Chapter 9 Mechanical and Noninvasive Ventilation
2 What is the difference between conventional and noninvasive ventilation?
 The conventional approach to mechanical ventilation involves use of an airway device inserted directly into a patient’s trachea.
The conventional approach to mechanical ventilation involves use of an airway device inserted directly into a patient’s trachea.
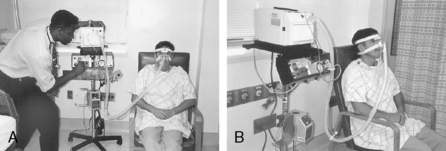
 Noninvasive ventilation is mechanical ventilation without the use of an endotracheal tube or tracheotomy. See Figure 9-1.
Noninvasive ventilation is mechanical ventilation without the use of an endotracheal tube or tracheotomy. See Figure 9-1.
4 What are the advantages of noninvasive ventilation compared with conventional mechanical ventilation with an endotracheal tube?
6 Which patients with acute respiratory failure are most likely to benefit from noninvasive ventilation?
21 What are the complications unique to noninvasive ventilation?
Key Points Mechanical Ventilation
1. The primary indications for mechanical ventilation are inadequate oxygenation, inadequate ventilation, and elevated work of breathing.
2. The patient populations most likely to benefit from noninvasive ventilation are those with acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder, cardiogenic pulmonary edema, and immune compromise.
3. The assist control mode provides a guaranteed minute ventilation and full support of all patient-initiated breaths.
4. Pressure support ventilation requires intact respiratory drive from the patient; tidal volume and minute ventilation are variable and depend on patient effort.
5. Low tidal volume mechanical ventilation can lead to improved outcomes in the patient with acute respiratory distress syndrome.
1 Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Network: Ventilation with lower tidal volumes as compared with traditional tidal volumes for acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:1301–1308.
2 Calfee C.S., Matthay M.A. Recent advances in mechanical ventilation. Am J Med. 2005;118:584–591.
3 Squadrone V., Coha M., Cerutti E., et al. Continuous positive airway pressure for treatment of postoperative hypoxemia: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2005;293:589–595.