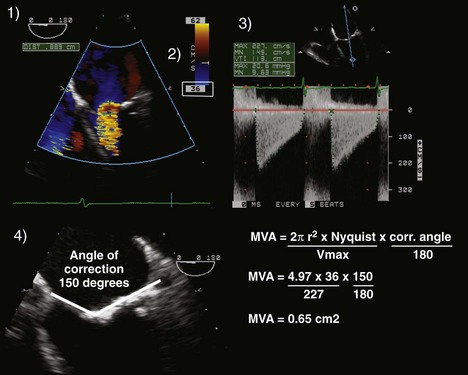
PISA (Proximal Isovelocity Surface Area) Method (Figure 2-14)
Key Points
Careful! All elements of the PISA equation should have the same units (i.e., cm or cm/s).
If those conditions are present, the PISA equation simplifies to:
In summary, one can calculate the regurgitant orifice area (ROA) using the following formula:
Regurgitant Volume
Modern echocardiography machines automatically calculate the RV and regurgitant fraction (RF).
Regurgitant Fraction
Key Points
A summary of the methods used to quantify is shown in Table 2-4.
Functional Mitral Regurgitation
Mechanism of Functional Mitral Regurgitation
Key Points
Echo Evaluation of Functional Mitral Regurgitation
Left Ventricular Outflow Obstruction, Systolic Anterior Motion, and Mitral Regurgitation
Echocardiographic Signs of Left Ventricular Outflow Tract Obstruction (Figure 2-16)
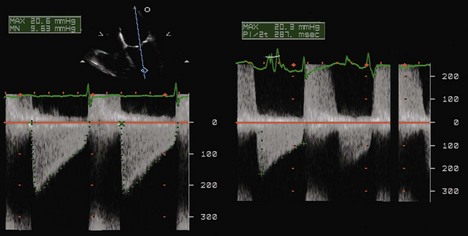
Mitral Stenosis
Etiology
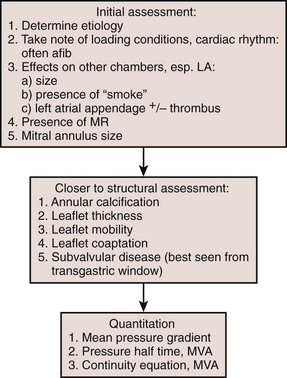
Step 1: Determine the Etiology
Acquired
Evaluation of Mitral Stenosis
Step 1: 2D Appearance
Step 2: Color Flow Doppler
Step 3: Spectral Doppler
The Rest of the Heart: Nonvalvular Indicators of Severe Valvular Disease
Mitral Valve Endocarditis
Surgical Management of Mitral Valve Disease
Surgical Management of Mitral Regurgitation
Key Points
Post-Bypass Assessment in Mitral Valve Procedures
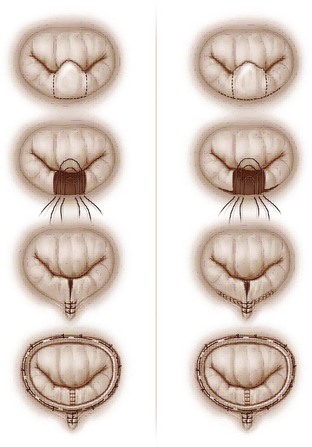
Mitral Repair for Mitral Regurgitation
Mitral Replacement (See Chapter 5)
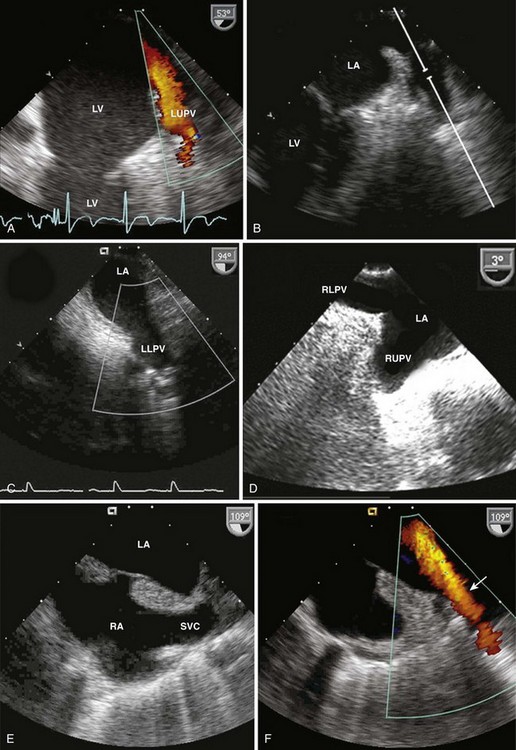
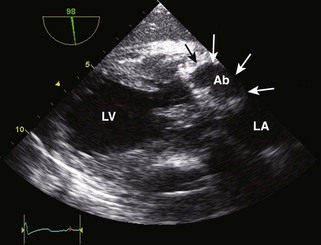
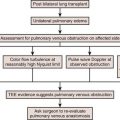
Evaluation of Surrounding Structures
1 Quiñones MA, Douglas PS, Foster E, et al. ACC/AHA Clinical Competence Statement on Echocardiography: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association/American College of Physicians–American Society of Internal Medicine Task Force on Clinical Competence. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003;41:687-708.
2 Shanewise JS, Cheung AT, Aronson S, et al. ASE/SCA guidelines for performing a comprehensive intraoperative multiplane transesophageal echocardiography examination: Recommendations of the American Society of Echocardiography Council for Intraoperative Echocardiography and the Society of Cardiovascular Anesthesiologists Task Force for Certification in Perioperative Transesophageal Echocardiography. Anesth Analg. 1999;89:870-884.
