43
Lichen planus

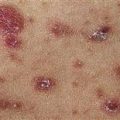
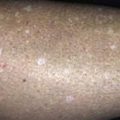
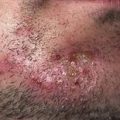
Primary lesion (early): Skin-colored to red, flat-topped papule with angulated border. White, reticulated surface lines are called Wickham striae.
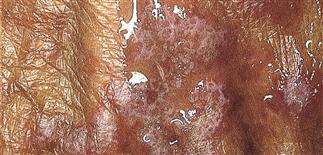
Mineral oil accentuates the reticulated lines. Lesions become purple, thicker, and more numerous with time.
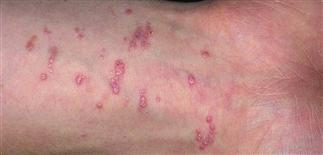
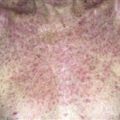
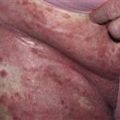
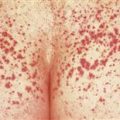
Papules appear most often on the flexor surfaces of wrists and forearms, ankles, and lumbar region. Lesions may be much more extensive.
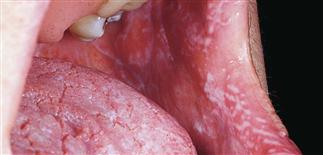
White, lacy pattern on buccal mucosa. Similar lesions appear on the penis and vaginal mucosa.
DESCRIPTION
Chronic, difficult to treat, characteristic eruption of unknown etiology. Skin, scalp hair follicles, mouth, penis, vaginal mucosa, and nails may be affected.
HISTORY
• Uncommon; rare in children. • Itching highly variable. • Family history in 10%. • May last 2 or more years. • May be drug-induced. • Oral lichen planus degenerates to squamous cell carcinoma in 3% of cases.
PHYSICAL FINDINGS
• Many different presentations. • Primary lesion is a flat-topped, red to purple, angulated papule. Highly characteristic lacy white lines (Wickham striae) appear on the surface. Lines are accentuated by mineral oil. • Most common presentation: papules on flexor wrists and forearms, ankles, and lumbar region. • Lesions may develop in areas of injury (Koebner). • Lesions become thick and dark purple. • Very thick lesions on shins are called hypertropic lichen planus.
• Always examine the oral mucosa. Some patients have a lacy white pattern on the buccal mucosa. Similar lesions may appear on the penis and vaginal mucosa. Erosive lesions may appear in mouth and oral mucosa.
TREATMENT
• Group I or II topical steroids: confined to lesions b.i.d. for 2 weeks, then stop for 1 week. • Intralesional triamcinolone acetonide: Kenalog 5–10 mg/mL for thick lesions. • Prednisone: for generalized skin or erosive mucosal involvement; a 4-week course starting at 1 mg/kg q.d. and gradually decrease dosage. • Triamcinolone acetonide in adhesive base (Orabase): apply b.i.d. to oral lesions. • Tacrolimus (Protopic): 0.1% ointment b.i.d. sometimes effective for erosive mucosal lesions. • Sedating antihistamines: for itching (hydroxyzine 10–25 mg every 4 h). • Dapsone, retinoids (Acitretin), ciclosporin: considered for severe, recalcitrant disease. • Azathioprine or hydroxychloroquine: for severe, recalcitrant oral lesions.