Chapter 12 Lichenoid skin eruptions
Katta R: Lichen planus, Am Fam Physician 61:3319–3324, 2000.
Carrozzo M: How common is oral lichen planus? Evid Based Dent 9:112–113, 2008.
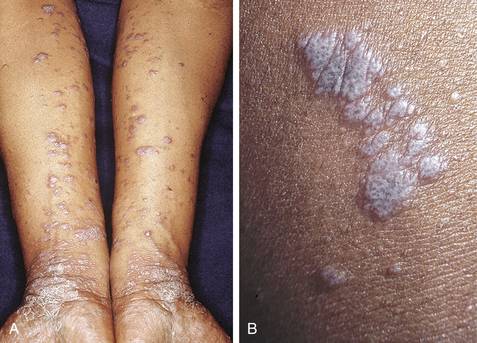
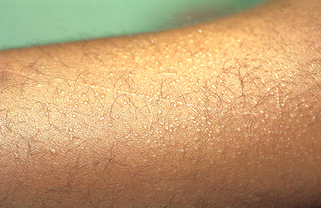
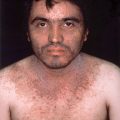
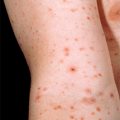
Primary lesions of the skin are 1 to 5 mm, flat-topped, violaceous, shiny papules (Fig. 12-1). While papules are often clustered, individual lesions tend to be discrete, with angulated (polygonal) borders. Wickham’s stria, a lacy white network present on the surface of the papules, is often of great diagnostic value.
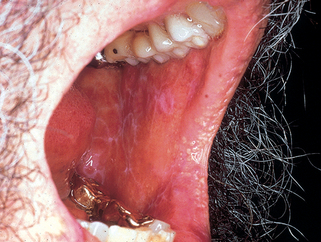
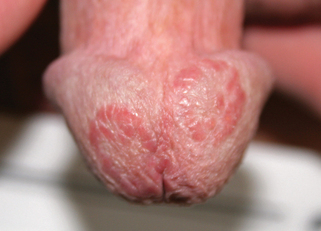
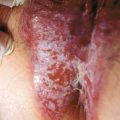
Figure 12-2. Lichen planus, showing reticulated leukoplakia of the buccal mucosa.
(Courtesy of James E. Fitzpatrick, MD.)
Dissemond J: Oral lichen planus: an overview, J Dermatol Treat 15:136–140, 2004.
Bruce AJ, Rogers RS 3rd: Lichenoid contact stomatitis, Arch Dermatol 140:1524–1525, 2004.
Table 12-1. Common Etiologic Drug Classes in LP-like Drug Eruptions
| Antihypertensives Beta-blockers ACE inhibitors Thiazides Furosemide Methyldopa Antimicrobials Acyclovir Isoniazid Tetracyclines Antiinflammatory agents Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs Gold salts Sulfones |
Antimalarials Chloroquine Quinacrine Anticonvulsants Carbamazepine Phenytoin Neurologic agents Benzodiazepines Phenothiazines Lipid-lowering agents Lovastatin Fluvastatin Biologic response modifiers Tumor necrosis factor α antagonists (infliximab, etanercept, adalimumab) Imatinib mesylate |
Miscellaneous Sulfonylureas Chlorpropamide Allopurinol Penicillamine Sildenafil Misoprostol |
Ellgehausen P, Elsner P, Burg G: Drug-induced lichen planus, Clin Dermatol 16:325–332, 1998.
Key Points: Lichen Planus