21 Melomental folds
Summary and Key Features
• The melomental folds result from a variety of aging processes
• Melomental folds have been found to have a detrimental effect on self-perception as well as perception by others
• They are more recalcitrant to correction than other rhytides
• Melomental folds generally benefit from injection of a heavier weight filler in the deep dermal plane
• Cross-hatching or fanning technique is generally effective for effacing melomental folds
• Adjunctive techniques such as botulinum toxin injection of the depressor anguli oris muscles may prove helpful in this area
Injection strategies for melomental fold correction
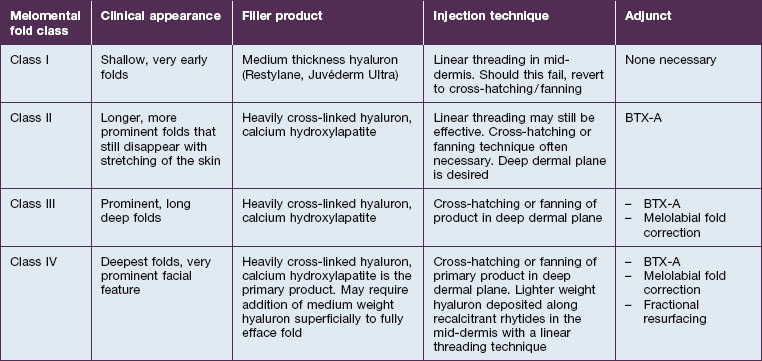
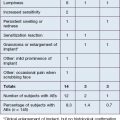
While ultimately a treatment plan must be individualized for a given patient, there are some broad generalizations that may be made. The Validated Melomental Fold Scoring System allows for division of MMFs into four classes based on severity, as summarized in Table 21.1. An excellent and thorough discussion of this classification may be found in the article by Carruthers et al in the Further reading section. This scoring system will be used to more concisely discuss treatment strategies for patients based on the severity of their MMFs.
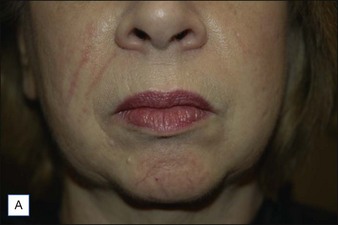
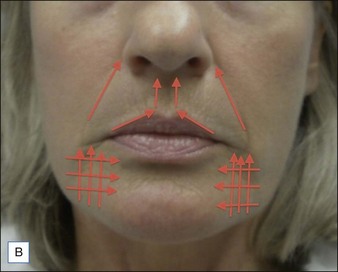
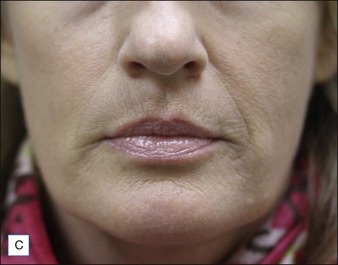
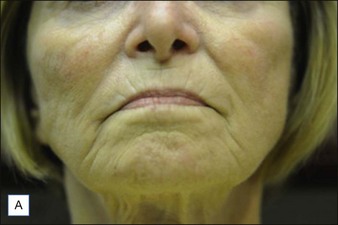
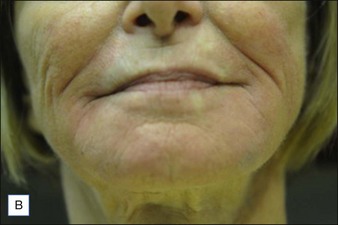
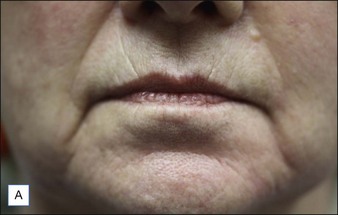
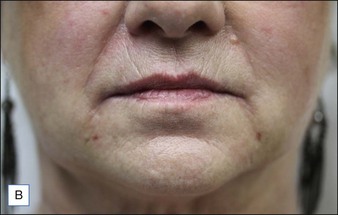
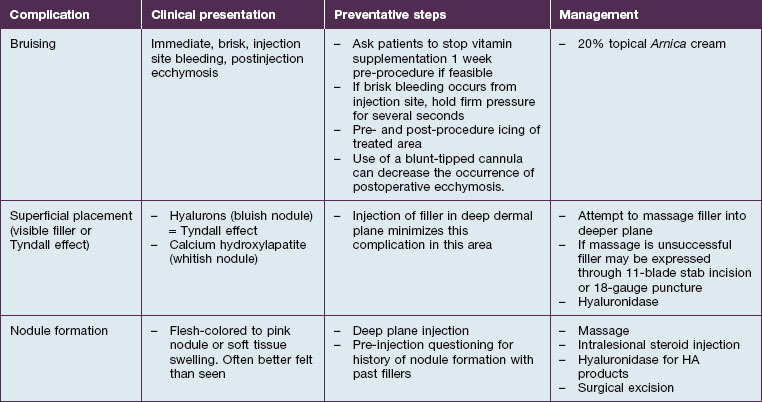
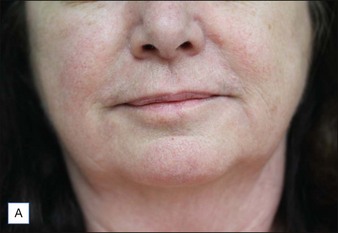
Class II folds are slightly deeper than their class I counterparts, but still will disappear upon stretching of the skin. These folds may require the use of a thicker product that consequently must be injected in the deep dermal plane. Should linear deposition of filler fail to efface these folds, a cross-hatching pattern of filler placement should be adopted. Figure 21.1 demonstrates the use of Radiesse in this area.
