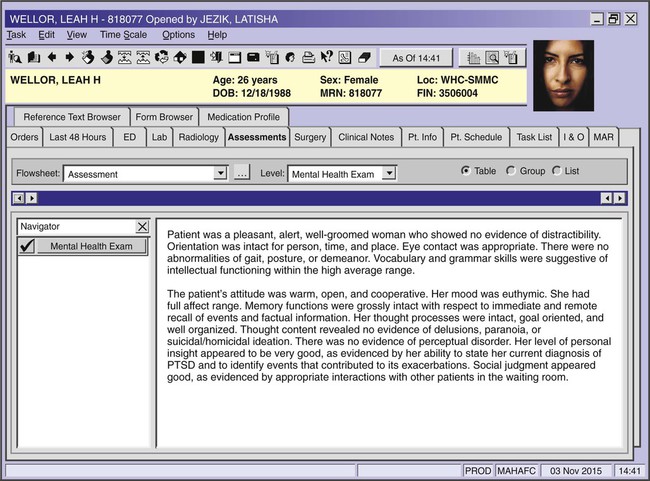
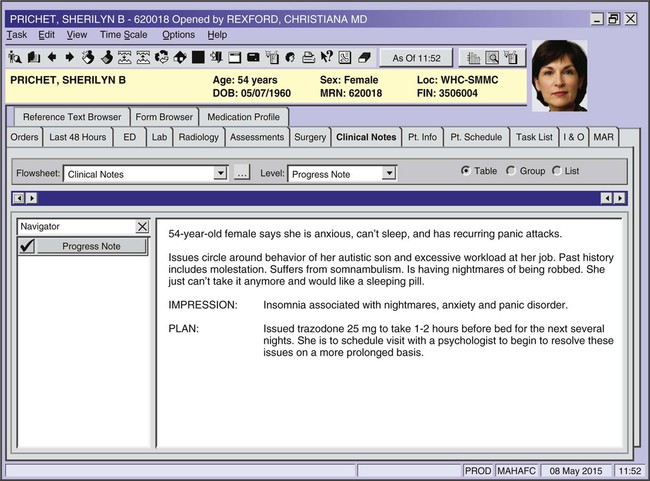
Mental and Behavioral Disorders
Introduction to Mental and Behavioral Health
• One of every four American adults and children has been diagnosed with a mental condition.
• More than 30% of the 20 top-selling medications are for psychiatric disorders.
• The fourth most common diagnostic category for inpatient admissions is substance-related mental disorders.
• Approximately 40 million Americans are diagnosed with anxiety.
• The number of discharges for patients with substance-related mental health disorders has sharply escalated, from 20,000 in 1998 to 110,000 in 2008.
• Approximately 7.5 million Americans are classified as mentally retarded.
• Given these statistics, the terminology related to mental and behavioral disorders is content that cannot be ignored.
Similar to previous chapters, this chapter examines disorders that result when an individual has a maladaptive response to his or her environment (internal or external). (See Chapter 11 for an explanation of the anatomy and physiology of the brain and nervous system.) However, even though some mental illnesses have organic causes in which neurotransmitters and other known brain functions play a role, there is no mental “anatomy” per se. Instead, behavioral health is a complex interaction among an individual’s emotional, physical, mental, and behavioral processes in an environment that includes cultural and spiritual influences.
