Chapter 8 Medial Branch Block and Radiofrequency Lesioning
Treatment objectives
Medial Branch Block
The treatment objectives are to diagnose and treat facet joint syndrome. Facet joints are one of the most common sources of back pain. Facet joint syndrome cannot be diagnosed clinically or radiographically but can be identified with MBB or facet joint injection [1–5]. A series (3-5 times) of local anesthetic injections with or without corticosteroids sometimes achieves long-term relief of back pain.
Radiofrequency Neuromodulation (Pulsed Radiofrequency Lesioning) or Neuroablation (Radiofrequency Thermocoagulation) of the Medial Branch
The treatment objective of radiofrequency lesioning is to treat facet joint syndrome. This procedure offers pain relief by modulating (pulsed radiofrequency lesioning [PRFL]) or denaturing (radiofrequency thermocoagulation [RFTC]) medial branches that innervate the painful facet joints. The typical durations of pain relief experienced after such procedures are as follows [6]:
Preoperative preparation
History Taking and Physical Examination
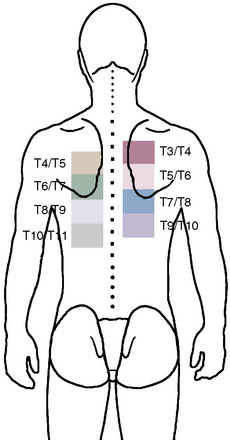
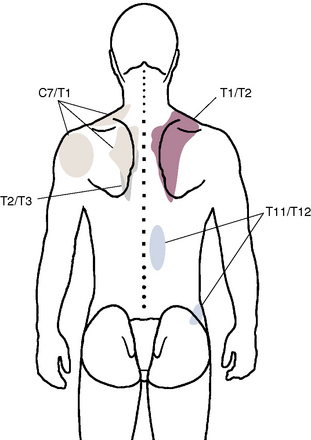
Figure 8–7 A composite map shows pain referral patterns from the T3-T4 to the T10-T11 thoracic facet joints.
(Modified from Dreyfuss P, Tibiletti C, Dreyer S: Thoracic zygapophyseal joint pain patterns. Spine 1994:19;807-811.)
Indications
Medial Branch Block
Indications for MBB in the cervical spine include the following:
Indications for MBB in the thoracic spine include the following:
 Radiologic signs such as severe kyphoscoliosis, osteoporosis, vertebral compression fracture, and facet osteoarthritis
Radiologic signs such as severe kyphoscoliosis, osteoporosis, vertebral compression fracture, and facet osteoarthritisIndications for MBB in the lumbar spine include the following:
Contraindications
Contraindications to MBB, PRFL, and RFTC are as follows:
 Coagulopathy (International Normalized Ratio [INR] value > 1.5 or platelet count < 50,000/mm3) or anticoagulant therapy
Coagulopathy (International Normalized Ratio [INR] value > 1.5 or platelet count < 50,000/mm3) or anticoagulant therapyComplications
Anatomy
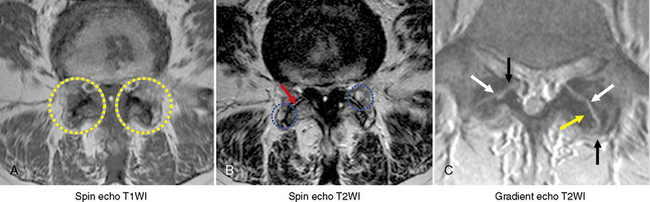
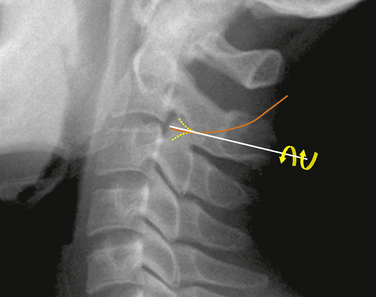
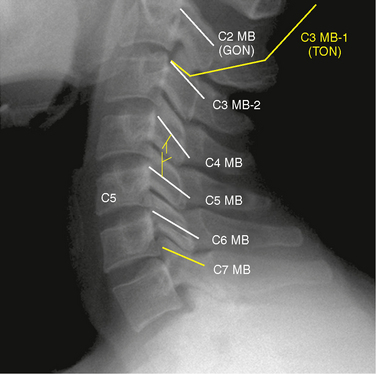
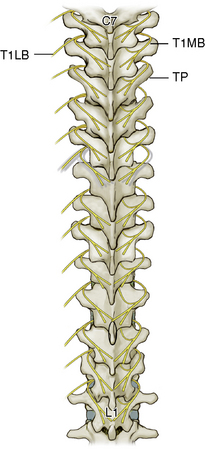
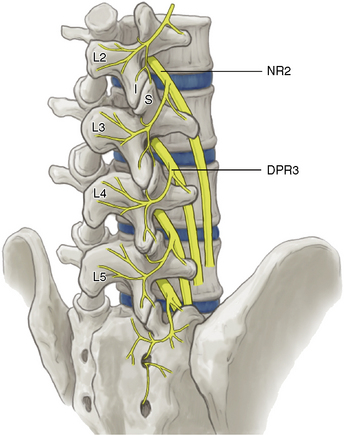
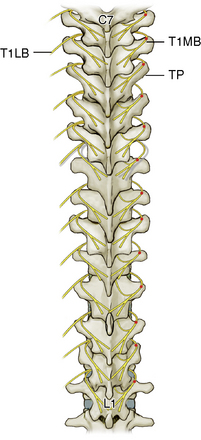
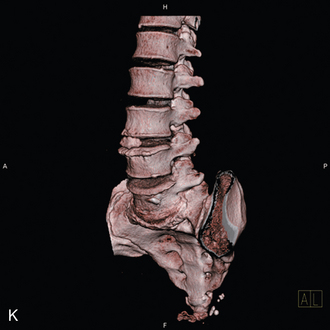
At each level, facet joint innervation is derived from the medial branch of the adjacent spinal nerve, as well as the medial branches located one level above and perhaps one level below. Figures 8-10 through 8-12 show facet joint innervation of the three regions of the spine.
Instruments and solutions
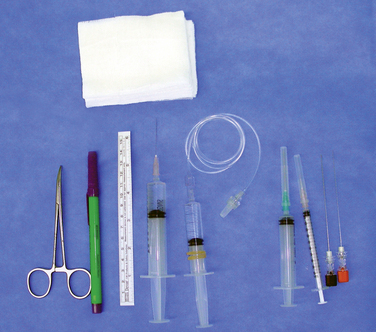
Medial Branch Block
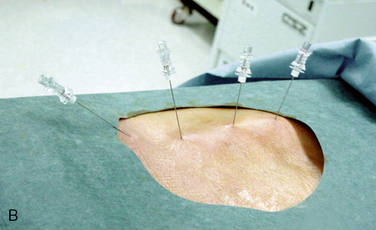
The instruments (Fig. 8-13) and solutions used in MBB are as follows:
Pulsed Radiofrequency Lesioning or Radiofrequency Thermocoagulation of the Medial Branch
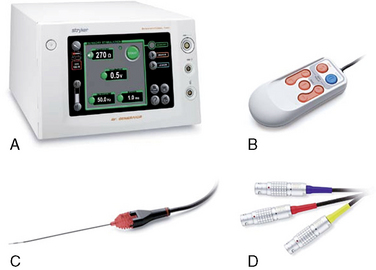
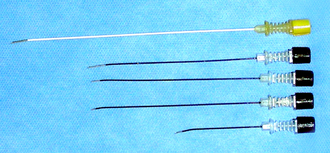
The following instruments and solutions are used in PRFL and RFTC:
Basic mechanisms of radiofreqency lesioning
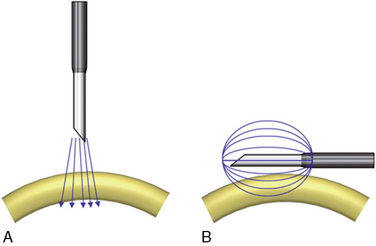
Figure 8-16 illustrates the difference in lesioning between PRFL and RFTC. RFTC cannot produce a lesion distal to cannula tip, as PRFL does. Instead, RFTC produces lesions only circumferentially around the shaft of the uninsulated active tip; the RFTC cannula must lie parallel to and within 2 mm of the target nerve.
Radiofrequency Lesioning
Radiofrequency thermocoagulation
The following principles apply to RFTC:
 Impedance should be checked before lesioning and should register less than 500 ohms; if the impedance is greater than 500 ohms, the probe should be removed, 0.5 mL of local anesthetics should be injected, and the probe should be re-inserted.
