CHAPTER 10 LIVER PATHOLOGY
HANDLING OF THE LIVER BIOPSY SPECIMEN
PROLONGED NEONATAL CHOLESTASIS
INTRODUCTION
EXTRAHEPATIC BILIARY ATRESIA
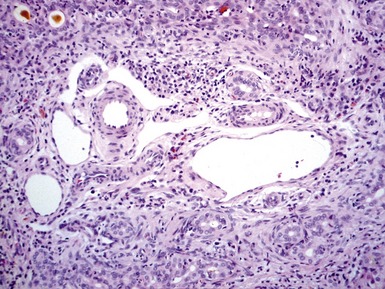
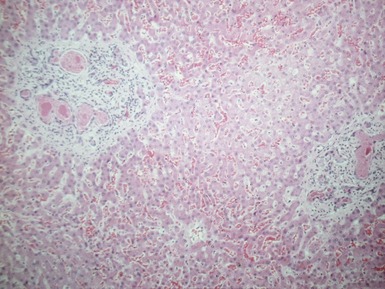
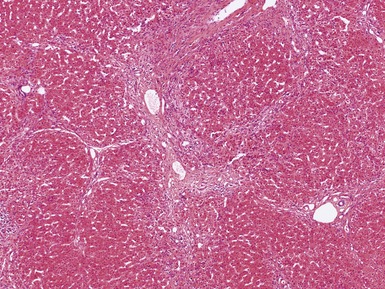
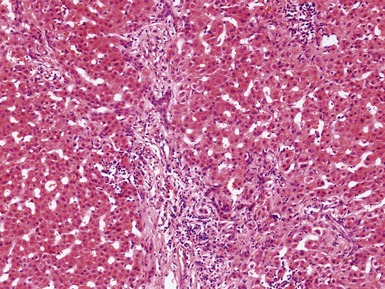
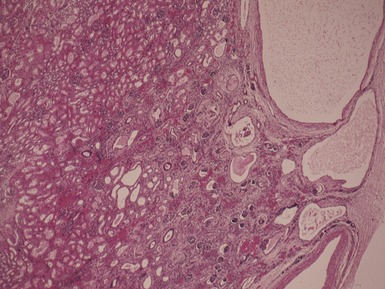
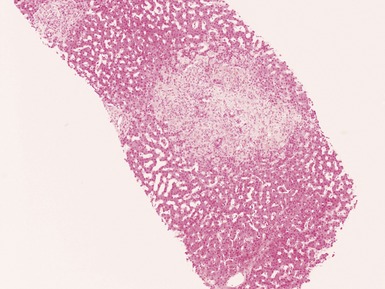
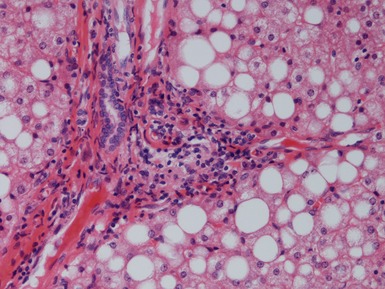
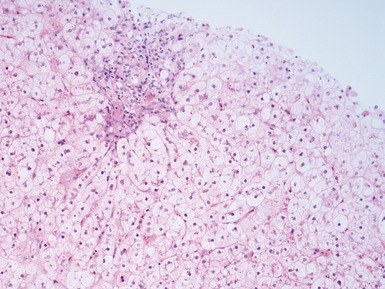
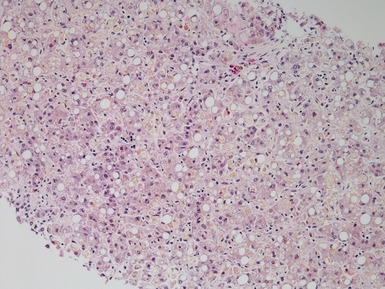
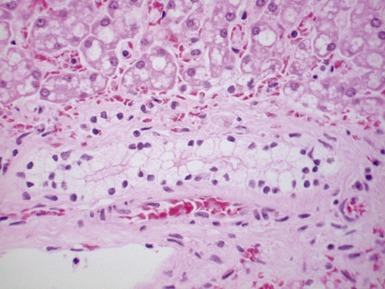
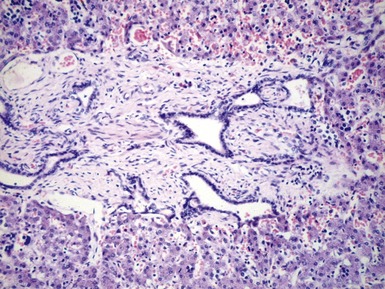
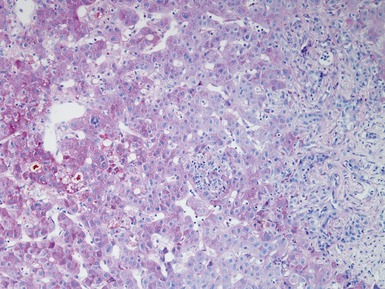
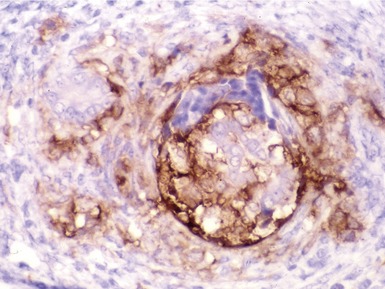
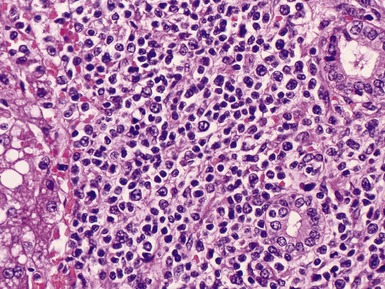
Histopathological features (Figs 10.1–10.3)
Differential diagnoses and pitfalls
CHOLEDEDOCHAL CYST
Clinical features
NEONATAL HEPATITIS
ALPHA-1-ANTITRYPSIN DEFICIENCY
CYSTIC FIBROSIS
PROGRESSIVE FAMILIAL INTRAHEPATIC CHOLESTASIS (PFIC)
BILE ACID SYNTHESIS DEFECTS
LYMPHEDEMA–CHOLESTASIS SYNDROME
ARTHROGRYPOSIS–RENAL DYSFUNCTION–CHOLESTASIS SYNDROME
NIEMANN–PICK DISEASE TYPE C
Clinical features
MITOCHONDRIAL CYTOPATHIES
Genetics
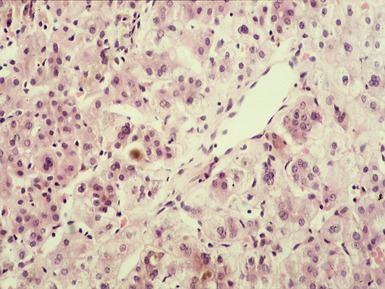
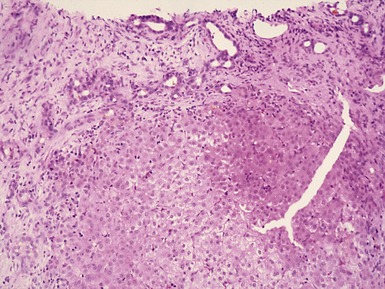
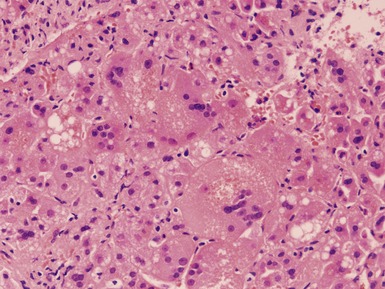
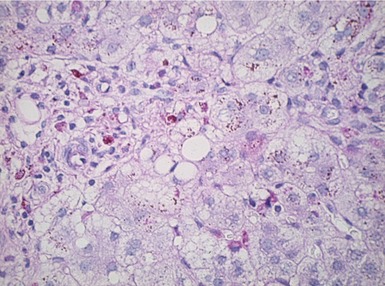
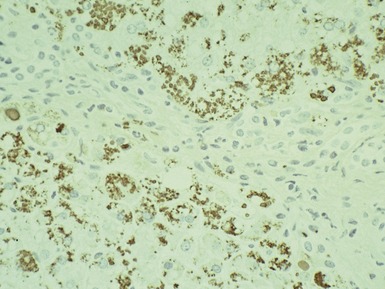
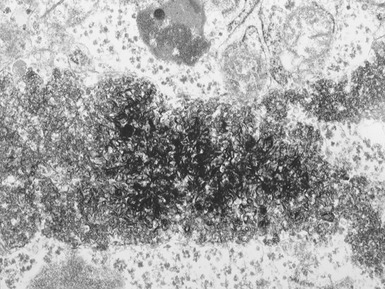
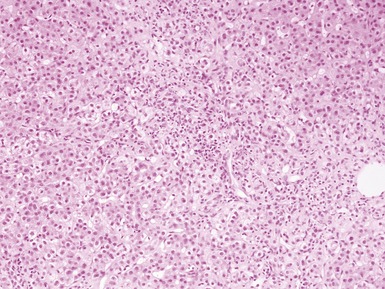
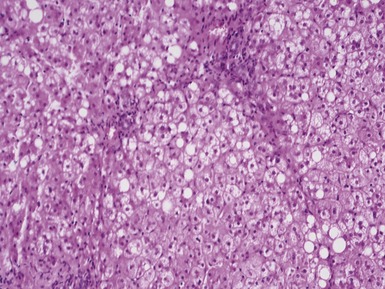
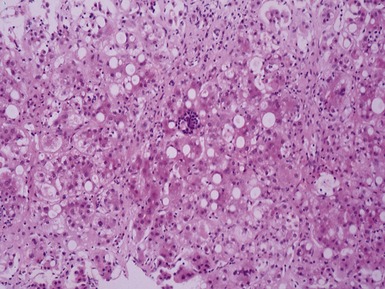
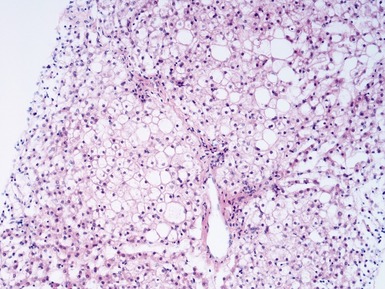
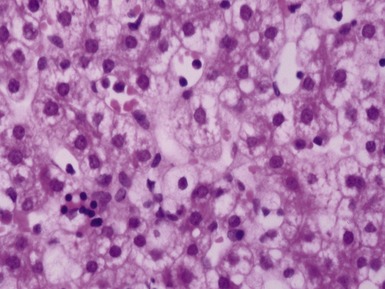
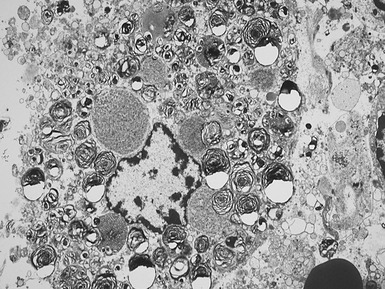
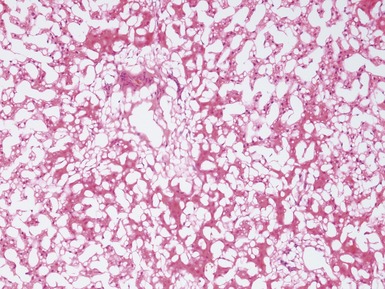
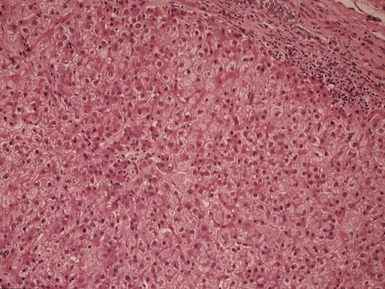
