226 Marfan’s syndrome
Salient features
Examination
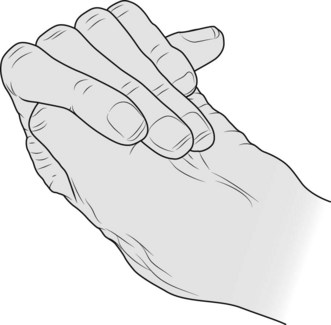
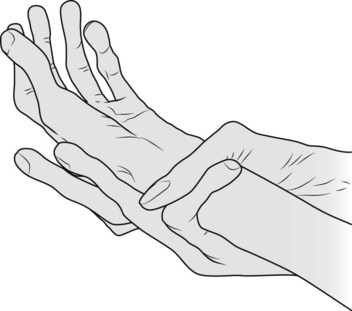
• hands for hypermobile joints and spidery fingers or arachnodactyly; confirmed by:
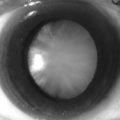
• eyes, for iridodonesis or ectopia lentis (subluxation upwards): the patient may be wearing thick spectacles; blue sclera
• head, for long-headedness: dolichocephalic with bossing of frontal eminences and prominent supraorbital ridges
• palate for high arched palate
• skin for small papules in the neck (Miescher’s elastoma)
• chest for pectus excavatum, cystic lung disease (Thorax 1984;39:780–4)
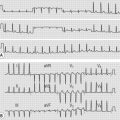
• heart for mitral valve prolapse, aortic aneurysm and aortic regurgitation
Questions
What are the criteria for Marfan syndrome?
• People with no family history require, apart from skeletal features (including pectus carinatum or excavatum, reduced upper-to-lower segment ratio, arm-span-to-height ratio >1.05, scoliosis and reduced elbow extension), involvement of at least two other systems and one of the major criteria (these include ectopia lentis, dilatation of the aortic root or aortic dissection and lumbosacral dural ectasia by CT or MRI).
• Patients with a family history need features in at least two systems.