Impedance should be checked before lesioning and should register less than 500 ohms; if the impedance is greater than 500 ohms, the probe should be removed, 0.5 mL of local anesthetics should be injected, and the probe should be re-inserted. After injection of 0.5 mL of local anesthetics, a lesion is made by raising the temperature of the cannula tip to 80°C for 90 seconds. Thereafter, the curved tip of the cannula is rotated cephalad and caudad by rotation of the cannula hub, and second and third lesions are made using the same parameters (Figs. 8-19 and 8-21 for the cervical spine; Fig. 8-25 for the thoracic spine; and Fig. 8-27 for the lumbar spine).
After injection of 0.5 mL of local anesthetics, a lesion is made by raising the temperature of the cannula tip to 80°C for 90 seconds. Thereafter, the curved tip of the cannula is rotated cephalad and caudad by rotation of the cannula hub, and second and third lesions are made using the same parameters (Figs. 8-19 and 8-21 for the cervical spine; Fig. 8-25 for the thoracic spine; and Fig. 8-27 for the lumbar spine). After RFTC, 5 mg of triamcinolone per segment is injected through the cannula for relief of postprocedural pain attributable to the trauma of the cannula insertion and the thermal lesion around the target nerve.
After RFTC, 5 mg of triamcinolone per segment is injected through the cannula for relief of postprocedural pain attributable to the trauma of the cannula insertion and the thermal lesion around the target nerve.Procedure
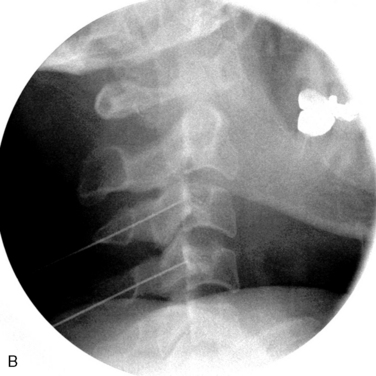
Technical problems of the radiofrequency procedure may affect its efficacy. For accurate placement of the cannula, it is usually preferable to perform motor stimulation of the medial branch with 2 Hz and less than 0.5 V, followed by radiofrequency lesioning with the rotating curved needle technique (Figs. 8-19, 8-21, and 8-25).
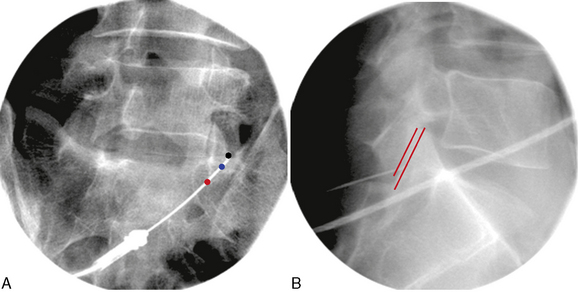
Care must be taken, during injection of local anesthetics as well as during removal and re-insertion of the probe before radiofrequency lesioning, to avoid displacement of cannula, which can easily occur. Tandem placement of another block needle for injection of local anesthetics near the radiofrequency cannula has been suggested as an alternative method to avoid cannula displacement during the manipulation of the probe (Fig. 8-17).
If paravertebral rhythmic contractions cannot be elicited despite repeated attempts at motor stimulation, lesioning of a broader area can be performed on the basis of the radiographic anatomy. For PRFL based on the radiographic anatomy, the cannula tip is usually located 2 to3 mm behind the cannula tip position for RFTC, because the PRFL lesion is made from the tip of the cannula (Fig. 8-16).
If motor stimulation yields any of the following abnormal findings, RFTC should not be performed:
Procedures at the Cervical Level
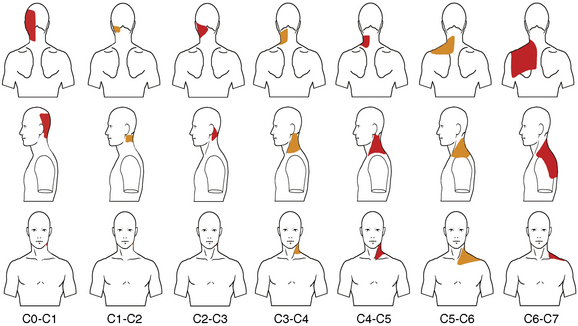
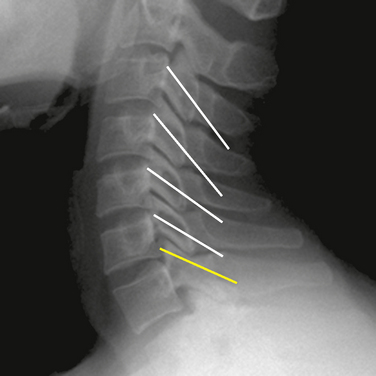
The most commonly involved facet joints in patients with whiplash injury are the C2-C3 and C5-C6 facet joints [2].
