Chapter 46 Leukemic and lymphomatous infiltrates of the skin
Cutaneous Lymphoma Foundation. CTCL-MF fast facts. Available at: http://www.clfoundation.org/publications/publications.htm. Accessed December 6, 2006.
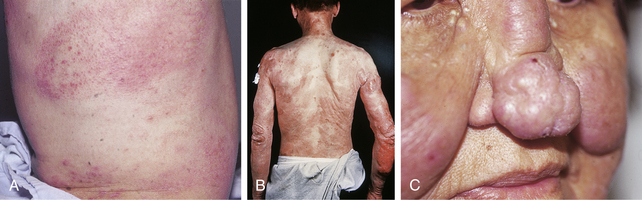
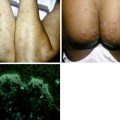
Large-plaque parapsoriasis presents as palm-sized or larger lesions located most frequently on the thighs, buttocks, hips, lower abdomen, and shoulder girdle areas (Fig. 46-2). The lesions may be pink, red-brown, or salmon-colored. They often have fine scale and show epidermal atrophy with cigarette-paper wrinkling. Some patients may have lesions with a netlike or reticular pattern with telangiectasia and fine scale. This clinical type of lesion is referred to as retiform parapsoriasis or poikiloderma atrophicans vasculare. Between 15% and 20% of patients with large-plaque parapsoriasis eventually develop mycosis fungoides.
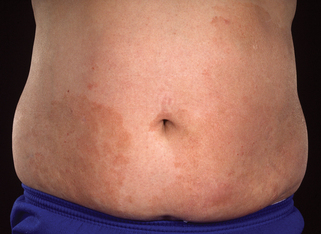
Figure 46-2. Large-plaque parapsoriasis. The lesion was unresponsive to topical treatment.
(Courtesy of the Fitzsimons Army Medical teaching files.)
Sehgal VN, Srivastava G, Aggarwal AK: Parapsoriasis: a complex issue, Skinmed 6:280–286, 2007.
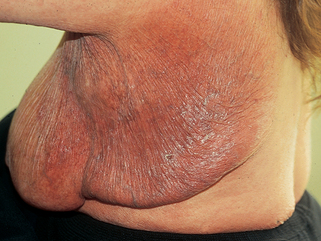
A rare variant of mycosis fungoides is granulomatous slack skin disease (Fig. 46-3). This disorder is characterized by the slow development of lax erythematous skin that eventually develops large pendulous folds of redundant integument. Histologic examination shows a dense atypical granulomatous infiltrate with destruction and phagocytosis of elastic tissue.
National Cancer Institute. Mycosis fungoides and the Sézary syndrome treatment. Available at: http://www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/pdq/treatment/mycosisfungoides/healthprofessional/allpages. Accessed December 6, 2006.
Table 46-2. Cells Marked by CD Antigens
| CD2 | T cells (E rosette receptor) |
| CD3 | T-cell receptor |
| CD4 | Helper T cells |
| CD5 | Mature thymocytes, some B-cell subsets |
| CD7 | T cells, natural killer (NK) cells |
| CD8 | T cells, NK cells |
| CD10 | Pre-B cells, lymphoblastic leukemia cells |
| CD14 | Monocytes |
| CD15 | Reed-Sternberg cells, myeloid cells |
| CD19 | Pan-B cells |
| CD20 | Pan-B cells, dendritic cells |
| CD21 | Receptor for complement 2 and Epstein-Barr virus |
| CD23 | Activated B cells, monocytes, eosinophils, and platelets |
| CD25 | Activated T and B cells, monocytes (interleukin-2 receptor) |
| CD30 | Ki-1–related cells, Reed-Sternberg cells, T-cell NHL |
| CD34 | Lymphoid and myeloid precursor cells |
| CD43 | T cells, myeloid cells |
| CD45 | Leukocytes |
| CD45R | T cells, myeloid cells |
| CD56 | NK cells |
| CD74 | HLA-invariant chain |
| CD75 | Follicular center cells |
CD, Cluster of differentiation; HLA, histocompatibility locus antigen; NHL, non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma.