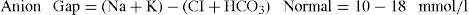1.9 Making ABG interpretation easy
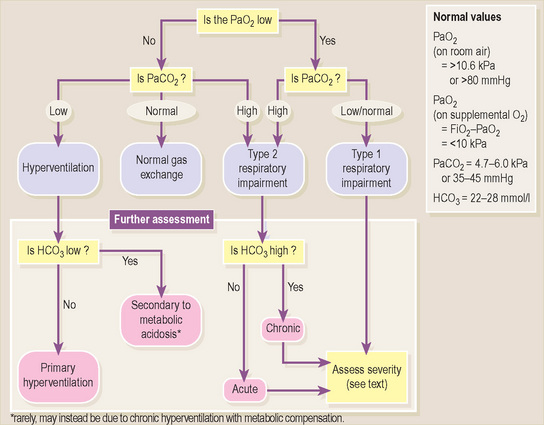
Assessing pulmonary gas exchange
• If there is type 2 respiratory impairment, establish whether it is chronic or acute, then assess severity of hypercapnia and hypoxaemia (boxes 1 & 2)
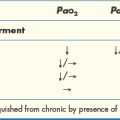
| PaO2 | SaO2 | |
| Mild | 8–10.6 kPa | 90–94% |
| 60–79 mmHg | ||
| Moderate | 5.3–7.9 kPa | 75–89% |
| 40–59 mmHg | ||
| Severe | < 5.3 kPa | < 75% |
| < 40 mmHg | ||
| or: High FiO2 requirements to maintain adequate Pao2 |
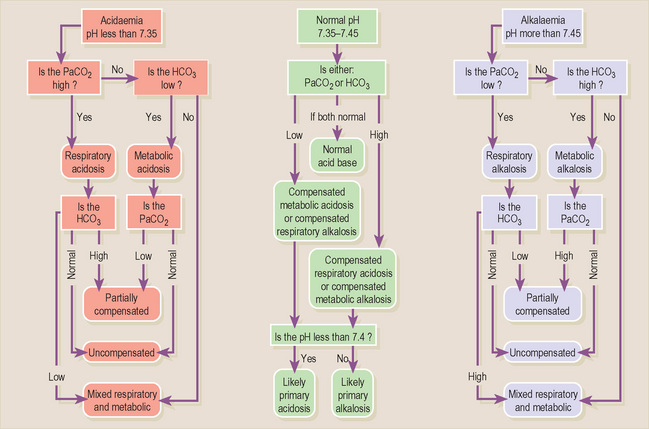
Interpreting acid-base status
• If the patient has a metabolic acidosis, calculate the anion gap to narrow down the differential diagnosis.
• If the precise acid-base derangement is not immediately clear (e.g. middle column) then remember the following points: