57. Marfan Syndrome
Definition
Marfan syndrome is an autosomal dominant genetic defect of the connective tissue protein, fibrillin. It results in myriad clinical problems, predominately in the cardiac, musculoskeletal, and ocular systems.
Incidence
The incidence of Marfan syndrome is estimated to range from 1:5000 to 1:10,000.
Etiology
FBN 1 locus on chromosome 15 codes for the connective tissue protein, fibrillin. Mutations of the FBN 1 locus are believed to be responsible for Marfan syndrome.
Signs and Symptoms
Cardiovascular System
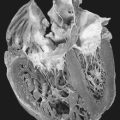
• Ascending aorta dilation
• Ascending aorta dissection
• Mitral valve annulus calcification
• Mitral valve prolapse
• Pulmonary artery dilation
• Thoracic or abdominal aorta dilation or dissection
Ocular System
• Abnormally flat cornea
• Ectopic lentis
• Hypoplastic ciliary muscle
• Hypoplastic iris
• Increased axial length of the globe
• Myopia
Pulmonary System
• Apical blebs
• Spontaneous pneumothorax
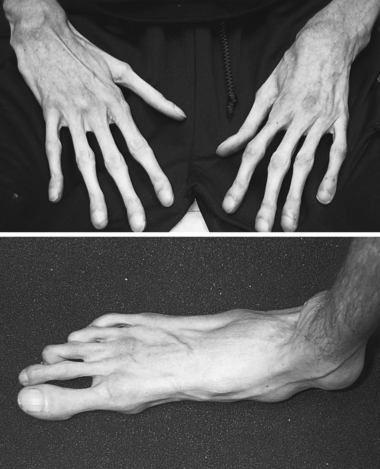 |
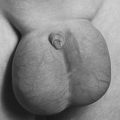
| Marfan Syndrome. This young man has prominent arachnodactyly of both fingers and toes. Note the clubbing due to associated cardiopulmonary problems and the flattening of the arch of his foot. |
Skeletal System
• Arachnodactyly
• Dolichocephaly
• Dolichostenomelia
• Downsloping palpebral fissures
• Enophthalmos
• High-arched palate with dental crowding
• Increased arm span–to-height ratio (>1.05)
• Joint hypermobility
• Malar hypoplasia
• Pectus carinatum
• Pectus excavatum
• Positive Steinberg sign (thumb extends beyond ulnar border when flexed in the palm)
• Positive wrist sign (thumb-index overlap when encircling the wrist)
• Progressive hindfoot collapse leading to pes planovalgus
• Protrusio acetabuli
• Reduced upper-to-lower segment ratio (distance from head to pubic symphysis divided by distance from pubic symphysis to soles) <0.85
• Retrognathia
• Scoliosis >20 degrees
• Spondylolisthesis
• Thoracolumbar scoliosis
Skin and Integumentary System
• Recurrent or incisional hernia
• Striae atrophicae not associated with pregnancy or repetitive stress
Medical Management
The primary focus of Marfan syndrome is the prevention of cardiovascular compromise. β-Blocking medications reduce inotrophy and chronotrophy as well as reduce the stress on the aorta, particularly the aortic root. Nitroprusside is added to the treatment regimen to lower the systemic vascular resistance, which reduces the afterload and reduces the stress on the heart. Combined administration of β blockers and nitroprusside provide a synergistic effect of reduced aortic stiffness, lower vascular resistance, and improved cardiac compliance.
Mitral valve prolapse frequently becomes so severe that surgical replacement is required. Often the defective valve is found to have a dilated annulus, redundant and flaccid cusps, and ruptured chordae tendineae. Frequently the ascending aorta and/or incompetent aortic valve must also be surgically repaired or replaced. Composite graft repair is the intervention of choice for a widely dilated ascending aorta, significantly attenuated aortic cusps, and acutely dissected aortic root. Composite grafting repair is also frequently recommended as a prophylactic measure for a patient with a history of increasing aortic dilation and/or a family history of sudden cardiovascular death.
Scoliosis is another symptom in Marfan syndrome for which surgical intervention is required. Nonsurgical management (conservative treatment) is often attempted initially, usually in the form of bracing, but it is not typically successful. Scoliosis curve progression in a Marfan syndrome patient may be as rapid as 7 to 10 degrees every year after onset of the disease. The degree of scoliosis combined with poor musculature and chest deformities can result in significant respiratory compromise. Chest wall deformities (specifically pectus excavatum) can be very severe—so severe, in fact, that cardiopulmonary function may be impaired. In such cases, the deformity can be surgically corrected to allow improvement of cardiopulmonary function.
Complications
• Abdominal aortic dilation
• Abdominal aortic dissection
• Aortic root dilation
• Aortic root dissection
• Bacterial endocarditis
• Cor pulmonale
• Death
• Descending aortic dilation
• Descending aortic dissection
• Heart failure
• Kyphotic deformity
• Mitral valve annulus calcification
• Mitral valve regurgitation
• Moderate-to-severe scoliosis
• Pneumothorax
Anesthesia Implications
The primary focus of the preoperative evaluation of a patient with Marfan syndrome concerns the cardiovascular system. Specifically, the focus is to determine the presence of imminent compromise or to specifically rule out imminent compromise. The cardiac evaluation must be thorough and include both electrocardiography and echocardiography. Aortic dilation, dissection, and rupture can develop quickly at any age. The anesthetist should guard against extreme fluctuations in blood pressure and, in particular, sustained elevation in blood pressure, as well as avoid sudden elevations in myocardial contractility because of the fragility of the patient’s aorta. Administration of a β-blocking medication is useful in managing the patient’s blood pressure.
The patient with Marfan syndrome is prone to valvular heart disease. Prophylactic antibiotic coverage is needed for any procedure that may put the patient at risk for development of bacteremia. This is especially true with regard to any dental procedures or surgical interventions.
The patient should be monitored invasively throughout the perioperative period, especially during longer, more intricate surgical procedures. The monitoring devices should include an arterial pressure catheter and a transesophageal echocardiograph, where available.
A patient with Marfan syndrome has loose joint ligaments and is prone to frequent joint dislocations. Of particular interest to the anesthetist is the frequency and relative ease with which the temporomandibular joint may dislocate. Joint laxity also affects the cervical spine. The patient must be carefully positioned to avoid injury to the cervical spine, including joint dislocations and subluxations. As a result, the anesthetist should anticipate that the patient will be difficult to intubate.
As mentioned above, hypertension in the patient with Marfan syndrome is particularly dangerous. Additionally, lability of blood pressure can be very detrimental. The periods of intubation and emergence/extubation are extremely stimulating events that are liable to compound the sympathetic stimulation. Adequate pain control is an integral aspect in controlling the blood pressure throughout the course of the anesthesia, from induction through the immediate postoperative period. In addition to pain control, anxiolysis is an important component and will work synergistically with pain control and β-blocking medications to better control the patient’s blood pressure.