Knee and Lower Leg
Robert F. LaPrade, Nicholas I. Kennedy
Regional Anatomy
Osteology
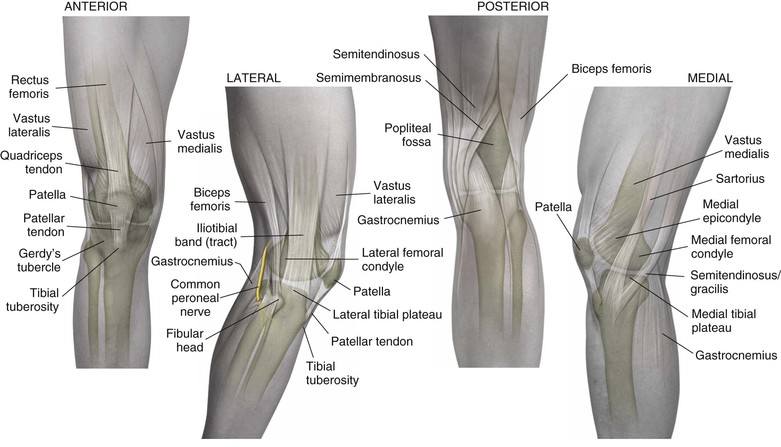
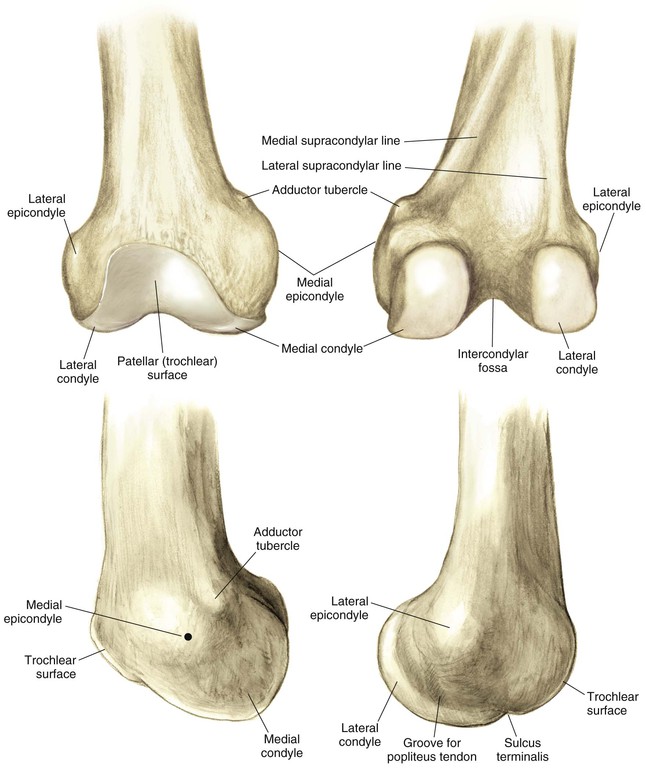
Distal Femur (Fig. 7-1)
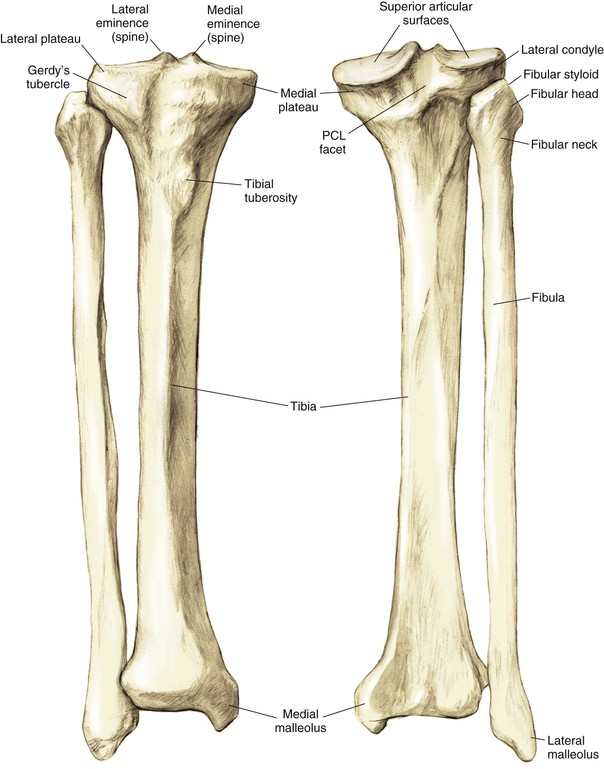
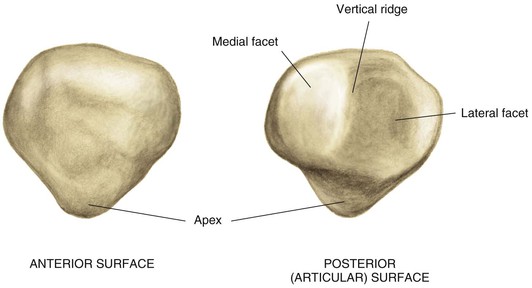
Proximal Tibia (Fig. 7-2)
The tibia is the second longest bone in the body
The plateau areas match the corresponding femoral condyle
• The medial tibial plateau is broad and concave
• The lateral tibial plateau is smaller and convex
The tibial eminences (spines) define the borders of the cruciate ligament insertions
• The ACL lies between the eminences
The tubercles serve as attachments for tendons
• The tibial tubercle (or tuberosity) serves as the patellar tendon attachment
Arthrology
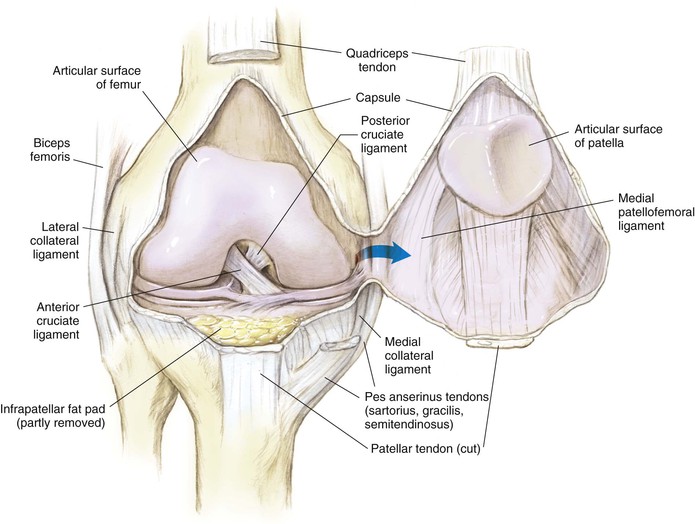
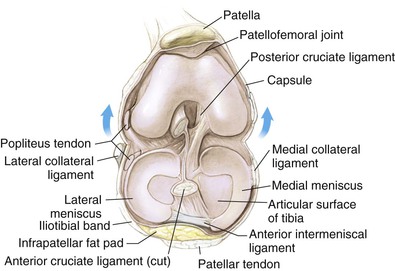
Knee Joint (Figs. 7-4 and 7-5)
The knee joint is the largest joint in the body
The knee joint is a ginglymus (hinge) joint that allows rolling and sliding
• ACL—resists anterior translation
• PCL—resists posterior translation
• MCL—resists valgus displacement
• LCL—resists varus displacement
• Popliteus tendon—resists external rotation
• Posteromedial and posterolateral capsular structures—resist rotation
• Menisci
• Medial—semicircular and broader posteriorly
• Lateral—more circular and covers a larger portion of the articular surface
Muscles
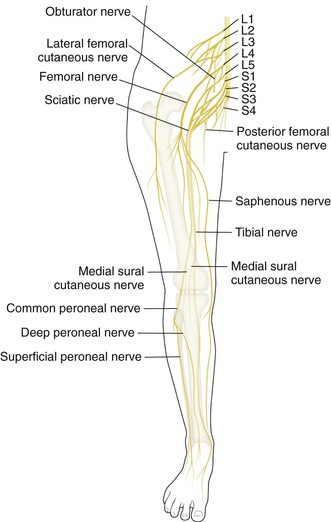
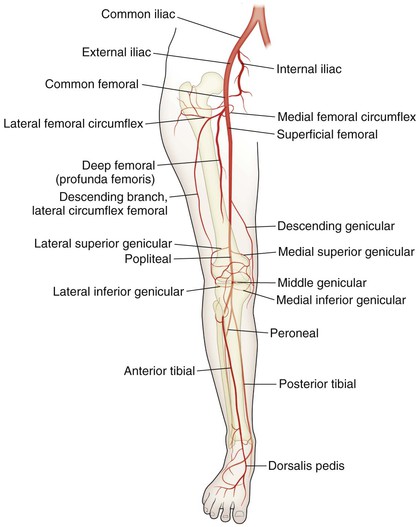
Knee and leg muscles are best considered in groups or compartments (Figs. 7-6 and 7-7; Tables 7-1 and 7-2)
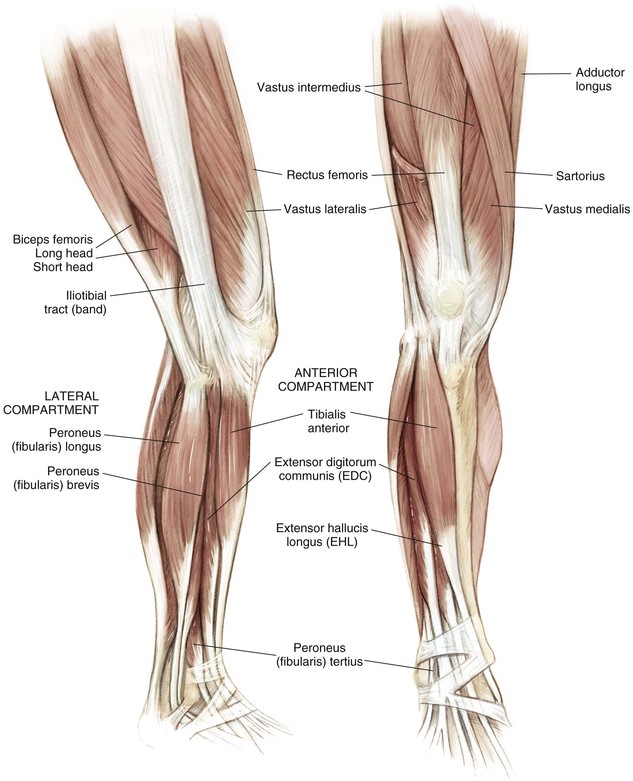
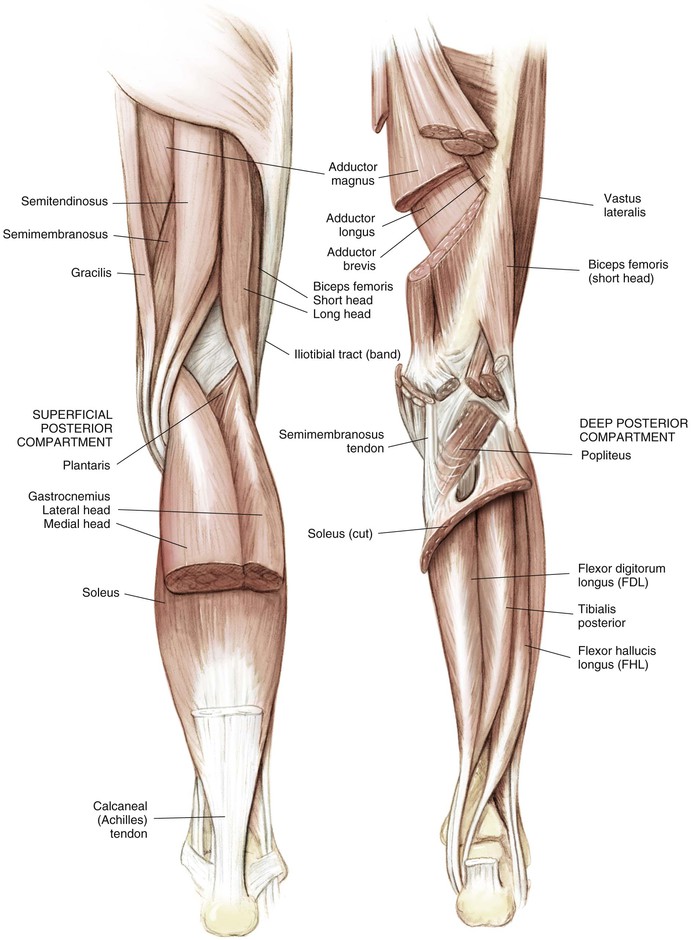
Table 7-1
Muscles of the Thigh
| MUSCLE | ORIGIN | INSERTION | INNERVATION |
| Vastus lateralis | Iliotibial line/greater trochanter/lateral linea aspera | Lateral patella | Femoral |
| Vastus medialis | Iliotibial line/medial linea aspera/supracondylar line | Medial patella | Femoral |
| Vastus intermedius | Proximal anterior femoral shaft | Patella | Femoral |
| Biceps (long head) | Medial ischial tuberosity | Fibular head/lateral tibia | Tibial |
| Biceps (short head) | Lateral linea aspera/lateral intermuscular septum | Fibular styloid/posterolateral joint capsule | Peroneal |
| Semitendinosus | Distal medial ischial tuberosity | Anterior tibial crest | Tibial |
| Semimembranosus | Proximal lateral ischial tuberosity | Oblique popliteal ligament | Tibial |
| Posterior capsule | |||
| Posterior/medial tibia | |||
| Fabella/lateral gastrocnemius tendon | |||
| Medial meniscus |
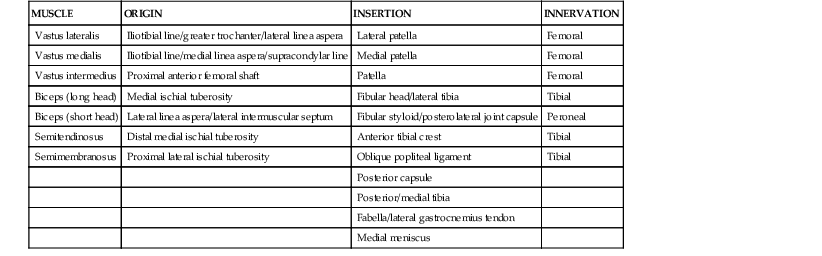
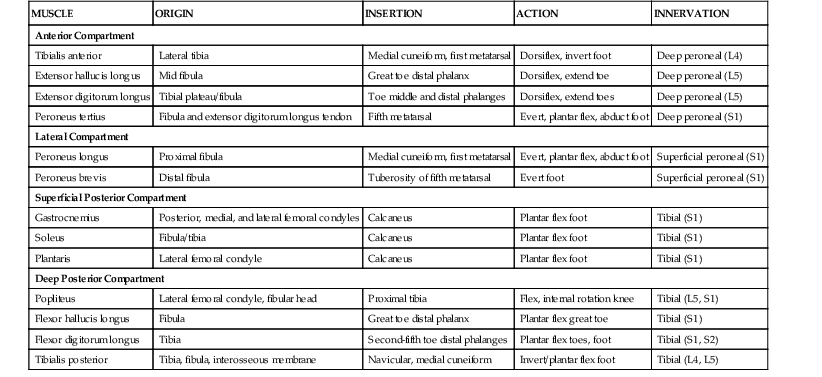
Table 7-2
Muscles of the Leg
| MUSCLE | ORIGIN | INSERTION | ACTION | INNERVATION |
| Anterior Compartment | ||||
| Tibialis anterior | Lateral tibia | Medial cuneiform, first metatarsal | Dorsiflex, invert foot | Deep peroneal (L4) |