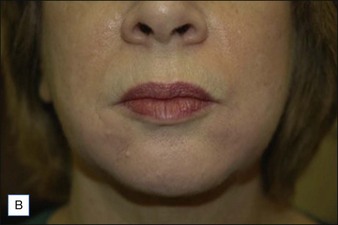
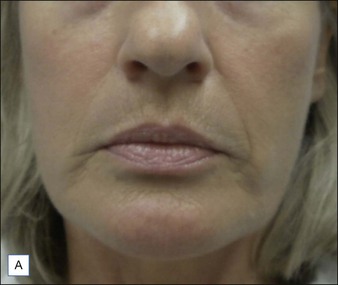
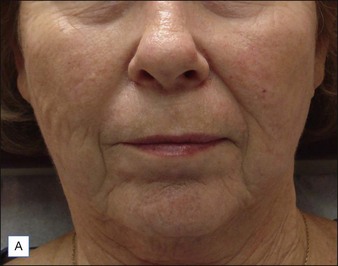
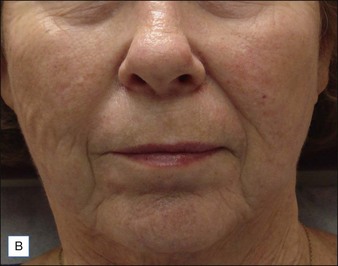
Class III MMFs are prominent, long, and deep. Deep dermal placement in a cross-hatched pattern is the rule. Figure 21.2 demonstrates a patient with class III folds injected with Juvéderm Ultra Plus. Class IV folds are the deepest and the most difficult to correct. They often require vertical layering of multiple filler products to achieve full correction. Even with meticulous technique, deep-plane injection of a thicker filler product may leave remnants of the MMF. This can be dealt with by the addition of a less viscous filler, normally a lower cross-linkage HA product (Restylane, Juvéderm Ultra). This lighter weight filler is injected in the mid-dermis after deep dermal injection of the thicker product to efface the MMF remnant. Normally, the linear threading technique is ideal for this superficially placed filler. Figures 21.3 and 21.4 depict patients with class IV folds who were treated with differing modalities.
Blunt-tipped cannulas offer an opportunity to provide excellent outcomes for filler patients while minimizing the risk of bruising. The authors frequently use these to enhance results in the lower face. A 25-gauge needle is used to make a puncture site on the mandibular margin inferior to the oral commissure. A 27-gauge, 1.5-inch (3.8 cm) cannula is then introduced into this puncture site and used to inject the deep-filling agent. From this single access point, the cannula can atraumatically access the entire area to be filled (Fig. 21.5). The video supplement shows an example of this technique.
