CHAPTER 15 METABOLIC DISEASE PATHOLOGY
APPROACH TO METABOLIC DISEASE PATHOLOGY
Overview (Nyhan et al 2005)
LACTIC ACIDEMIAS
DISORDERS OF CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM
MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDOSES
LIPID STORAGE DISORDERS
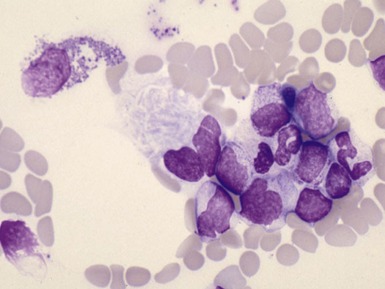
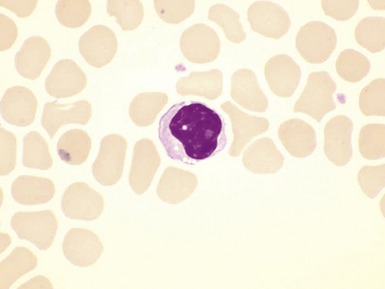
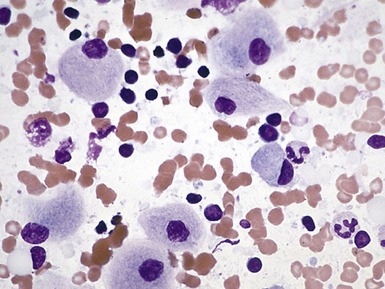
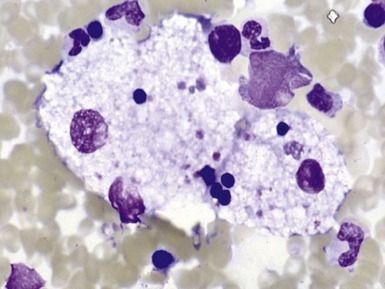
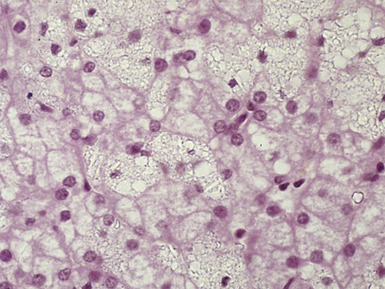
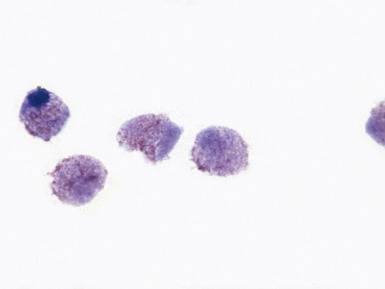
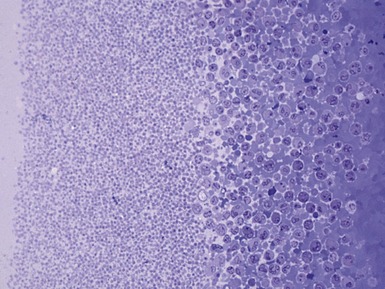
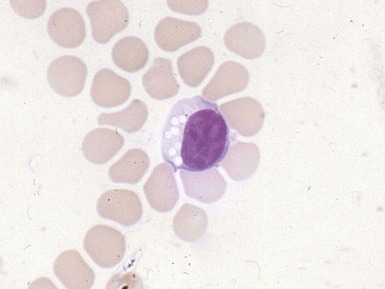
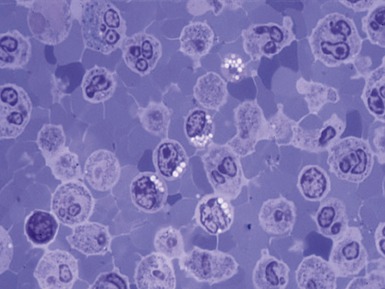
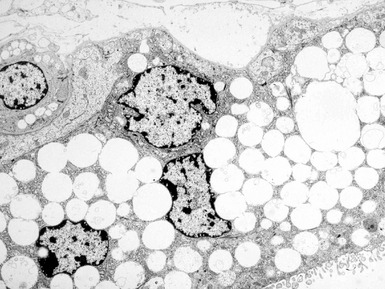
Fig 15.6 Photomicrograph of bone marrow aspirate showing large lipid laden macrophages with fibrillary cytoplasm in Gaucher disease.
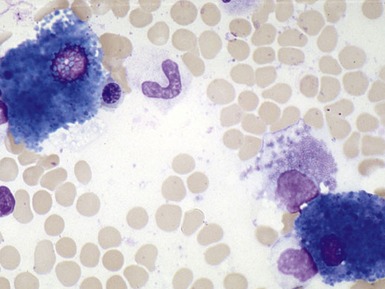
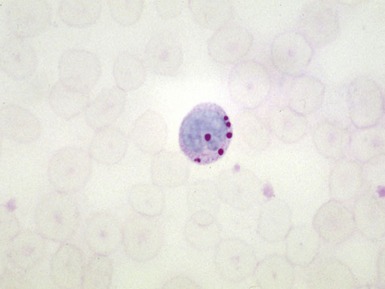
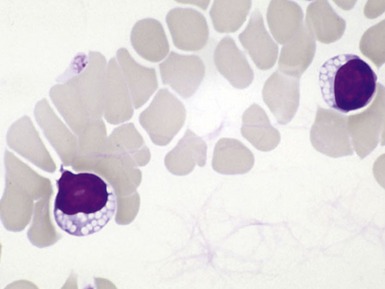
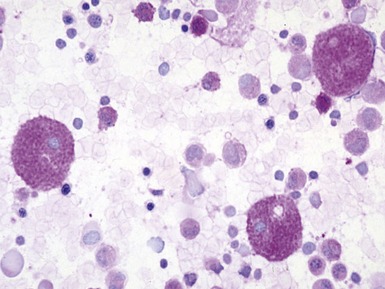
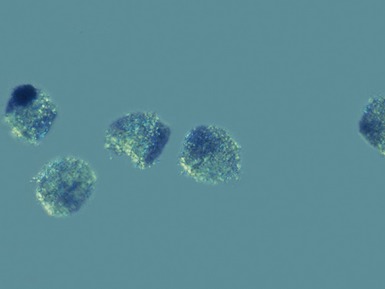
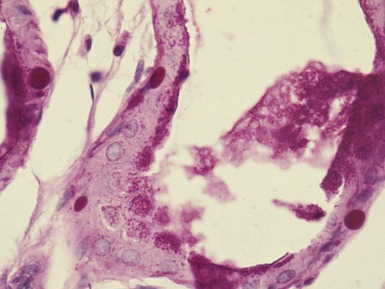
Fig 15.12 Photomicrograph of bone marrow aspirate showing sea-blue histiocytes in Niemann–Pick type C. (MGG)
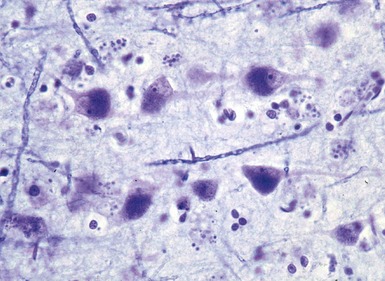
BATTEN DISEASE (NEURONAL CEROID LIPOFUSCINOSIS)
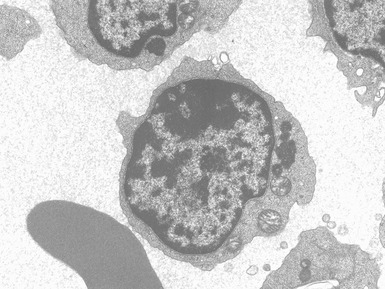
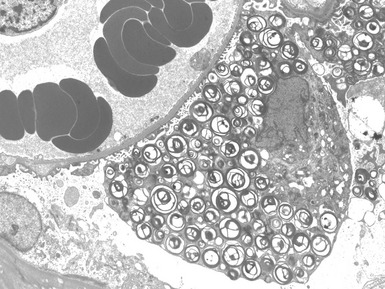
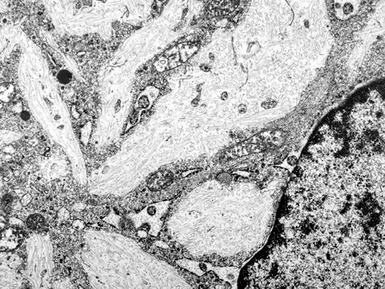
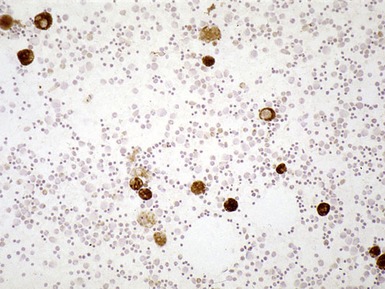
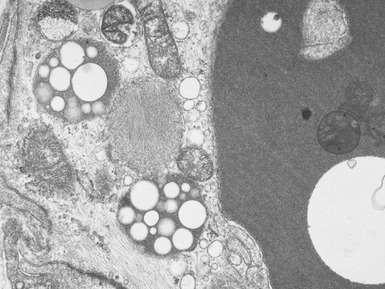
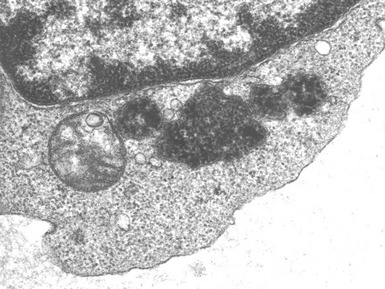
