Chapter 15 Methods of administration
Enteral Administration
• Advantages
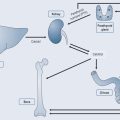
Administration via the Rectum
Different Types of Oral Delivery System
General Gastrointestinal Tract Health
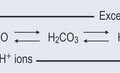
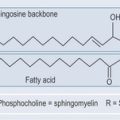
The pH can affect the degree of disassociation of a substance, resulting in increased absorption if the substance remains fully associated and non-polar (see Figures 8.2, 8.3 and 8.4, pp. 55–57). Drugs are designed for certain pHs, if these are not correct (due to poor gut health) then the drugs will not be as effective.
A healthy gastrointestinal tract ensures the correct content of commensals, as these are an important part of the gut chemistry, particularly the enterohepatic cycle (see Chapter 17 ‘Metabolism’, p. 131). If there is an imbalance then drugs might not be utilized properly or might remain in the body for an extended period of time, resulting in toxicity.
Factors Affecting Absorption
Parenteral Administration
Mucous Membranes
Lungs
This is a possible method of delivering herbal remedy, e.g. steam bath for respiratory conditions.
Vagina
Possible method of delivering herbal remedy for the local treatment of conditions such as thrush.
Topical/Transdermal
Qualities required for absorption by this method: