Chapter 37 Metabolic disorders
Pituitary Gland
The ‘master gland’ of the body; possesses two lobes:
Anterior Pituitary Gland
The anterior pituitary gland secretes:
The anterior pituitary gland responds to:
Posterior Pituitary Gland
The posterior pituitary gland secretes:
Thyroid Gland (see Chapter 41 ‘scientific tests’ Table 41.1, p. 340, Table 41.2, p. 341)
Dysfunction of this gland is commonly encountered in clinical practice.
Iodine is necessary for the production of both hormones. Disorders of the thyroid include:
Hyperthyroidsm
• Symptomatic Relief
Non-selective beta-blockers, 235 because tremor usually responds to beta-2 and not beta-1-blockers (see Chapter 31 ‘The nervous system’, p. 235).
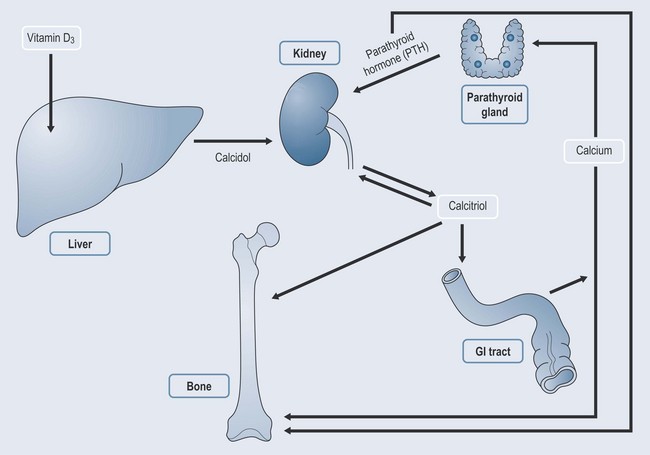
Parathyroid Gland
Calcium Regulation in the Body
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis can occur when the rate of bone resorption is greater than its formation. Although osteoporosis is thought to be a postmenopausal problem it is possible even in children. Osteoporosis is caused by more than one factor. Risk factors are:
There is also an element of genetic and lifestyle factors.
• Assessment of Osteoporosis or Osteopaenia
• Treatment
Conservative Treatment
Pancreas
Diabetes
Treatment of Type 1 Diabetes
Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes
The pancreatic islet cells are still functioning.
• Orthodox Medication
Biguanides: Metformin
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
The cause is not properly understood.
• Signs and Symptoms
Other Metabolic Conditions
Metabolic Syndrome X
Gout
Purines are excreted by soluble uric acid, but uric acid and urates are only just water soluble. This becomes a problem when the urine becomes particularly acidic (high meat intake, particularly red meat full of purines and pyrimidines; see Chapter 18 ‘Drug excretion’, p. 134). High levels of uric acid in the blood (uraemia) can result in uric acid crystals in the joints, most frequently the first metatarsophalangeal joint. The attacks are acute and very painful. Repeated attacks lead to tissue damage and arthritic malformations.
• Treatment
1) Reducing the immune response to uric acid deposits:
3) Reduce Uric Acid Synthesis
Allopurinol is a competitive inhibitor (see Chapter 19 ‘Pharmacodynamics: how drugs elicit a physiological effect’, p. 138) and attaches so securely to the enzyme-binding site that the normal substrate cannot attach itself and take part in the necessary reaction. This reduces the production of uric acid, leaving more soluble products in the blood, which are likely to deposit as crystals in the joints. It is used between attacks. There are few adverse effects.