Lichenoid eruptions
Lichen planus and other disorders with a lichenoid appearance of shiny flat-topped papules are presented here.
Lichen planus
The cause is unknown, but an immune pathogenesis for lichen planus is suspected as T cells infiltrate the skin, immunoglobulin M is found at the dermoepidermal junction, a lichenoid eruption is part of graft-versus-host disease (p. 83) and there is an association with some autoimmune diseases.
Pathology
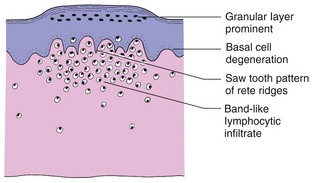
In lichen planus, the granular layer is thickened, basal cells show liquefaction degeneration and lymphocytes infiltrate the upper dermis in a band-like fashion (Fig. 1).
Clinical presentation
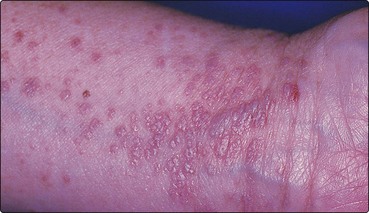
Two-thirds of cases occur in the 30–60-year-old age group. It is uncommon at the extremes of age, and the sex incidence is equal. Lichen planus tends to start on the limbs. It may spread rapidly to become generalized within 4 weeks, but the commoner localized forms progress more slowly. Typical lesions are very itchy flat-topped polygonal papules, a few millimetres in diameter, which may show a surface network of delicate white lines (Wickham’s striae). Initially, the papules are red, but they become violaceous (Fig. 2).
The eruption is symmetrical and affects:
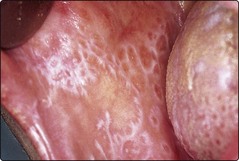
Mucous membrane involvement, especially of the buccal mucosa, occurs in up to two-thirds of cases, and may be present without skin lesions (Fig. 3). Lichen planus also shows the Koebner phenomenon (p. 19) which may explain some linear lesions. Follicular and other variants are found (see below). In most cases, papules flatten after a few months to leave pigmentation, but some become hypertrophic. Half of all patients are clear within 9 months, but 15% have continuing symptoms even after 18 months. Up to 20% have a further attack. Lichen planus may be confused with other conditions, as shown in Table 1.
| Type of lichen planus | Differential diagnosis |
|---|---|
| Generalized | Lichenoid drug eruptionGuttate psoriasisAtypical pityriasis rosea |
| Genital | Psoriasis, scabiesLichen sclerosus |
| Hypertrophic | Lichen simplex |
Variants of lichen planus
A number of variants of lichen planus exist:
 Annular. Found in 10% of cases, commonly on the glans penis.
Annular. Found in 10% of cases, commonly on the glans penis.
 Atrophic. Rare, may be seen with hypertrophic lesions.
Atrophic. Rare, may be seen with hypertrophic lesions.
 Bullous. Blisters appear infrequently in lichen planus.
Bullous. Blisters appear infrequently in lichen planus.
 Follicular. May occur with typical lichen planus; can affect the scalp alone (scarring alopecia; p. 67).
Follicular. May occur with typical lichen planus; can affect the scalp alone (scarring alopecia; p. 67).
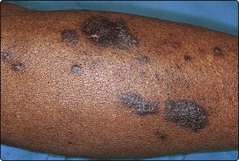
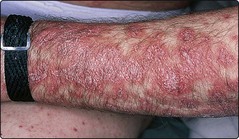
 Hypertrophic. Verrucous plaques affect the lower legs or arms (Fig. 4); may persist for years.
Hypertrophic. Verrucous plaques affect the lower legs or arms (Fig. 4); may persist for years.
 Mucous membrane. Any mucosal surface may be affected, with or without lesions elsewhere. In the mouth, may represent contact allergy to mercury in amalgam fillings (see Fig. 3).