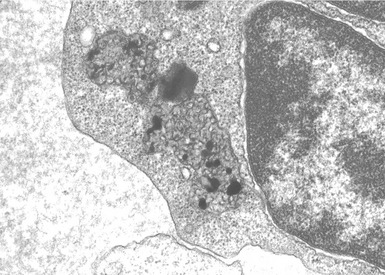
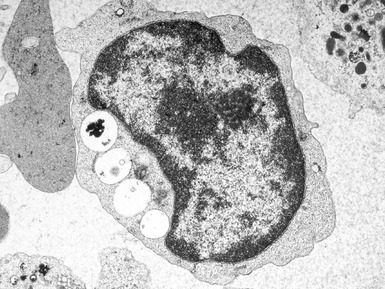
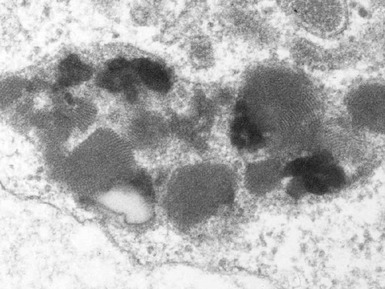
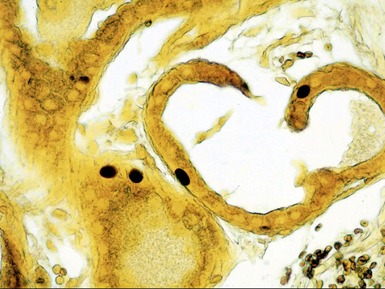
Fig 15.24 Electron photomicrograph of a lymphocyte showing membrane bound granular osmophilic inclusions (GRODs) in a case of infantile Batten disease / NCL.
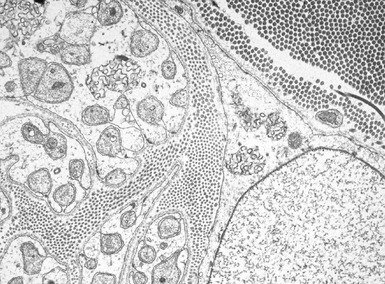
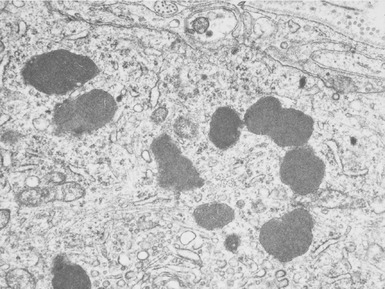
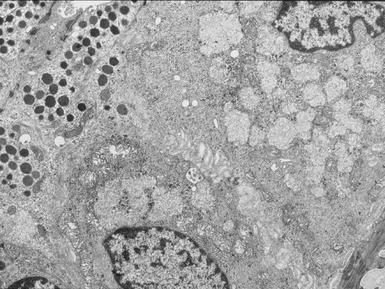
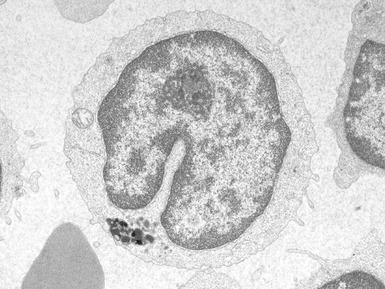
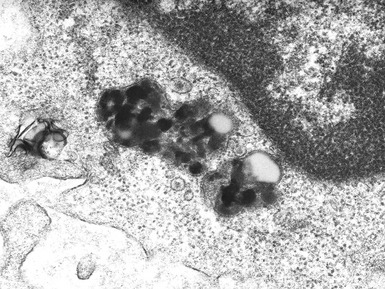
Fig 15.30 Electron photomicrograph of a neuron showing membrane bound curvilinear inclusions in a case of late infantile Batten disease / NCL.
