MALE GENITAL PROBLEMS
PAINFUL TESTICLE
If a male complains of a painful testicle, examine both testicles. Look for discoloration or swelling. If a testicle has been injured by a blow, provide support with an improvised jockstrap and apply ice packs. If a testicle suddenly becomes painful, particularly in an adolescent, and appears swollen and/or discolored, usually without a penile discharge, it may be twisted, or torsed. Since this usually happens if the testicle rotates inward (toward the midline) (Figure 175), gently see if you can rotate it outward within the scrotum. If this causes a dramatic relief of pain, you may have saved the testicle. If the maneuver increases the pain and appears to shorten the “hang” of the testicle, you may be worsening the torsion and might attempt rotating the testicle in the opposite direction.
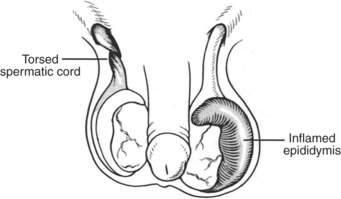
Figure 175 Rotation of the right testicle in a torsion; an inflamed epididymis of the left testicle.
If a testicle is swollen and the victim complains of pain or burning on urination, he may suffer from an infection or inflammation of the epididymis, which is part of the sperm-collection pathway (Figure 175). Other symptoms include lower abdominal, flank, or groin pain. If the case is severe, the victim may suffer fever, chills, nausea, and muscle aches. This should be treated with doxycycline (100 mg twice a day), tetracycline (500 mg four times a day), levofloxacin (250 mg daily), norfloxacin (400 mg twice a day), or trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (one double-strength tablet twice a day) for 10 days.
PENILE DISCHARGE
If a male complains of a discharge from his penis, particularly if it follows sexual intercourse by a few days and is yellow or greenish in color, you must suspect gonorrhea. In this case, it is safest to treat the victim for both gonorrhea and a chlamydial infection. If more than 24 hours will pass before a doctor can be reached, start the victim on tetracycline 500 mg four times a day or doxycycline 100 mg two times a day for 10 days (to treat Chlamydia). Azithromycin 1 g in a single dose is also effective against chlamydial infection. To treat the gonorrhea, administer cefixime 400 mg orally as a single dose. Alternative single-dose therapies for gonorrhea are cefpodoxime 200 mg, cefuroxime 1000 mg, ciprofloxacin 500 mg, ofloxacin 400 mg, azithromycin 2 g, and norfloxacin 800 mg. To treat gonorrhea and chlamydial infection at the same time (the two germs often “travel” together), you can use the one-dose azithromycin therapy. Syphilis may also have been transmitted, so the victim should be tested on return to civilization, even if the victim was treated with a 2 g dose of azithromycin, since there is occasionally resistance of the causative spirochete (Treponema pallidum) to azithromycin.