Mucous membrane. Any mucosal surface may be affected, with or without lesions elsewhere. In the mouth, may represent contact allergy to mercury in amalgam fillings (see Fig. 3).
Complications
Lichen sclerosus
Clinical presentation
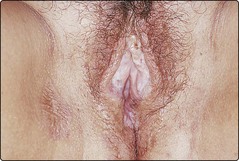
Lichen sclerosus occurs 10 times more frequently in women. It is commonest in middle age, although it may develop in childhood (with a better prognosis). Genital lesions are almost invariable, but involvement of the trunk or arms is seen. Individual lesions are a few millimetres in diameter, porcelain white and slightly atrophic, and may aggregate into wrinkled plaques (Fig. 5). Hyperkeratosis, telangiectasia, purpura and even blistering occur. Vulval and perianal lesions cause itching and soreness. Involvement in the male results in urethral stricture and phimosis (balanitis xerotica obliterans). Occasionally, lesions are found in the mouth. Lichen sclerosus is chronic and usually permanent in adults. Spontaneous resolution is most likely at puberty in childhood cases.
Differential diagnosis
Female genital involvement may resemble lichen simplex chronicus (p. 39), Bowen’s disease (p. 104) and extramammary Paget’s disease. Male genital lesions mimic lichen planus, psoriasis and some rare inflammatory and premalignant forms of balanitis (p. 121).
Lichen nitidus
Clinical presentation and management
The eruption is asymptomatic, often noticed by chance, and usually occurs in children or young adults. Uniform pinhead-sized papules, which may be grouped, are seen on the forearms, penis, abdomen and buttocks. The main differential diagnosis is lichen planus (with which it may coexist) and keratosis pilaris (p. 90).
Treatment is usually unnecessary. Lichen nitidus may resolve in weeks or persist indefinitely.
Lichen planus-like drug eruption
An eruption resembling lichen planus can follow the ingestion of several drugs.
Clinical presentation
A lichen planus-like rash has been recognized with gold and mepacrine therapy for many years. The eruption, which can be severe, is often more ‘psoriasiform’ and hyperpigmented than true lichen planus (Fig. 6) and, on histology, shows a greater number of eosinophils. Resolution after withdrawal of the drug is often slow. Table 2 lists some of the drugs responsible.
| Type of agent | Drug |
|---|---|
| Antiarthritic | Gold, penicillamine, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs |
| Antibiotic | Streptomycin, tetracyclines |
| Antimalarial | Chloroquine, mepacrine, quinine |
| Antituberculous | Isoniazid, ethambutol |
| Diuretic | Thiazides, furosemide |
| Antihypertensive | Captopril, enalapril, beta-blockers, amlodipine |
| Antidiabetic | Tolbutamide, chlorpropamide |
| Antipsychotic | Phenothiazines, lithium |
| Statin | Simvastatin, pravastatin |
Lichenoid eruptions
 Lichen planus is a relatively common pruritic papular eruption, which resolves in most cases within 18 months.
Lichen planus is a relatively common pruritic papular eruption, which resolves in most cases within 18 months.
 Lichen planus-like drug eruption resembles lichen planus but is more persistent; it is seen, for example, with gold, chloroquine and thiazides.
Lichen planus-like drug eruption resembles lichen planus but is more persistent; it is seen, for example, with gold, chloroquine and thiazides.
 Lichen nitidus is a rare, asymptomatic eruption of fine monomorphic papules on the abdomen, arms and penis.
Lichen nitidus is a rare, asymptomatic eruption of fine monomorphic papules on the abdomen, arms and penis.
 Lichen sclerosus is most common in women, and frequently affects the genitalia. Vulval shrinkage may occur. Topical steroids are helpful. There is a risk of malignant change.
Lichen sclerosus is most common in women, and frequently affects the genitalia. Vulval shrinkage may occur. Topical steroids are helpful. There is a risk of malignant change.