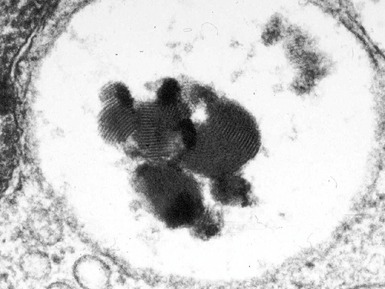
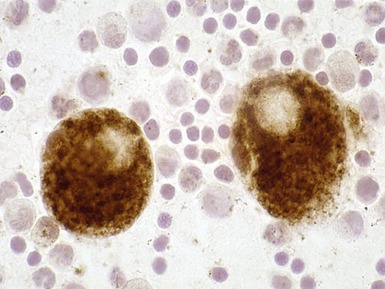
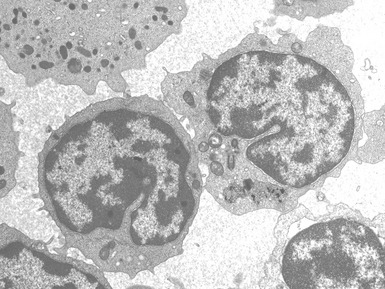
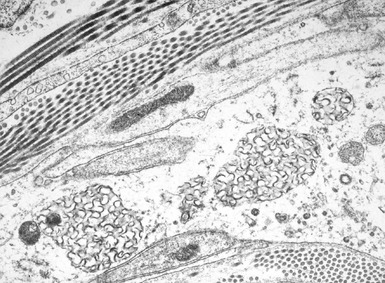
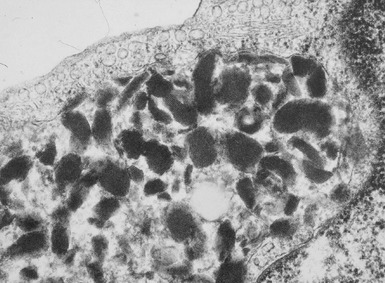
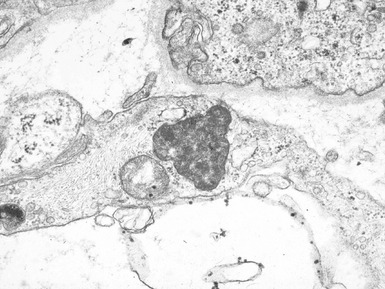
Fig 15.35 Electron photomicrograph of a lymphocyte showing fingerprint inclusions in a case of juvenile Batten disease / NCL.
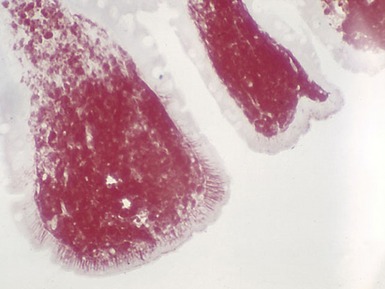
CHORIONIC VILLUS SAMPLES
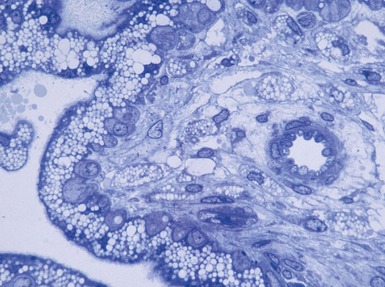
A range of metabolic diseases may also be diagnosed prenatally based on ultrastructural examination of chorionic villus samples (Figs 15.40–15.46)
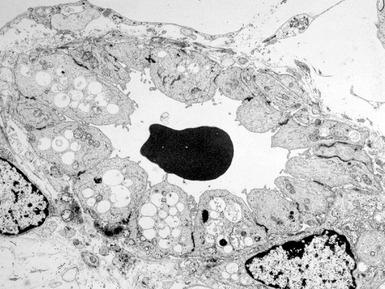
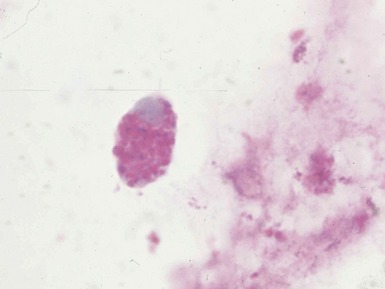
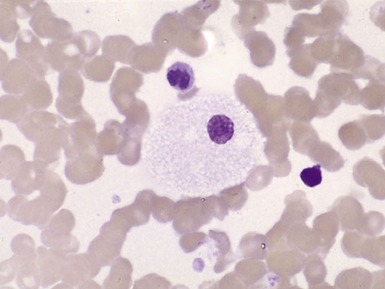
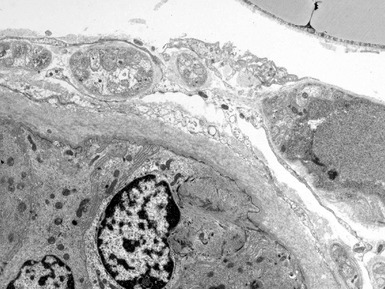
Fig 15.43 Electron photomicrograph of a chorionic villous sample showing extensive vacuolation of endothelial cells in a case of sialic acid storage disease.
Boldrini R, Devito R, Biselli R, Filocamo M, Bosman C. Wolman disease and cholesteryl ester storage disease diagnosed by histological and ultrastructural examination of intestinal and liver biopsy. Pathol Res Pract. 2004;200:231-240.
Bove KE, Daugherty C, Grabowski GA. Pathological findings in Gaucher disease type 2 patients following enzyme therapy. Hum Pathol. 1995;26:1040-1045.
Brod RD, Packer AJ, Van Dyk HJ. Diagnosis of neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis by ultrastructural examination of peripheral blood lymphocytes. Arch Ophthalmol. 1987;105:1388-1393.
Carson NA, Biggart JD, Bittles AH, Hereditary Donovan D. tyrosinemia. Clinical, enzymatic, and pathological study of an infant with the acute form of the disease. Arch Dis Child. 1976;51:106-113.
Dimmick JE, Applegarth DA. Pathology of peroxisomal disorders. Perspect Pediatr Pathol. 1993;17:45-98.
Elleder M. Sequelae of storage in Fabry disease – pathology and comparison with other lysosomal storage diseases. Acta Pediatr Suppl. 2003;92:46-53.
Ikonen E, Hölttä-Vuori M. Cellular pathology of Niemann–Pick type C disease. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2004;15:445-454.
Jmoudiak M, Futerman AH. Gaucher disease: pathological mechanisms and modern management. Br J Hematol. 2005;129:178-188.
Kuemmel TA, Thiele J, Schroeder R, Stoffel W. Pathology of visceral organs and bone marrow in an acid sphingomyelinase deficient knock-out mouse line, mimicking human Niemann–Pick disease type A. A light and electron microscopic study. Pathol Res Pract. 1997;193:663-671.
Linthorst GE, De Rie MA, Tjiam KH, Aerts JM, Dingemans KP, Hollak CE. Misdiagnosis of Fabry disease: importance of biochemical confirmation of clinical or pathological suspicion. Br J Dermatol. 2004;150:575-577.
Nyhan WL, Barshop BA, Ozand PT. Atlas of metabolic diseases, 2nd edn. London: Hodder Arnold; 2005.
Parkin JL, Brunning RD. Pathology of the Gaucher cell. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1982;95:151-175.
Powers JM. The pathology of peroxisomal disorders with pathogenetic considerations. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1995;54:710-719.
Prive L. Pathological findings in patients with tyrosinemia. Can Med Assoc J. 1967;97:1054-1056.
Roels F, Espeel M, De Craemer D. Liver pathology and immunocytochemistry in congenital peroxisomal diseases: a review. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1991;14:853-875.
Roels F, Espeel M, Poggi F, Mandel H, van Maldergem L, Saudubray JM. Human liver pathology in peroxisomal diseases: a review including novel data. Biochimie. 1993;75:281-292.
Russo P, O’Regan S. Visceral pathology of hereditary tyrosinemia type I. Am J Hum Genet. 1990;47:317-324.
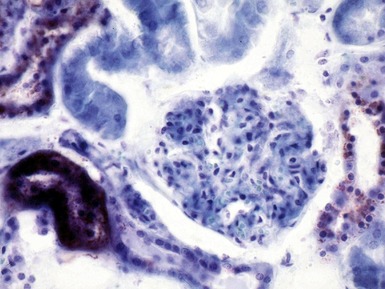
Sessa A, Meroni M, Battini G, et al. Renal pathological changes in Fabry disease. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2001;24:66-70.
Tyynelä J, Suopanki J, Santavuori P, Baumann M, Haltia M. Variant late infantile neuronal ceroid-lipofuscinosis: pathology and biochemistry. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1997;56:369-375.
Williams RS, Lott IT, Ferrante RJ, Caviness VSJr. The cellular pathology of neuronal ceroid-lipofuscinosis. A golgi-electronmicroscopic study. Arch Neurol. 1977;34:298-305.