3 Lambert AS, Miller JP, Merrick SH, et al. Improved evaluation of the location and mechanism of mitral valve regurgitation with a systematic transesophageal echocardiography examination. Anesth Analg. 1999;88:1205-1212.
4 Cheitlin MD, Armstrong WF, Aurigemma GP, et al. ACC/AHA/ASE 2003 guideline update for the clinical application of echocardiography: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (ACC/AHA/ASE Committee to Update the 1997 Guidelines for the Clinical Application of Echocardiography). J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003;42:954-970.
5 Zoghbi WA, Enriquez-Sarano M, Foster E, et al. Recommendations for evaluation of the severity of native valvular regurgitation with two-dimensional and Doppler echocardiography: A report from the American Society of Echocardiography’s Nomenclature and Standards Committee and The Task Force on Valvular Regurgitation. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2003;16:777-802.
6 Baumgartner H, Hung J, Bermejo J, et al. Echocardiographic assessment of valve stenosis: EAE/ASE recommendations for clinical practice. Eur J Echocardiogr. 2009;10:1-25.
7 Bonow RO, Carabello BA, Chatterjee K, et al. ACC/AHA 2006 guidelines for the management of patients with valvular heart disease: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;48:e1-e148.
8 Zoghbi WA, Chambers JB, Dumesnil JG, et al. Recommendations for evaluation of prosthetic valves with echocardiography and Doppler ultrasound: A report from the American Society of Echocardiography’s Guidelines and Standards Committee and the Task Force on Prosthetic Valves. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2009;22:975-1014.
9 Baddour LM, Wilson WR, Bayer AS, et al. Infective endocarditis: Diagnosis, antimicrobial therapy, and management of complications. Circulation. 2005;111:3167-3184.
10 Ayres NA, Miller-Hance W, Fyfe DA, et al. Indications and guidelines for performance of transesophageal echocardiography in the patient with pediatric acquired or congenital heart disease: A report from the Task Force of the Pediatric Council of the American Society of Echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2005;18:91-98.
11 Roberts BJ, Grayburn PA. Color flow imaging of the vena contracta in mitral regurgitation: Technical considerations. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2003;16:1002-1006.
12 Kahn RA, Mittnacht AJ, Anyanwu AC. Systolic anterior motion as a result of relative “undersizing” of a mitral valve annulus in a patient with Barlow’s disease. Anesth Analg. 2009;108:1102-1104.