Complications
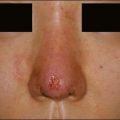
One of the most attractive features of fillers as a cosmetic option is their low rate of adverse effects. Table 21.2 summarizes common complications, and their management. As with any injection, pain is something that must be considered. Strategies for dealing with intraoperative pain management have been addressed earlier in the chapter, and the rate of postoperative pain has consistently been found to be quite low. Bruising is a commonly observed postoperative complication of filler injection (Fig. 21.6). During filler placement it may be prevented by holding firm, direct pressure over any entry points that exhibit brisk bleeding. Postoperative application of ice to the treated areas may also decrease the extent of ecchymosis. Application of 20% topical Arnica has been shown to decrease the duration of post-laser bruising, and has been touted by some experts as a useful agent for managing post-filler bruising as well. Additionally, some injectors find that the use of blunt-tipped cannulas decreases the rate of postoperative bruising (see Fig. 21.5).
Adjunctive treatments
Multiple aging processes affect the perioral cosmetic unit and, as such, filler injection of the MMFs may not be entirely sufficient to restore the area to the desired standard. There are several useful adjuncts that should be considered and these are summarized in Table 21.3.
| Adjunctive measure | When to consider | Why it works |
|---|---|---|
| Botulinum toxin injection of depressor anguli oris |
(e.g. chemical peels, fractional photothermolysis)
An important contributing factor for MMF formation is mid-facial descent with festooning of the cheek and upper lip over the MMF. Mid-facial injection of filler, such as melolabial fold correction, may provide an upward vector for the mid-face, thus attenuating its descent and hence the MMF as in Figure 21.2. Advanced MMF almost universally corresponds with significant skin quality and pigmentation issues. As patients desire not only correction of the fold itself, but correction of their problem, addressing pigment issues with topical products such as retinoids, hydroquinone, or kojic acid can enhance results and has minimal potential morbidity. If a more aggressive approach is needed then resurfacing techniques such as fractional laser resurfacing or chemical peels can address texture and pigmentation issues, as well as fine rhytides, which a filler cannot.
Carruthers A, Carruthers J, Hardas B, et al. A validated grading scale for marionette lines. Dermatologic Surgery. 2008;34(suppl 2):S167–S172.
Carruthers A, Carruthers J, Monheit GD, et al. Multicenter, randomized, parallel-group study of onabotulinum toxin A and hyaluronic acid dermal fillers (24-mg/ml smooth, cohesive gel) alone and in combination for lower facial rejuvenation: satisfaction and patient-reported outcomes. Dermatologic Surgery. 2010;36(suppl 4):2121–2134.
Dayan SH, Lieberman ED, Thakkar NN, et al. Botulinum toxin A can positively impact first impression. Dermatologic Surgery. 2008;34:S40–S47.
Don Parsa F, Parsa N, Murariu D. Surgical correction of the frowning mouth. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2010;2:667–676.
Finzi E, Wasserman E. Treatment of depression with botulinum toxin A: a case series. Dermatologic Surgery. 2006;32:645–649.
Graivier MH, Bass L, et al. Calcium hydroxylapatite for correction of the mid- and lower face: consensus recommendations. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2007;120(suppl 6):55S–66S.
Park TH, Seo SW, Kim JK, et al. Clinical experience with hyaluronic acid filler complications. Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgery. 2011;64(7):892–896.
Requena L, Requena C, Christensen L, et al. Adverse reactions to injectable fillers. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 2011;64(1):1–34.
Solish NJ. Assessment of recovery time for the collagen products Dermicol-P35 27G and 30G. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 2010;62(5):824–830.
Tzikas TA. 52-month summary of results using calcium hydroxylapatite for soft tissue augmentation. Dermatologic Surgery. 2008;34:S9–S15.
Van Eijk T, Braun MI. A novel technique to inject hyaluronic acid: the fern technique. Journal of Drugs in Dermatology. 2007;6:806–808.
Weinkle S. Injection techniques for revolumization of the perioral region with hyaluronic acid. Journal of Drugs in Dermatology. 2010;9:367–371.