15 Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
Definition of magnetic resonance imaging
| A non-invasive technique that uses radio-frequency radiation in the presence of a powerful magnetic field to produce high-quality images of the body in any plane |
| Acquisitions (Number of Excitations, Signal Averages) | The gathering of enough information to spatially encode one complete data set |
| Dephasing | When the RF pulse is switched off, the spinning protons go out of phase resulting in a reduction in the received signal |
| Echo Time (TE) | |
| Flip Angle (α) | The degree by which the proton is tipped in relation to the main magnetic field when a RF pulse is applied to it |
| Fourier Transform | |
| Gradient Echo | |
| Image Space | An MRI image |
| Inversion Recovery (IR) | |
| k-space | |
| Larmor Equation | At a given field strength, the nuclei of different elements will precess at different frequencies, the equation is used to calculate the frequency of the RF pulse |
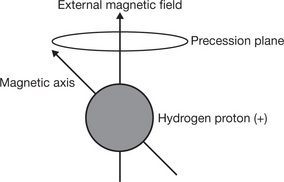
| Larmor Frequency | The rate at which the protons spin when a magnetic field is applied |
| Magnetic Field Gradient | The loss or increase of magnetic strength over distance controlled by the electrical current passing through the coil |
| Noise | Unwanted electrical signals causing grain on the image |
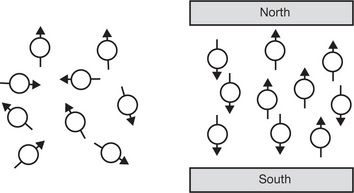
| Precession | Is the circular movement of the magnetic axis of a spinning proton which is prescribed when an external magnetic field is applied to the proton |
| Pulse Sequence | The bursts of electromagnetic energy produced by the radio-frequency coils |
| Radio-frequency (RF) Pulse | A burst of electromagnetic energy at right angles to the magnetic field |
| Relaxation Time | The time taken for the spinning protons to release the energy obtained and return to their original state |
| Repetition Time (TR) | The time between the beginning of one radio-frequency pulse sequence to the start of the next, e.g. 300 ms or 500 ms at 1.5 Tesla |
| Resonance | When an object (a proton) responds to an alternating force (a radio-frequency signal) causing movement |
| Saturated Recovery (SR) | |
| Saturation | The maximum degree of magnetisation that can be achieved in a substance |
| Signal to Noise Ratio | Image quality = Signal (information required from image)/Noise (unwanted information on an image) |
| Can be improved by: | |
| Spatial Encoding | The prediction of the strength of the magnetic field and the movement of the protons at a set point along a gradient |
| Spin Echo (SE) | |
| Spin Polarisation | |
| T1 Relaxation Time | |
| T2 Relaxation Time | |
| Tesla |
| Cryocooler | A closed container: |
| Cryostat | A container for: |
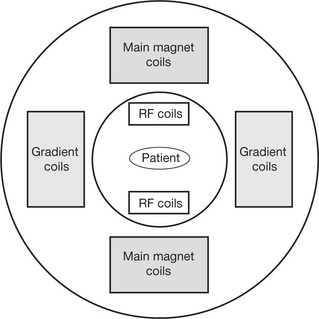
| Gradient Coils (Secondary Magnetic Coils) | Are magnetic coils that are designed to increase or decrease the strength of the main magnetic field |
| Magnets | Produce the main magnetic field
Magnets have to have strength and straight, parallel lines of force in the iso centre |
| Phased Array Coils | |
| Radio-frequency (RF) Coils | |
| Solenoid Technology (ST) Coils | A type of open radio-frequency coil that encloses the area of interest, e.g. a neck coil giving: |
| Surface Coils | Small radio-frequency coils positioned close to the area of interest |
Basic principles of image recording
| Hydrogen | |
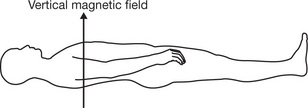
| Strong Magnetic Field Applied to the Patient | |
| Gradient Coils | Determine the plane to be recorded |
| Pulses of Radio Waves | |
| Radio-frequency Coils | |
| Scanning | |
| Image | |
| Contrast Agents | Examples |
| Advantages of MRI | |
| Disadvantages of MRI
Are usually contraindicated due to the potential movement of the object or the heating of the metal by induction, but note that titanium is not affected by the magnetic field |
| Cylindrical System with Improved Solenoid Technology (Philips) | |
| Diffusion Weighted Imaging (DWI) | |
| Functional MRI (Echo Planar Imaging EPI) | |
| Example applications | |
| Magnetic Resonance Angiography | |
| MR Guided Therapy | Using MRI to assist with, e.g. |
| MRI PAT (Parallel Acquisition Techniques) | |
| Open Magnetic Resonance Imaging | |
| Perfusion MRI | |
| Three Dimensional Imaging |
| Holmes J E, Bydder G M 2005 MR imaging with ultrashort TE (UTE) pulse sequences: basic principles. Synergy, January | |
| Hussain Z, Roberts N, Whitehouse G 1995 The application of T1 and T2 and proton density measurements to optimise detection of hepatic metastases using MRI. Radiography Today 61(695):April | |
| Jones T 1998 Gradient echo pulse sequences decoded. Synergy, September | |
| Radiography Technical Support 2006 Solenoid technology improving imaging with open magnets. Synergy, November | |
| Talbot J 2000 MRI artefacts: the good, the bad and the ugly. Synergy, October | |
| Talbot J 2001 What is noise and why is it a problem? Synergy, January | |
| Weal P, Kilkenny J 2003 The practical applications of parallel imaging techniques using standard radio-frequency coils. Synergy, November | |
| Westbrook C 1998 MR advances – the future. Synergy, February |