Pathology

Terms Related to Signs and Symptoms Involving Cognition, Perception, Emotional State, and Behavior and Speech and Voice (R4Ø-R49)
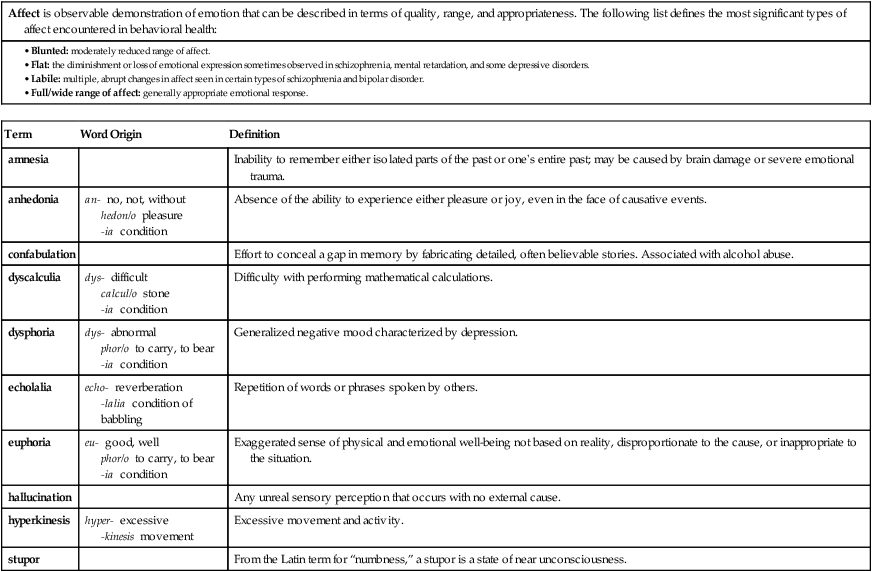
| Affect is observable demonstration of emotion that can be described in terms of quality, range, and appropriateness. The following list defines the most significant types of affect encountered in behavioral health: |
|
• Blunted: moderately reduced range of affect. • Flat: the diminishment or loss of emotional expression sometimes observed in schizophrenia, mental retardation, and some depressive disorders. • Labile: multiple, abrupt changes in affect seen in certain types of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. • Full/wide range of affect: generally appropriate emotional response. |
| Term | Word Origin | Definition |
| amnesia | Inability to remember either isolated parts of the past or one’s entire past; may be caused by brain damage or severe emotional trauma. | |
| anhedonia | an- no, not, without hedon/o pleasure -ia condition |
Absence of the ability to experience either pleasure or joy, even in the face of causative events. |
| confabulation | Effort to conceal a gap in memory by fabricating detailed, often believable stories. Associated with alcohol abuse. | |
| dyscalculia | dys- difficult calcul/o stone -ia condition |
Difficulty with performing mathematical calculations. |
| dysphoria | dys- abnormal phor/o to carry, to bear -ia condition |
Generalized negative mood characterized by depression. |
| echolalia | echo- reverberation -lalia condition of babbling |
Repetition of words or phrases spoken by others. |
| euphoria | eu- good, well phor/o to carry, to bear -ia condition |
Exaggerated sense of physical and emotional well-being not based on reality, disproportionate to the cause, or inappropriate to the situation. |
| hallucination | Any unreal sensory perception that occurs with no external cause. | |
| hyperkinesis | hyper- excessive -kinesis movement |
Excessive movement and activity. |
| stupor | From the Latin term for “numbness,” a stupor is a state of near unconsciousness. |

8. condition of without pleasure ____________________________________________________________________
9. excessive movement _____________________________________________________________________________
Terms Related to Mental Disorders Due to Known Physiological Conditions (FØ1-FØ9)
| Term | Word Origin | Definition |
| dementia | de- down, lack of ment/o mind -ia condition |
Lack of normal mental functioning due to injury or disease. May include changes to personality as well as memory and reasoning. |
Terms Related to Mental and Behavioral Disorders Due to Psychoactive Substance Use (F1Ø-F19)
| Term | Word Origin | Definition |
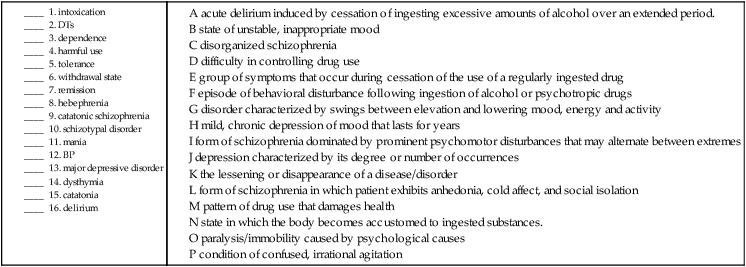
| delirium tremens (DTs) | Acute and sometimes fatal delirium induced by the cessation of ingesting excessive amounts of alcohol over a long period. | |
| dependence | Difficulty in controlling use of a drug. | |
| intoxication | in- in toxic/o poison -ation process of |
Episode of behavioral disturbance following ingestion of alcohol or psychotropic drugs. ICD-10-CM provides a code for blood alcohol level. |
| withdrawal state | Group of symptoms that occur during cessation of the use of a regularly taken drug. |

Terms Related to Schizophrenia, Schizotypal and Delusional, and Other Non-Mood Psychotic Disorders (F2Ø-F29)
| Term | Word Origin | Definition |
| catatonia | cata- down ton/o tension -ia condition |
Paralysis or immobility from psychological or emotional, rather than physical, causes. |
| catatonic schizophrenia | cata- down ton/o tension -ic pertaining to schiz/o split phren/o mind -ia condition |
Also called schizophrenic catalepsy. This form of schizophrenia is dominated by prominent psychomotor disturbances that may alternate between extremes, such as hyperkinesis and stupor, and may be accompanied by a dreamlike (oneiric) state and hallucinations. |
| delirium | Condition of confused, unfocused, irrational agitation. In mental disorders, agitation and confusion may also be accompanied by a more intense disorientation, incoherence, or fear, and illusions, hallucinations, and delusions. | |
| hebephrenia | hebe goddess of youth phren/o mind -ia condition |