Third Occipital Nerve and Medial Branch Blocks
Target medial branches for third occipital nerve and medial branch blocks are as follows:
 For upper neck pain (usually C2-C3 through C4-C5 joint problems): third occipital nerve, C3 to C5 medial branches
For upper neck pain (usually C2-C3 through C4-C5 joint problems): third occipital nerve, C3 to C5 medial branches For lower neck or upper back pain (usually C4-C5 through C6-C7 joint problems): C4 through C7 medial branches
For lower neck or upper back pain (usually C4-C5 through C6-C7 joint problems): C4 through C7 medial branchesThe procedure for third occipital nerve block or MBB is as follows:
Pulsed Radiofrequency Lesioning or Radiofrequency Thermocoagulation of the Medial Branch
At the third occipital nerve
The procedure for PRFL or RFTC at the third occipital nerve is as follows:
At the C3-C4 through C7-T1 facet joints
The procedure for PRFL or RFTC at the C3-C4 through C7-T1 facet joints is as follows:
If paravertebral rhythmic contractions cannot be elicited despite repeated attempts at motor stimulation, lesioning of a broader area can be performed on the basis of the radiographic anatomy. The needle trajectories for different cervical levels are shown in Figures 8-22 and 8-23. Sensory stimulation is not mandatory.
Procedures at the Thoracic Region
Targets for MBB in the thoracic region are as follows:
 For T11 and T12 medial branches: the junctions between the superior articular processes and transverse processes
For T11 and T12 medial branches: the junctions between the superior articular processes and transverse processesMedial Branch Block
The procedure for MBB in the thoracic region is as follows:
Pulsed Radiofrequency Lesioning or Radiofrequency Thermocoagulation of the Medial Branch
The procedure for PRFL or RFTC in the thoracic region is as follows:
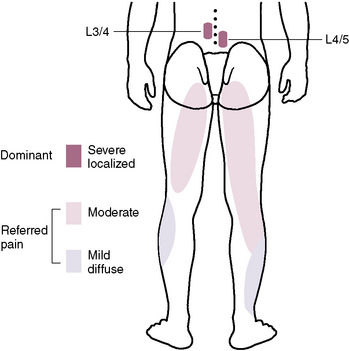
Procedures in the Lumbar Region
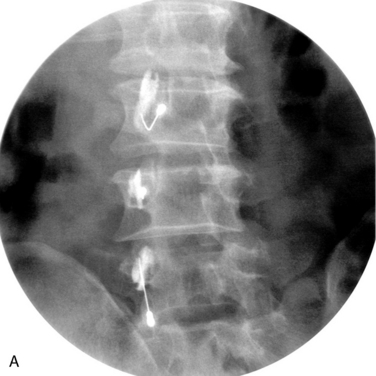
Medial Branch Block (L1-L4) or Dorsal Ramus Block (L5)
At the L1-L2 through L4-L5 facet joints
The procedure for MBB at the L1-L2 through L4-L5 facet joints is as follows:
At the L5-S1 facet joint
The procedure for MBB at the L5-S1 facet joint is as follows:
Pulsed Radiofrequency Lesioning or Radiofrequency Thermocoagulation of the Medial Branch (L1-L4) or Dorsal Ramus (L5)
At the L1-L2 through L4-L5 facet joints
The procedure for PRFL or RFTC at the L1-L2 through L4-L5 facet joints is as follows:
At the L5-S1 facet joint
The procedure for PRFL or RFTC at the L5-S1 facet joint is as follows:
Postprocedural management
Pulsed Radiofrequency Lesioning or Radiofrequency Thermocoagulation of the Medial Branch
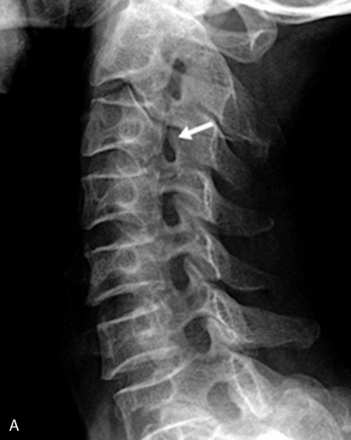
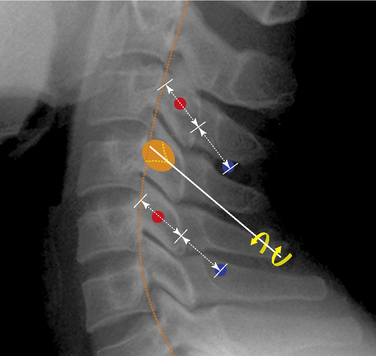
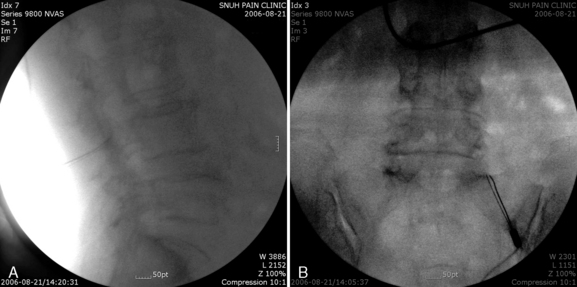
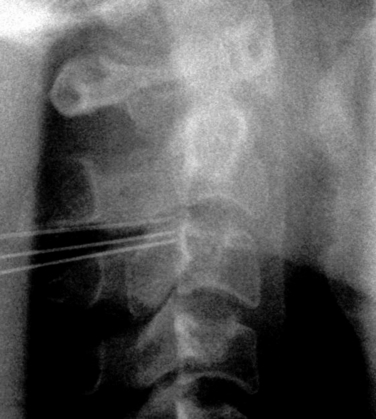
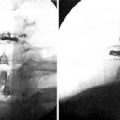
CASE STUDY 8.1 Cervical Medial Branch Radiofrequency Thermocoagulation
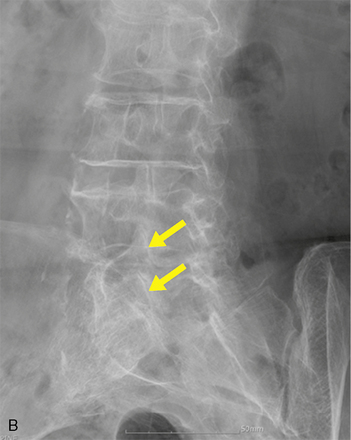
We proceeded with diagnostic MBB using 0.25% levobupivacaine, and the result of the procedure was positive (Fig. 8-30). Thereafter the patient was also treated with RFTC of the left C5 and C6 medial branches (Fig. 8-31). The patient had complete pain relief and improved range of motion of the neck for 3 weeks.
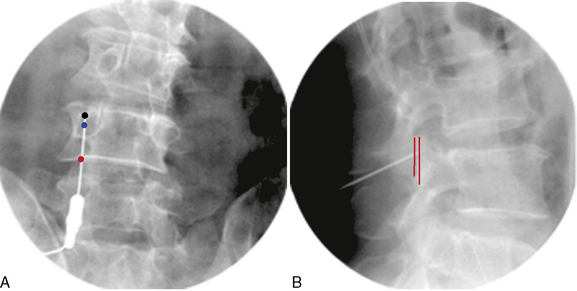
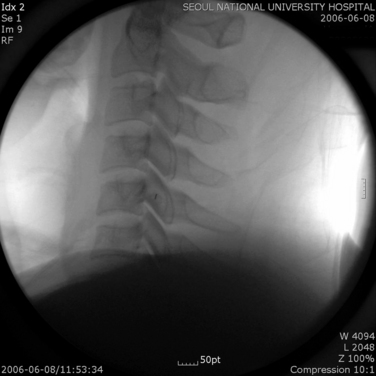
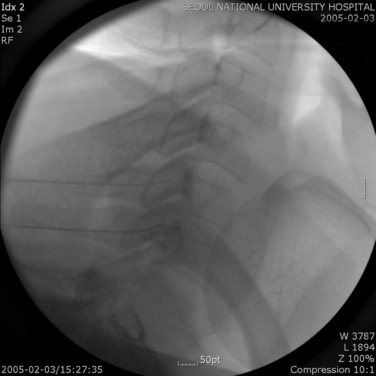
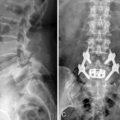
CASE STUDY 8.2 Lumbar Medial Branch Block and Medial Branch Radiofrequency Thermocoagulation
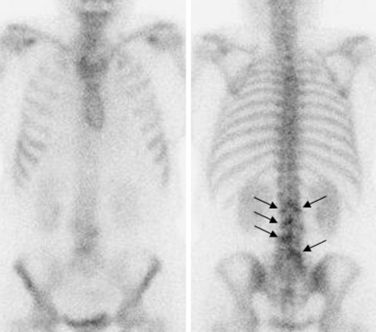
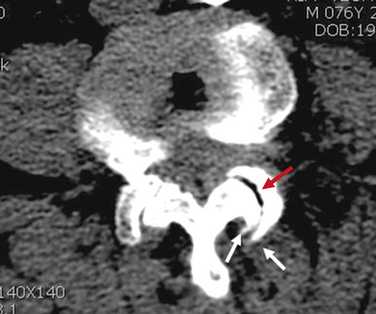