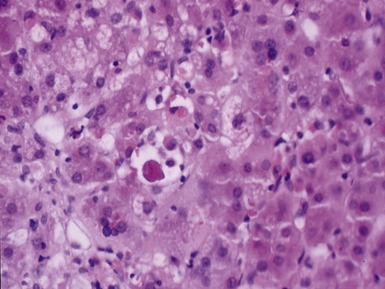
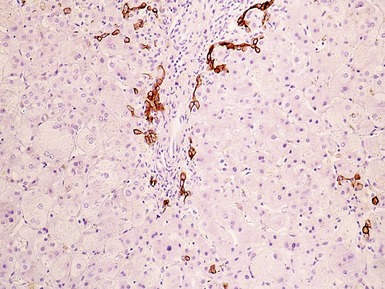
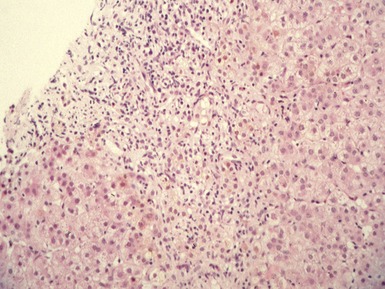
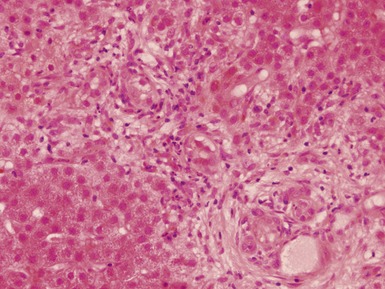
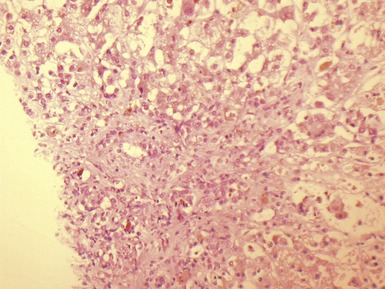
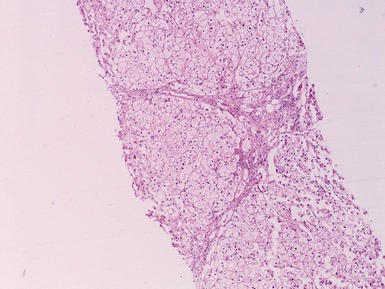
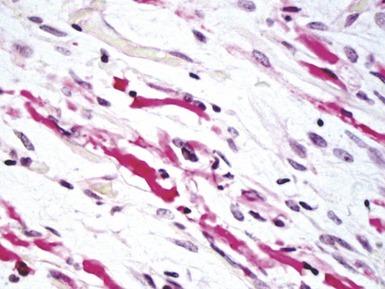
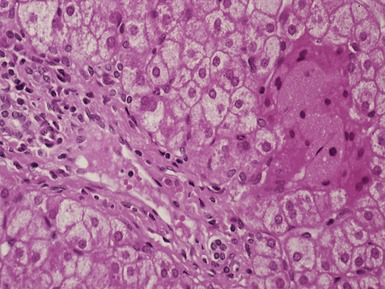
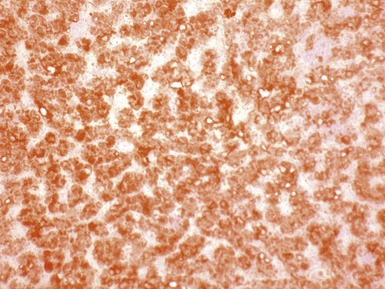
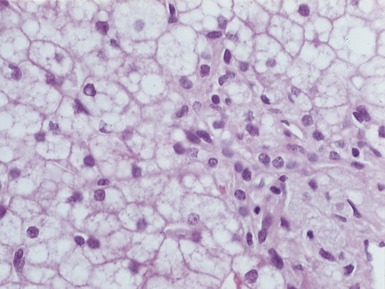
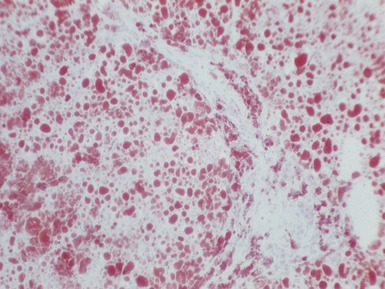
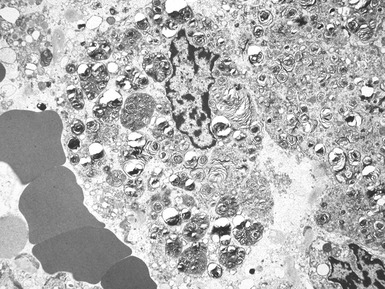
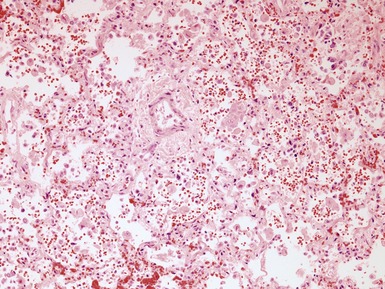
Histopathological features (Figs 10.20–10.25)
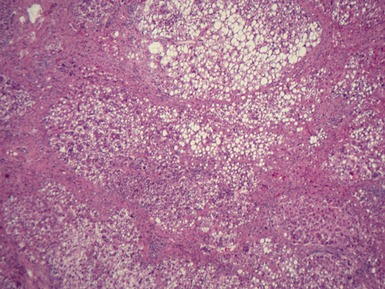
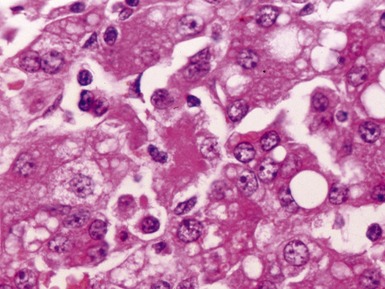
Fig 10.20 Photomicrograph of a liver biopsy from a child with cytochrome oxidase deficiency demonstrating patchy macro- and microvesicular steatosis.
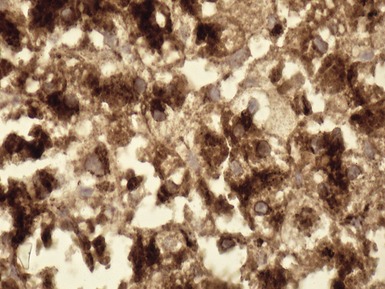
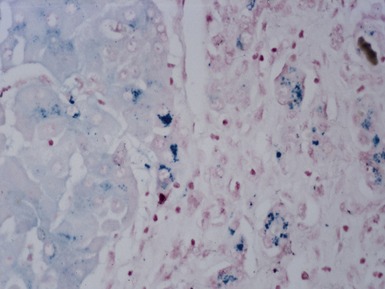
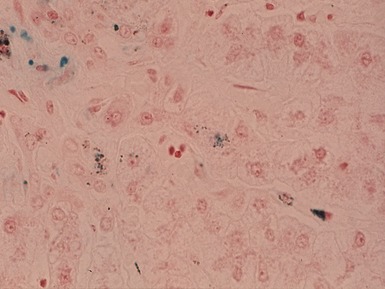
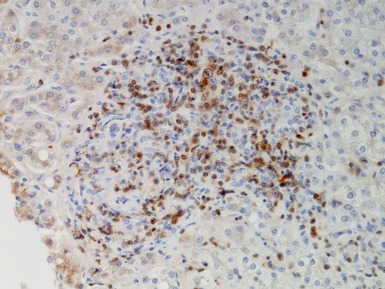
Fig 10.21 Photomicrograph of liver biopsy demonstrating histochemical stain for cytochrome oxidase in which some cells show absent staining in the same case as shown in Fig 10.20.