Although more often referred to as disorganized schizophrenia, hebephrenia was named for its original association with initial occurrence at the time of puberty. It is characterized by prominent affective changes, fleeting and fragmentary delusions and hallucinations, and irresponsible and unpredictable behaviors. Shallow, inappropriate mood, flighty thoughts, social isolation, and incoherent speech are also present. |
| oneirism | oneir/o dream -ism state |
A state of a dreamlike hallucination. |
| paranoia | para- abnormal -noia condition of the mind |
A type of delusional disorder, paranoia includes the inaccurate perception of suspicious thinking. Also called delusional disorder, or late paraphrenia. |
| psychosis | psych/o mind -osis abnormal condition |
Disassociation with or impaired perception of reality; may be accompanied by hallucinations, delusions, incoherence, akathisia (the inability to sit still), and/or disorganized behavior. |
| schizophrenia | schiz/o split phren/o mind -ia condition |
A group of disorders characterized by fundamental distortions of thinking and perception, coupled with affect that is inappropriate or blunted. The patient exhibits characteristic inability to recognize an appropriate perception of reality, although his/her intellectual capacity is usually intact (Fig. 12-1). |
| schizotypal disorder | Unlike the other forms of schizophrenia, patient exhibits anhedonia, eccentric behavior, cold affect, and social isolation. Also called borderline schizophrenia, latent schizophrenia and prodromal schizophrenia. |
Terms Related to Mood (Affective) Disorders (F3Ø-F39)
| Term | Word Origin | Definition |
| bipolar disorder (BP, BD) | bi- two pol/o pole -ar pertaining to |
Disorder characterized by swings between an elevation of mood, increased energy and activity (hypomania and mania), and a lowering of mood and decreased energy and activity (depression). |
| cyclothymia | cycl/o recurring -thymia condition of the mind |
Disorder characterized by recurring episodes of mild elation and depression that are not severe enough to warrant a diagnosis of bipolar disorder. |
| dysthymia | dys- difficult -thymia condition of the mind |
Mild, chronic depression of mood that lasts for years but is not severe enough to justify a diagnosis of depression. Euthymia is a normal range of moods and emotions. |
| major depressive disorder | Depression typically characterized by its degree (minimal, moderate, severe) or number of occurrences (single or recurrent, persistent). Patient exhibits dysphoria, reduction of energy, and decrease in activity. Symptoms include anhedonia, lack of ability to concentrate, and fatigue. Patient may experience parasomnias (abnormal sleep patterns), diminished appetite, and loss of self-esteem. SAD (seasonal affective disorder) is caused by decreased exposure to sunlight in autumn and winter. | |
| mania | mania from the Greek term for “madness” | A state of an unstable, inappropriate mood. |
17. schizophrenia __________________________________________________________________________________
18. paranoia _______________________________________________________________________________________
19. psychosis ______________________________________________________________________________________
20. cyclothymia ____________________________________________________________________________________
21. oneirism _______________________________________________________________________________________
Terms Related to Anxiety, Dissociative, Stress-Related, Somatoform, and Other Nonpsychotic Mental Disorders (F4Ø-F48)
| Term | Word Origin | Definition |
| acrophobia | acro- heights, extremes -phobia condition of fear, sensitivity |
Fear of heights. |
| agoraphobia | agora- marketplace -phobia condition of fear, sensitivity |
Fear of leaving home and entering crowded spaces. |
| androphobia | andr/o man, men -phobia condition of fear, sensitivity |
Fear of men. |
| anthropophobia | anthrop/o man -phobia condition of fear, sensitivity |
Fear of scrutiny by other people; also called social phobia. |
| anxiety | Anticipation of impending danger and dread accompanied by restlessness, tension, tachycardia, and breathing difficulty not associated with an apparent stimulus. | |
| claustrophobia | claustr/o a closing -phobia condition of fear, sensitivity |
Fear of enclosed spaces. |
| delusion | Persistent belief in a demonstrable untruth or a provable, inaccurate perception despite clear evidence to the contrary. | |
