CHAPTER 26 Laparoscopic and Open Pyloromyotomy
Step 1: Surgical Anatomy
Step 2: Preoperative Considerations
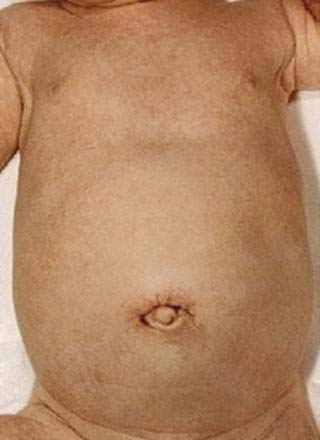
Presentation and Metabolic Abnormalities
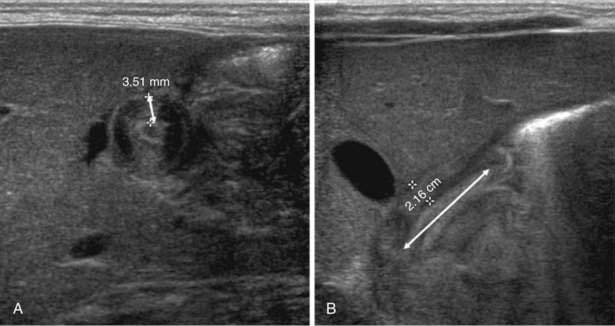
Diagnosis
Preoperative Resuscitation and Preparation
Step 3: Operative Steps
Laparoscopic Pyloromyotomy
Positioning and Preparation
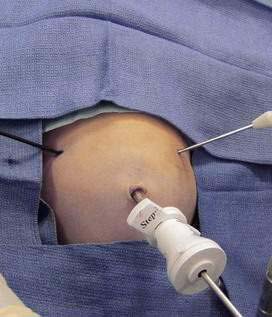
Instrument Placement
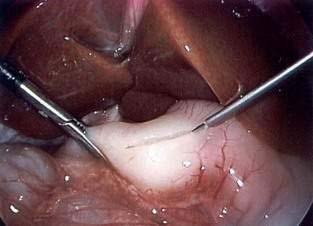
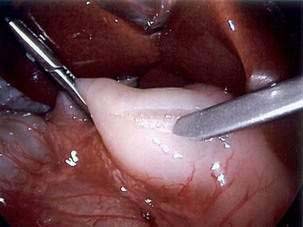
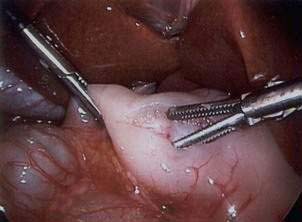
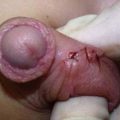
Pyloromyotomy Technique
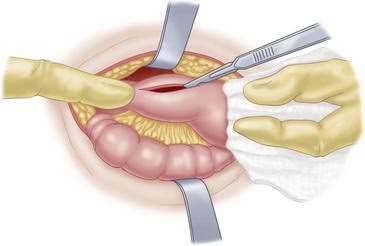
Open Pyloromyotomy
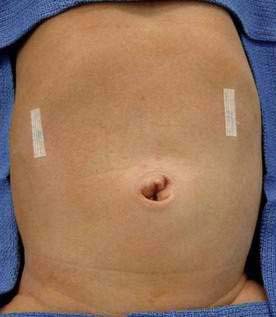
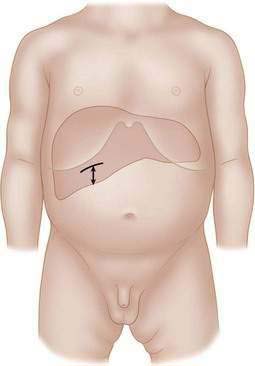
Incisions
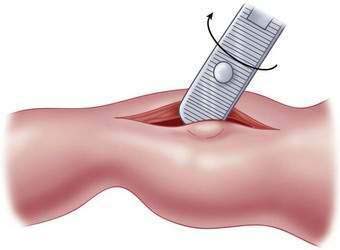
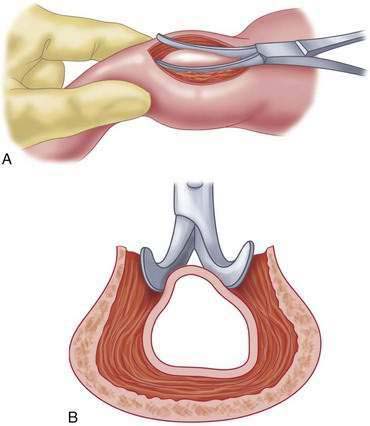
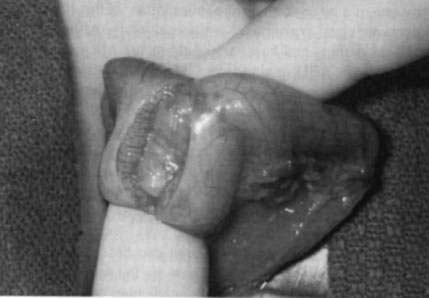
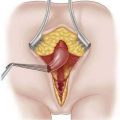
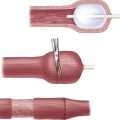
Pyloromyotomy Technique
Step 4: Postoperative Care
Recovery
Feeding Management
Pain Control
Step 5: Pearls and Pitfalls
Blumer RM, Hessel NS, van Baren R, et al. Comparison between umbilical and transverse right upper abdominal incision for pyloromyotomy. J Pediatr Surg. 2004;39:1091-1093.
Kim SS, Lau ST, Lee SL, et al. Pyloromyotomy: a comparison of laparoscopic, circumumbilical, and right upper quadrant operative techniques. J Am Coll Surg. 2005;201:66-70.
Leclair MD, Plattner V, Mirallie E, et al. Laparoscopic pyloromyotomy for pyloric stenosis: a prospective, randomized trial. J Pediatr Surg. 2007;42:692-698.
Ostlie DJ, Woodall CE, Wade KR, et al. An effective pyloromyotomy length in infants undergoing laparoscopic pyloromyotomy. Surgery. 2004;136:827-832.
St. Peter SD, Holcomb GWIII, Calkins CM, et al. Open versus laparoscopic pyloromyotomy for pyloric stenosis: a prospective, randomized trial. Ann Surg. 2006;244:363-370.