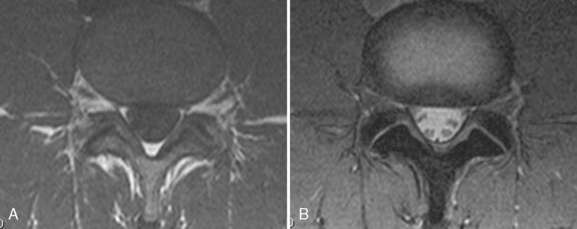
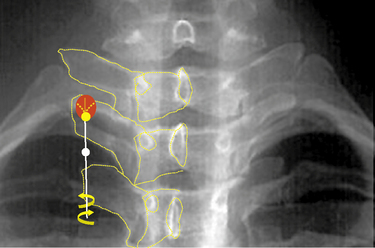
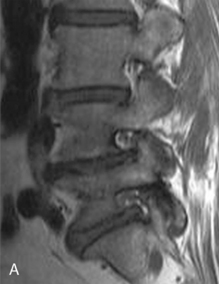
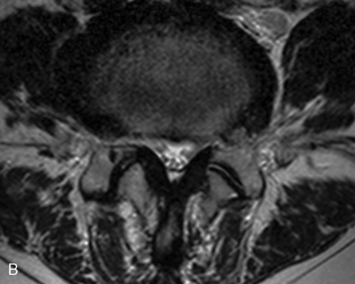
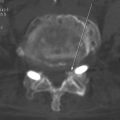
Motor and sensory test results were normal; results of the straight-leg raising test and Patrick test were negative. A bone scan demonstrated abnormal radiotracer uptake at the left lumbosacral junction and L4-L5 facet joint areas (Fig. 8-32). Magnetic resonance imaging showed left L4-L5 facet arthrosis (Fig. 8-33).
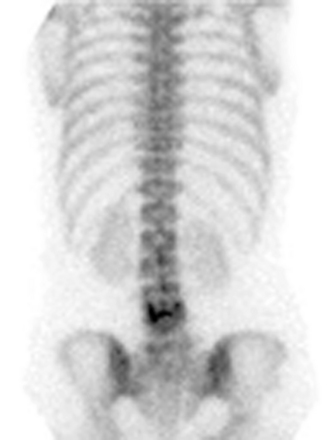
Figure 8–32 A bone scan demonstrating abnormal uptake at the left lumbosacral junction and the L4-L5 facet joint area.
1 Barnsley L., Lord S.M., Wallis B.J., et al. The prevalence of chronic cervical zygapophysial joint pain after whiplash. Spine. 1995;20:20-26.
2 Lord S.M., Barnsley L., Wallis B.J., et al. Chronic cervical zygapophysial joint pain after whiplash: A placebo-controlled prevalence study. Spine. 1996;21:1737-1745.
3 Barnsley L., Bogduk N. Medial branch blocks are specific for the diagnosis of cervical zygapophysial joint pain. Reg Anesth. 1993;18:343-350.
4 Barnsley L., Lord S.M., Bogduk N. Comparative local anaesthetic blocks in the diagnosis of cervical zygapophysial joint pain. Pain. 1993;55:99-106.
5 Lord S.M., Barnsley L., Bogduk N. The utility of comparative local anesthetic blocks versus placebo-controlled blocks for the diagnosis of cervical zygapophysial joint pain. Clin J Pain. 1995;11:208-213.
6 McDonald G.J., Lord S.M., Bogduk N. Long-term follow-up of patients treated with cervical radiofrequency neurotomy for chronic neck pain. Neurosurgery. 1999;45:61-67.
7 Lord S.M., Barnsley L., Wallis B.J., et al. Percutaneous radio-frequency neurotomy for chronic cervical zygapophyseal-joint pain. N Engl J Med. 1996;335:1721-1726.