| dissociative identity disorder | Maladaptive coping with severe stress by developing one or more separate personalities. A less severe form, dissociative disorder or dissociative reaction, results in identity confusion accompanied by amnesia, oneirism, and somnambulism. Formerly termed multiple personality disorder. | |
| dyslexia | dys- difficult lex/o word -ia condition |
Inability or difficulty with reading and/or writing. |
| generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) | Anxiety disorder characterized by excessive, uncontrollable, and often irrational worry about everyday things that is disproportionate to the actual source of worry. | |
| gynephobia | gyn/e female, women -phobia condition of fear, sensitivity |
Fear of women. |
| illusion | Inaccurate sensory perception based on a real stimulus; examples include mirages and interpreting music or wind as voices. | |
| obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) | Disorder characterized by recurrent, distressing, and unavoidable preoccupations or irresistible drives to perform specific rituals (e.g., constantly checking locks, excessive handwashing) that the patient feels will prevent some harmful event. | |
| panic disorder (PD) | Anxiety disorder characterized by recurring, severe panic attacks. Common symptoms of an attack include rapid heartbeat, perspiration, dizziness, dyspnea, uncontrollable fear, and hyperventilation. | |
| post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) | Extended emotional response to a traumatic event. Symptoms may include flashbacks, recurring nightmares, anhedonia, insomnia, hypervigilance, anxiety, depression, suicidal thoughts, and emotional blunting. | |
| somatoform disorder | somat/o body -form shape |
Any disorder that has unfounded physical complaints by the patient, despite medical assurance that no physiological problem exists. One type of somatoform disorder, hypochondriacal disorder, is the preoccupation with the possibility of having one or more serious and progressive physical disorders. |
Terms Related to Behavioral Syndromes Associated With Physiological Disturbances and Physical Factors (F5Ø-F59)
| Term | Word Origin | Definition |
| anorexia nervosa | an- without orex/o appetite -ia condition nervos/o nervous -a noun ending |
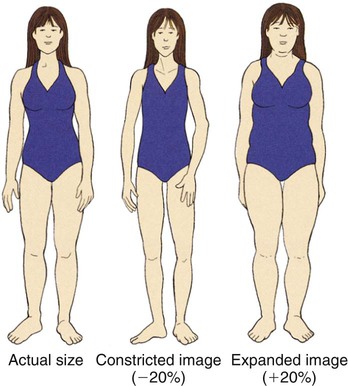
Prolonged refusal to eat adequate amounts of food and an altered perception of what constitutes a normal minimum body weight caused by an intense fear of becoming obese. Primarily affects adolescent females; emaciation and amenorrhea result (Fig. 12-2). |
| bulimia nervosa | Eating disorder in which the individual repetitively eats large quantities of food and then purges the body through self-induced vomiting or inappropriate use of laxatives. | |
| hypersomnia | hyper- excessive somn/o sleep –ia condition |
Excessive length or depth of sleep, especially during daytime. |
| hypoactive sexual desire disorder | hypo- under, deficient | Indifference or unresponsiveness to sexual stimuli; inability to achieve orgasm during intercourse. Formerly called frigidity. |
| idiopathic insomnia | in- not, without somn/o sleep -ia condition |
An inability to fall (or stay) asleep without a known cause. |
| nymphomania | nymph/o woman -mania condition of madness |
Relentless drive to achieve sexual orgasm in the female. In the male, the condition is called satyriasis. |
| somnambulism | somn/o sleep ambul/o to walk -ism condition |
Sleepwalking. |

18. condition of fear of the marketplace _____________________________________________________________
19. condition of fear of females _____________________________________________________________________
20. condition of without sleep ______________________________________________________________________
21. condition of woman madness ___________________________________________________________________
22. condition of fear of heights _____________________________________________________________________
23. condition of walking in sleep ___________________________________________________________________
Terms Related to Disorders of Adult Personality and Behavior (F6Ø-F69)
| Term | Word Origin | Definition |
| antisocial personality disorder | Disorder in which the patient shows a complete lack of interest in social obligations, to the extreme of showing antipathy for other individuals. Patients frustrate easily, are quick to display aggression, show a tendency to blame others, and do not change their behavior even after punishment. Also called dissocial personality disorder. | |
| borderline personality disorder (BPD) | Disorder characterized by impulsive, unpredictable mood and self-image, resulting in unstable interpersonal relationships and a tendency to see and respond to others as unwaveringly good or evil. | |
| fetishism | fetish/o charm -ism condition |
Reliance on an object as a stimulus for sexual arousal and pleasure. |
| kleptomania | klept/o to steal -mania condition of madness |
Uncontrollable impulse to steal. |
| necrophilia | necr/o death phil/o attraction -ia condition |
Abnormal sexual attraction to dead bodies. |
| obsessive-compulsive personality disorder (OCPD) | Characterized by recurrent and unavoidable preoccupations or irresistible drives to perform specific rituals (e.g., constantly checking locks, excessive handwashing) that the patient feels will prevent some harmful event. OCD differs from OCPD in that OCD patients find their preoccupations distressing, while those with OCPD consider them natural and normal. | |
| paranoid personality disorder | para- abnormal -oid resembling, like |
State in which the individual exhibits inappropriate suspicious thinking, self-importance, a lack of ability to forgive perceived insults, and an extreme sense of personal rights. |
| paraphilia | para- abnormal phil/o attraction -ia condition |
An abnormal sexual attraction to objects, situations, or individuals that is not part of normal stimulation. |
| pedophilia | ped/o child phil/o attraction -ia condition |
Sexual preference, either in fantasy or actuality, for children as a means of achieving sexual excitement and gratification. |
| pyromania | pyr/o fire -mania condition of madness |
Uncontrollable impulse to set fires. |
| schizoid personality disorder | schiz/o split -oid resembling, like |
Condition in which the patient withdraws into a fantasy world, with little need for social interaction. Most patients have little capacity to experience pleasure or to express their feelings. |
| trichotillomania | trich/o hair till/o to pull -mania condition of madness |
Uncontrollable impulse to pull one’s hair out by the roots. |
Terms Related to Mental Retardation (MR) (F7Ø-F79 )
| Condition of subaverage intellectual ability, with impairments in social and education functioning. The intelligence quotient (IQ) is a measure of an individual’s intellectual functioning compared with the general population. | ||
| Term | Word Origin | Definition |
| mild mental retardation | IQ range of 50-55 to 70; learning difficulties result. | |
| moderate mental retardation | IQ range of 35-40 to 50-55; support needed to function in society. | |
| profound mental retardation | IQ less than 20-25; severe self-care limitations. | |
| severe mental retardation | IQ range of 20-25 to 35-40; continuous need for support to live in society. | |
Terms Related to Pervasive and Specific Developmental Disorders (F8Ø-F89)
| Term | Word Origin | Definition |
| Asperger’s syndrome | Disorder characterized by impairment of social interaction and repetitive patterns of inappropriate behavior. Often considered a high-functioning form of autism. | |
| autistic disorder | Condition of abnormal development of social interaction, impaired communication, and repetitive behaviors. Also known as autism. | |
| pervasive developmental disorders (PDD) | A group of disorders characterized by impaired communication and social interaction that includes autism, and Rett’s and Asperger’s syndromes. Not to be confused with specific developmental disorders (SDD) such as dyslexia and dyscalculia. | |
| Rett’s syndrome | Condition characterized by initial normal functioning followed by loss of social and intellectual functioning. Usually diagnosed only in girls. |
Terms Related To Behavioral and Emotional Disorders with Onset Usually Occurring in Childhood and Adolescence (F9Ø-F98)
| Term | Word Origin | Definition |
| attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) | Series of syndromes that includes impulsiveness, inability to concentrate, and short attention span. | |
| conduct disorder | Any of a number of disorders characterized by patterns of persistent aggressive and defiant behaviors. | |
| oppositional defiant disorder (ODD) | A type of conduct disorder that is characterized by hostile, disobedient behavior. |

