6 Laser imaging
| Light and the Laser | White light
• Ranges from ultraviolet in the short wave, through visible light, to infrared in the long wavelengths
|
| Laser light | |
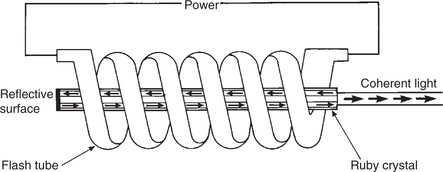
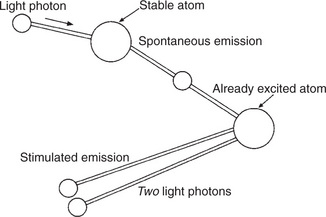
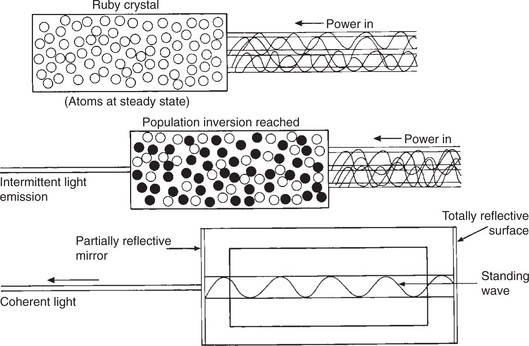
| The First Laser | Pulsed laser In 1960, Theodore Maiman, working at the Hughes Aircraft Electronic Research Laboratory, built the first laser • It was basically a photographer’s electronic flashgun wound around a crystal of synthetic ruby (aluminium oxide mixed with a small amount of chromium)
|
| Operator Keypad | This allows control of the parameters for imaging at the time of the examination These can include: |
| Exposure | The patient is imaged |
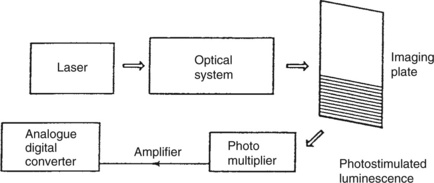
| Memory Store | All the digital image information required for one ‘film’ must be put into the memory store, before the image recording can start |
| An Interface | Transmits the digital information from the memory store to the laser |
| An Acoustic-optical Modulator | Modulates the laser beam in terms of brightness, grey levels, etc. |
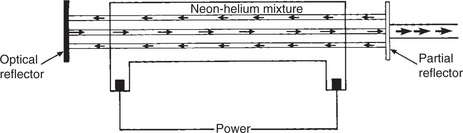
| The Laser |
• Lasers produce coherent beams of parallel light and therefore the scanning optics can be much simpler than if white light is used, which produces a divergent beam
|
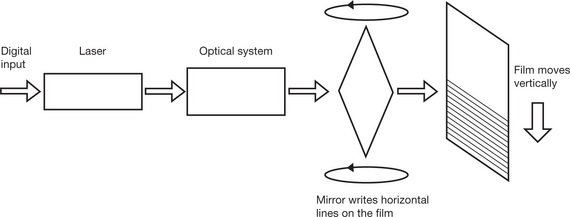
| An Optical System | A lens system is used to focus the laser beam onto a scanner |
| A (Mechanical) Scanner | A very accurate and fast Galvano scanner used to move the laser beam from side to side across the imaging field |
| A Mirror | Horizontal scanning |
| A (Mechanical) Film Transport System | Vertical imaging |
| Imaging | Takes between 8 and 30 seconds |
| Film Characteristics | |
| Note It is important that the correct film is purchased to match the type of laser used to obtain optimum results |
|
| Processing | |
| Digital Input Signal |
It is possible for the imagers to receive input signals at the same time as they are ‘writing’ an image and therefore there is no processing delay |
| Technology is available which utilises direct laser printing to produce an image without the use of processing chemicals | |
| Film Characteristics | |
| Imaging |
• The digital signal from the appropriate modality is fed into solid state laser diodes which then scan the film in a way similar to that of other laser printers
|
| Imaging System Characteristics |
• The laser imager is very susceptible to dust and vibration, particularly when the laser beam transfer is via a mirror
|