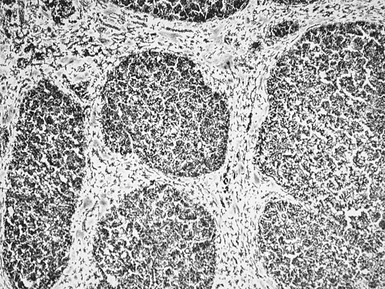
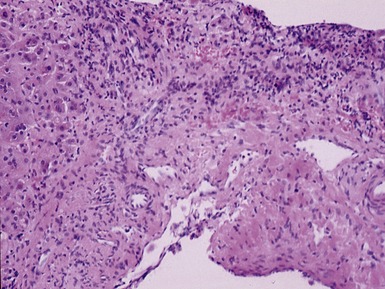
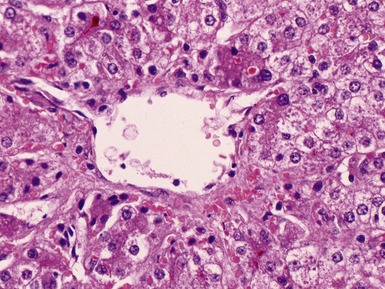
Fig 10.23 Photomicrograph of liver biopsy demonstrating histochemical stain for succinate dehydrogenase in a biopsy from the same patient as shown in Fig 10.22. This biopsy was taken when the child was 10 months old and demonstrates regenerative nodules. The child died shortly afterwards of overwhelming multi-organ failure.
PEROXISOMAL DISORDERS
PAUCITY OF INTRAHEPATIC BILE DUCTS
PRIMARY SCLEROSING CHOLANGITIS
Clinical features
SEPSIS AND TOTAL PARENTERAL NUTRITION-ASSOCIATED LIVER DISEASE
NEONATAL IRON OVERLOAD
INVESTIGATION OF HEPATOMEGALY
CLINICAL FEATURES
GLYCOGEN STORAGE DISEASES
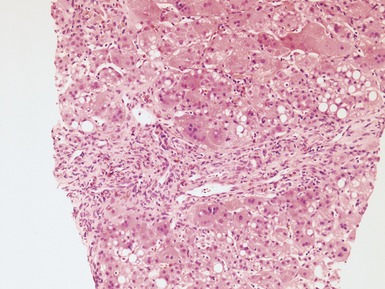
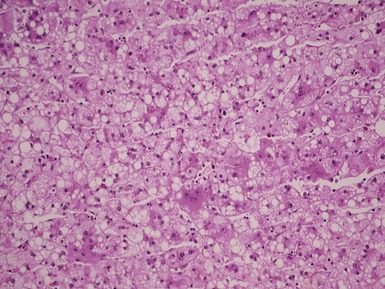
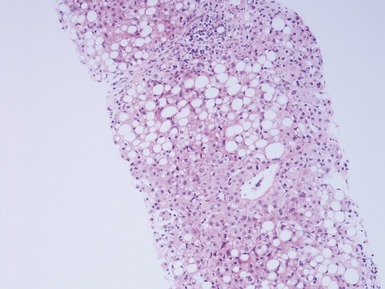