B. Match the terms with their definitions.

8. pyromania _____________________________________________________________________________________
9. trichotillomania _________________________________________________________________________________
10. necrophilia _____________________________________________________________________________________
Procedures
Diagnostic Procedures
Imaging
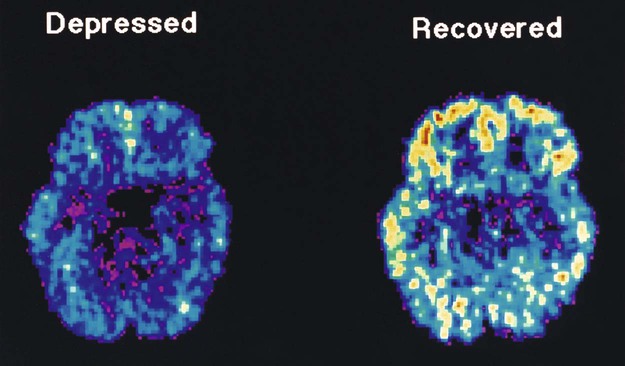
Imaging is most helpful in ruling out neurologic disorders and in research; it is less helpful in diagnosing or treating psychiatric problems. Computed tomography (CT) scans and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can be used to screen for brain lesions. Positron emission tomography (PET) scans can be used to examine and map the metabolic activity of the brain (Fig. 12-3). Central nervous system imaging in ICD-10-PCS is coded as plain radiography, fluoroscopy, CT scans, MRIs, or ultrasonography. The body part characters will be familiar from coverage of the nervous system, while the detail includes the type of contrast and whether it is unenhanced or enhanced.
Psychological Testing and Treatment
Bender Gestalt test: a test of visuomotor and spatial abilities; useful for children and adults.
Cognistat: also called the Neurobehavioral Cognitive Status Examination (NCSE), this is a test to measure a patient’s abilities in five areas to test their cognitive abilities. It is used to measure disability in patients with substance abuse, strokes, and traumatic brain injuries.
Draw-a-Person (DAP) Test: analysis of patient’s drawings of male and female individuals. Used to assess personality.
Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory (MMPI): assessment of personality characteristics through a battery of forced-choice questions.
Rorschach: a projective test using inkblots to determine the patient’s ability to integrate intellectual and emotional factors into his or her perception of the environment.
Thematic Apperception Test (TAT): a test in which patients are asked to make up stories about the pictures they are shown. This test may provide information about a patient’s interpersonal relationships, fantasies, needs, conflicts, and defenses.
Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS): a measure of verbal IQ, performance IQ, and full-scale IQ.
Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children (WISC): a measure of intellectual development in children.

Terms Related to Psychotherapy
| Term | Word Origin | Definition |
| behavioral therapy | Therapeutic attempt to alter an undesired behavior by substituting a new response or set of responses to a given stimulus. | |
| cognitive therapy | Wide variety of treatment techniques that attempts to help the individual alter inaccurate or unhealthy perceptions and patterns of thinking. | |
| psychoanalysis | psych/o mind ana- up, apart -lysis breaking down |
Behavioral treatment developed initially by Sigmund Freud to analyze and treat any dysfunctional effects of unconscious factors on a patient’s mental state. This therapy uses techniques that include analysis of defense mechanisms and dream interpretation. |
| psychodynamic therapy | psych/o mind dynam/o power -ic pertaining to |
Treatment that is based on revealing the motivations of behavior from past emotional experience and using the knowledge to effect change. |
Terms Related to Substance Abuse Treatment
| Term | Word Origin | Definition |
| detoxification | Removal of a chemical substance (drug or alcohol) as an initial step in treatment of a chemically dependent patient. | |
| pharmacotherapy | pharmac/o drug -therapy treatment |
The use of medication to affect behavior and/or emotions. Medications used and coded are: nicotine replacement, methadone maintenance, levo-alpha-acetyl-methadol (LAAM), Antabuse, naltrexone, naloxone, clonidine, bupropion. |
Terms Related to Other Therapeutic Methods
| Term | Word Origin | Definition |
| electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) | electr/o electricity con- together vuls/o to pull -ive pertaining to therapy treatment |
Method of inducing convulsions to treat affective disorders in patients who have been resistant or unresponsive to drug therapy. Treatment may include one or both hemispheres of the brain. |
| hypnosis | hypn/o sleep -sis state of, condition |
The induction of an altered state of consciousness to change an unwanted behavior or emotional response. |
| light therapy | Exposure of the body to light waves to treat patients with depression due to seasonal fluctuations (SAD) (Fig. 12-4). Sometimes called phototherapy. | |
| narcosynthesis | narc/o sleep, stupor -synthesis bring together |
The use of intravenous barbiturates to elicit repressed memories or thoughts. |
Pharmacology
antialcoholics: Discourage use of alcohol. Naltrexone (ReVia) can be used for alcohol and narcotic withdrawal. Disulfiram (Antabuse) is used to deter alcohol consumption.
