57 Mental Nerve Block
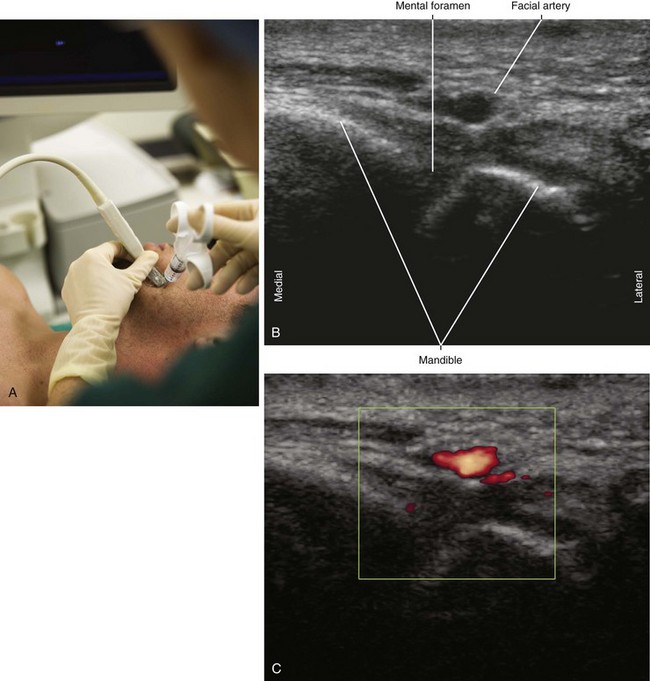
The mental nerve is a branch of the inferior alveolar nerve from the third division of the trigeminal nerve. The inferior alveolar nerve enters the mandibular foramen to travel within the mandibular canal and form the mental nerve. At its exit from the mental foramen, the mental nerve is divided into several branches.1 The mental nerve emerges from the mental foramen to supply the chin, lower lip, and teeth. The mental nerve can provide innervation to the lower incisors.2
The mental foramen lies about halfway between the upper and lower borders of the mandible, although the position of the foramen relative to the mandible varies with age.3,4 Elderly patients who are edentulous have decay of the alveolar ridge. This brings the mental foramen closer to the upper border of the mandible. A severely resorbed alveolar ridge can make identification of the mental foramen difficult.
Suggested Technique
The mental foramen typically has posterior or right-angled inclination.5 When the nerve emerges at right angles, it is funnel shaped. The longest diameter of the mental foramen is about 3 mm.6 The presence of multiple mental foramina is rare, being observed in about 2% of cases.3–57
Key Points
| Mental Nerve Block | The Essentials |
|---|---|
| Anatomy | The MTN exits the mental foramen, with nearby facial artery. |
| The MF is about 3 mm in diameter. | |
| Positioning | Supine |
| Operator | Standing at the side of the patient |
| Display | Across the table |
| Transducer | High-frequency linear, 23- to 38-mm footprint |
| Initial depth setting | 20 mm |
| Needle | 25 gauge, 38 mm in length |
| Anatomic location | Halfway between the upper and lower borders of mandible near the corner of the mouth |
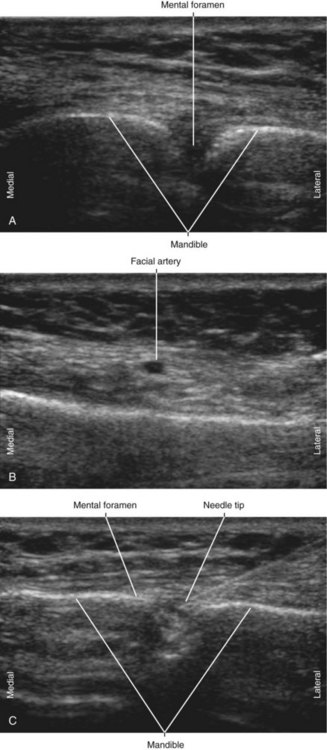
| Approach | Transverse view of MF, in-plane from lateral to medial |
| Place the needle tip into the MF. | |
| Sonographic assessment | Injection distribution observed within the MF |
| Anatomic variation | Multiple foramina (2%) |
Clinical Pearls
• Advance the block needle 6 mm into the mental canal for successful block.
• Local anesthetic injected within the mental foramen tracks centrally along the inferior alveolar nerve within the mandibular canal.
• Use a 25-gauge, 38-mm needle for placement in the mental canal.
• Facial hair can make imaging for mental canal block challenging.
• The facial artery and vein lie close to the mental foramen.
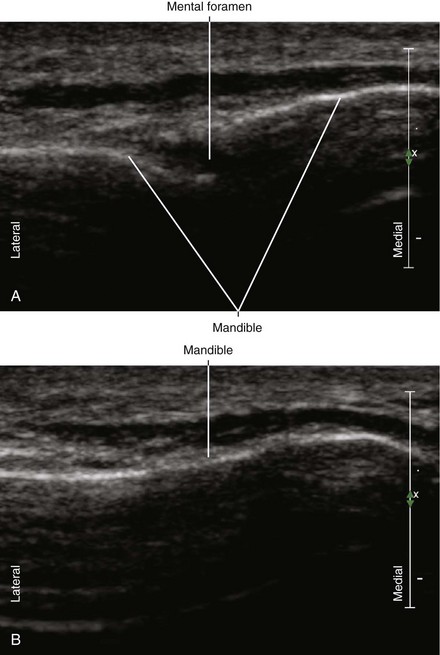
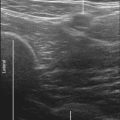
FIGURE 57-2 Ultrasound image of the mental foramen (A) contrasted with the smooth bony contour of the mandible (B).
1 Hu KS, Yun HS, Hur MS, et al. Branching patterns and intraosseous course of the mental nerve. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007;65:2288–2294.
2 Pogrel MA, Smith R, Ahani R. Innervation of the mandibular incisors by the mental nerve. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1997;55:961–963.
3 Vayvada H, Demirdover C, Yilmaz M, et al. An anatomic variation of the mental nerve and foramina: a case report. Clin Anat. 2006;19:700–701.
4 Oktem H, Oktem F, Sanli E, et al. An anatomic variation of mental nerve. Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2008;61:1408–1409.
5 Kieser J, Kuzmanovic D, Payne A, et al. Patterns of emergence of the human mental nerve. Arch Oral Biol. 2002;47:743–747.
6 Song WC, Kim SH, Paik DJ, et al. Location of the infraorbital and mental foramen with reference to the soft-tissue landmarks. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2007;120:1343–1347.
7 Agthong S, Huanmanop T, Chentanez V. Anatomical variations of the supraorbital, infraorbital, and mental foramina related to gender and side. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2005;63:800–804.