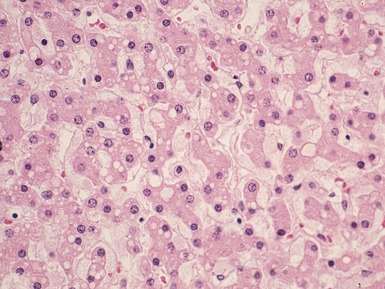
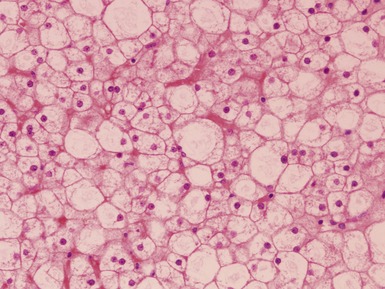
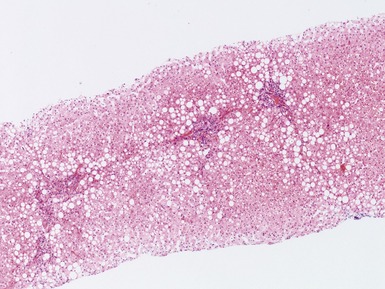
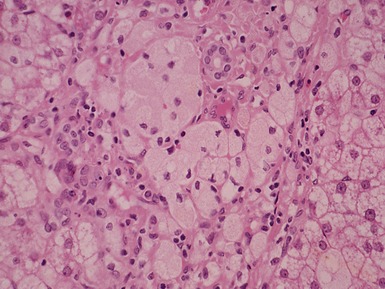
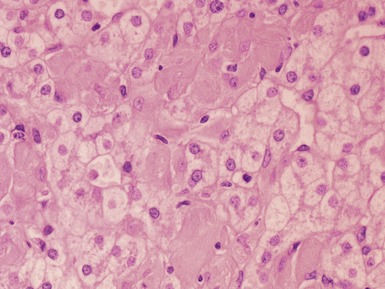
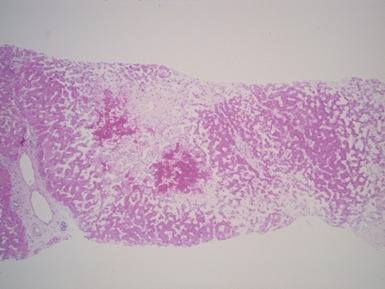
Histopathological features (Figs 10.38–10.42)
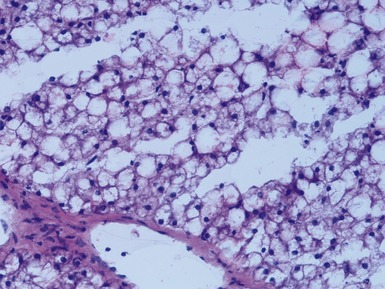
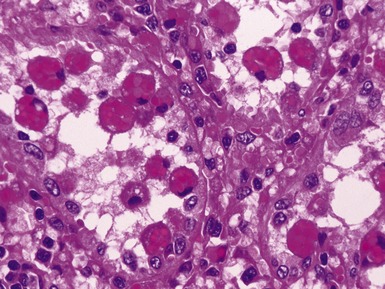
Fig 10.38 Photomicrograph of liver biopsy from a patient with Type I glycogen storage disease demonstrating a combination of enlarged pale hepatocytes together with many hepatocytes containing small fatty vacuoles.
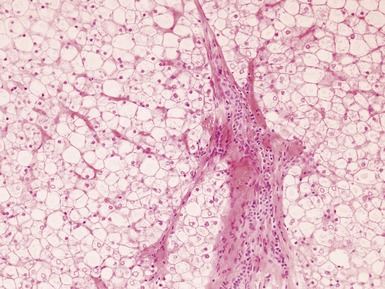
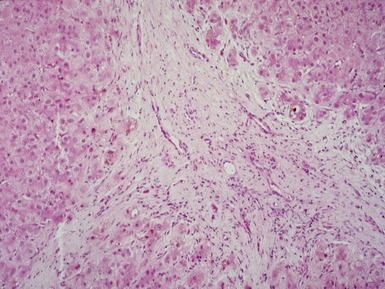
Fig 10.40 Photomicrograph of liver biopsy from the same patient as Fig 10.39 at higher power demonstrating portal fibrosis and enlarged pale hepatocytes.