antidepressants: Relieve symptoms of depressed mood. Many drug classes are available, including selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), and some newer unclassified agents. Examples include fluoxetine (Prozac), sertraline (Zoloft), mirtazapine (Remeron), bupropion (Wellbutrin), and venlafaxine (Effexor).
antipsychotics or neuroleptics: Control psychotic symptoms such as hallucinations and delusions. Haloperidol (Haldol) and chlorpromazine (Thorazine) are examples of typical antipsychotics; olanzapine (Zyprexa) and risperidone (Risperdal) are examples of the newer atypical antipsychotics.
anxiolytics: Relieve symptoms of anxiety. These drugs are often used as sedatives or sedative-hypnotics as well. Examples are lorazepam (Ativan), buspirone (BuSpar), and alprazolam (Xanax).
cholinesterase inhibitors: Combat the cognitive deterioration seen in disorders characterized by dementia, such as Alzheimer’s disease. Also known as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (AChEIs). Examples are donepezil (Aricept) and galantamine (Reminyl, Razadyne).
hypnotics: Promote sleep. Hypnotics, sedatives, sedative-hypnotics, and anxiolytics are often similar in effect and may be used interchangeably. Zolpidem (Ambien), zaleplon (Sonata), and flurazepam (Dalmane) are examples of hypnotics.
mood stabilizers: Balance neurotransmitters in the brain to reduce or prevent acute mood swings (mania or depression). Lithium (Lithobid) is the most well-known mood stabilizer. Some anticonvulsants such as valproic acid (Depakote) and lamotrigine (Lamictal) are also considered mood stabilizers.
NMDA receptor antagonists: Preserve cognitive function in patients suffering from progressive memory loss by blocking glutamate activity. Memantine (Namenda) is the only drug of this class currently used for this purpose.
sedatives and sedative-hypnotics: Exert a calming effect with or without inducing sleep. The most commonly used agents are benzodiazepines and barbiturates.
stimulants: Generally increase synaptic activity of targeted neurons to increase alertness. Examples include methylphenidate (Ritalin) and caffeine.

| Abbreviation | Meaning |
| ADHD | attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder |
| APA | American Psychiatric Association |
| BP, BD | bipolar disorder |
| BPD | borderline personality disorder |
| CBC | complete blood count |
| CT | computed tomography |
| DAP | Draw-a-Person Test |
| DSM | Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders |
| DTs | delirium tremens |
| ECT | electroconvulsive therapy |
| GAD | generalized anxiety disorder |
| GAF | Global Assessment of Functioning Scale |
| HIV | human immunodeficiency virus |
| IQ | intelligence quotient |
| MHA-TP | microhemagglutination assay for Treponema pallidum |
| MMPI | Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory |
| MR | mental retardation |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| MSE | mental status examination |
| NCSE | Neurobehavioral Cognitive Status Examination |
| OCD | obsessive-compulsive disorder |
| ODD | oppositional defiant disorder |
| OCPD | obsessive-compulsive personality disorder |
| PD | panic disorder |
| PDD | pervasive developmental disorder |
| PET | positron emission tomography |
| PTSD | post-traumatic stress disorder |
| RPR | rapid plasma reagin |
| SAD | seasonal affective disorder |
| SDD | specific developmental disorders |
| TAT | Thematic Apperception Test |
| WAIS | Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale |
| WISC | Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children |