| Extensor hallucis longus | Mid fibula | Great toe distal phalanx | Dorsiflex, extend toe | Deep peroneal (L5) |
| Extensor digitorum longus | Tibial plateau/fibula | Toe middle and distal phalanges | Dorsiflex, extend toes | Deep peroneal (L5) |
| Peroneus tertius | Fibula and extensor digitorum longus tendon | Fifth metatarsal | Evert, plantar flex, abduct foot | Deep peroneal (S1) |
| Lateral Compartment | ||||
| Peroneus longus | Proximal fibula | Medial cuneiform, first metatarsal | Evert, plantar flex, abduct foot | Superficial peroneal (S1) |
| Peroneus brevis | Distal fibula | Tuberosity of fifth metatarsal | Evert foot | Superficial peroneal (S1) |
| Superficial Posterior Compartment | ||||
| Gastrocnemius | Posterior, medial, and lateral femoral condyles | Calcaneus | Plantar flex foot | Tibial (S1) |
| Soleus | Fibula/tibia | Calcaneus | Plantar flex foot | Tibial (S1) |
| Plantaris | Lateral femoral condyle | Calcaneus | Plantar flex foot | Tibial (S1) |
| Deep Posterior Compartment | ||||
| Popliteus | Lateral femoral condyle, fibular head | Proximal tibia | Flex, internal rotation knee | Tibial (L5, S1) |
| Flexor hallucis longus | Fibula | Great toe distal phalanx | Plantar flex great toe | Tibial (S1) |
| Flexor digitorum longus | Tibia | Second-fifth toe distal phalanges | Plantar flex toes, foot | Tibial (S1, S2) |
| Tibialis posterior | Tibia, fibula, interosseous membrane | Navicular, medial cuneiform | Invert/plantar flex foot | Tibial (L4, L5) |
Cross-Sectional Anatomy (Fig. 7-10)
Thigh
Anterior Compartment
Vastus medialis, vastus intermedius, vastus lateralis, rectus femoris, and sartorius
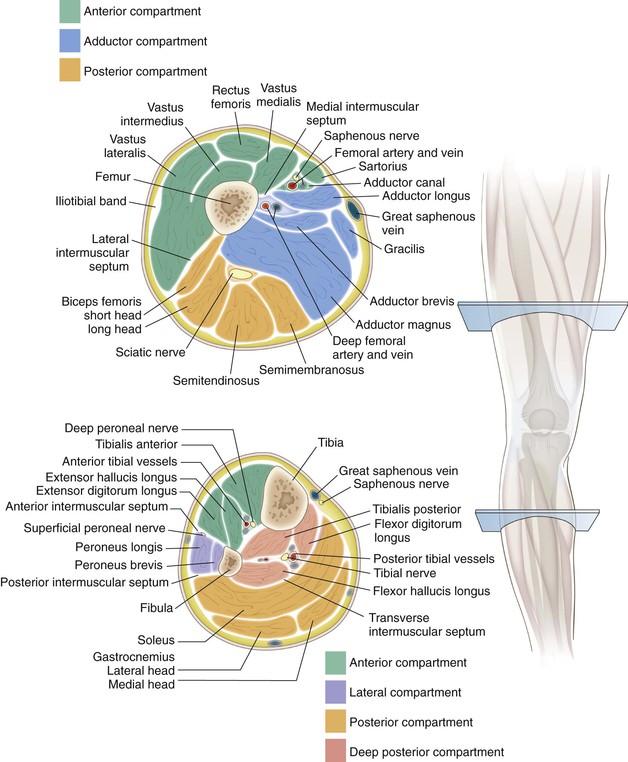
Lower Leg
Anterior Compartment
Deep Posterior Compartment
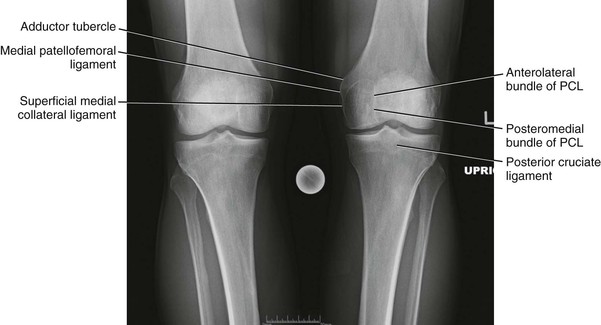
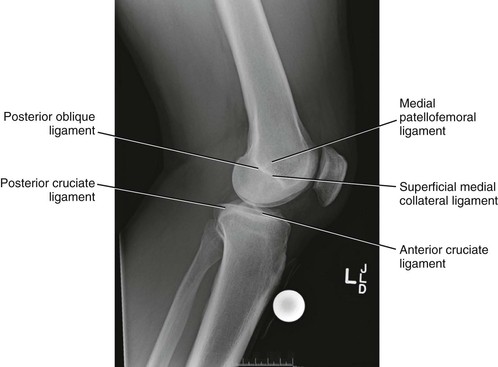
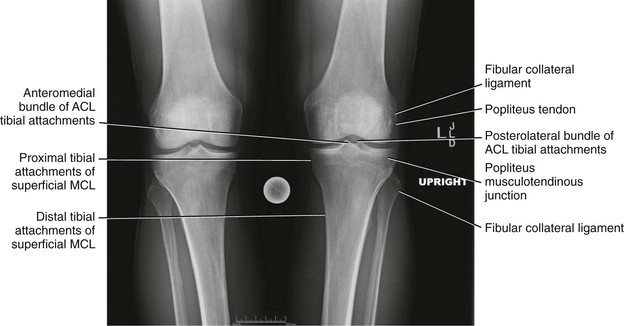
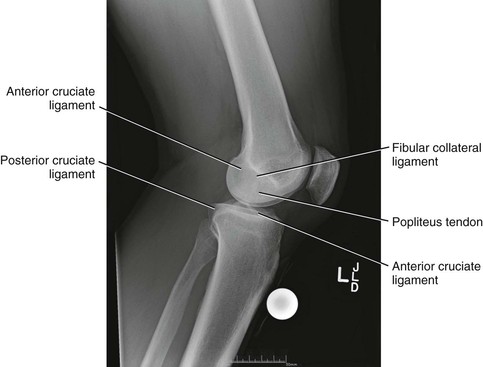
Radiologic Landmarks
(Figs. 7-12 through 7-15)
Surgical Approaches
Anterior Approaches to the Knee
Indications
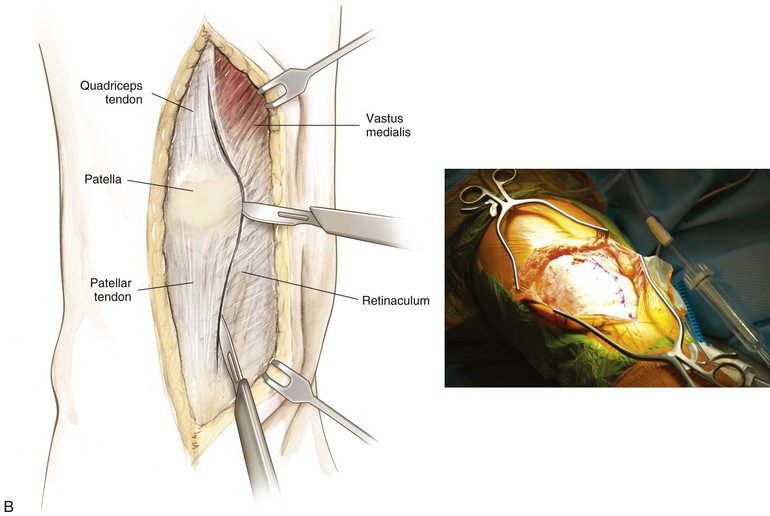
Standard Approach for Total Knee Arthroplasty (Fig. 7-17)
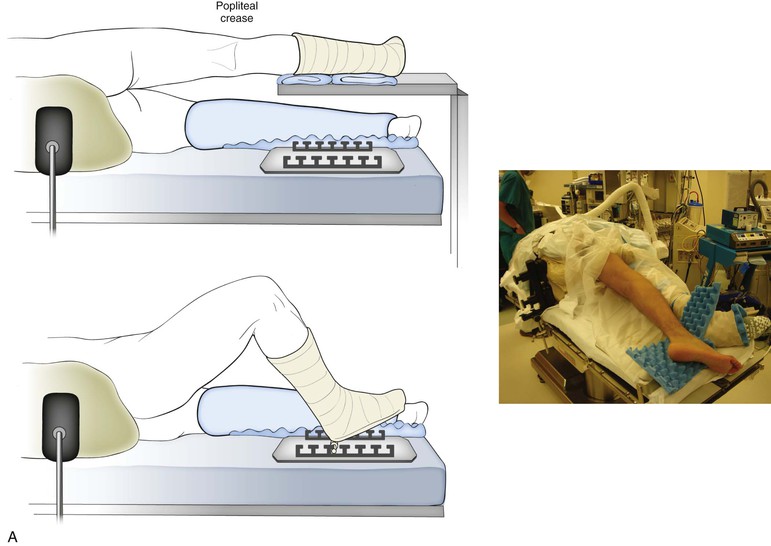
Positioning
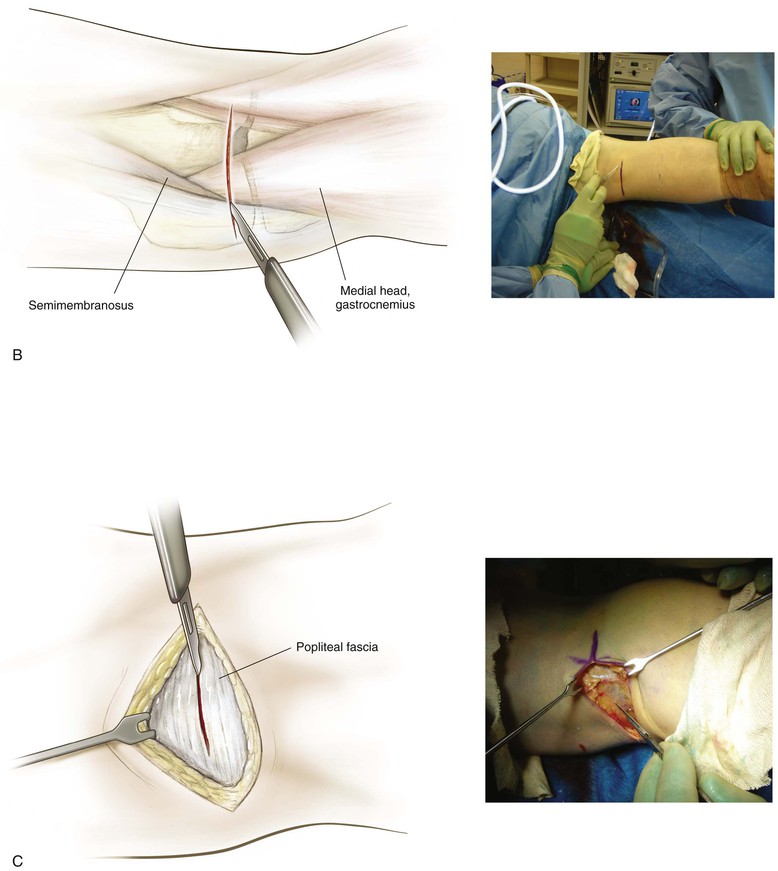
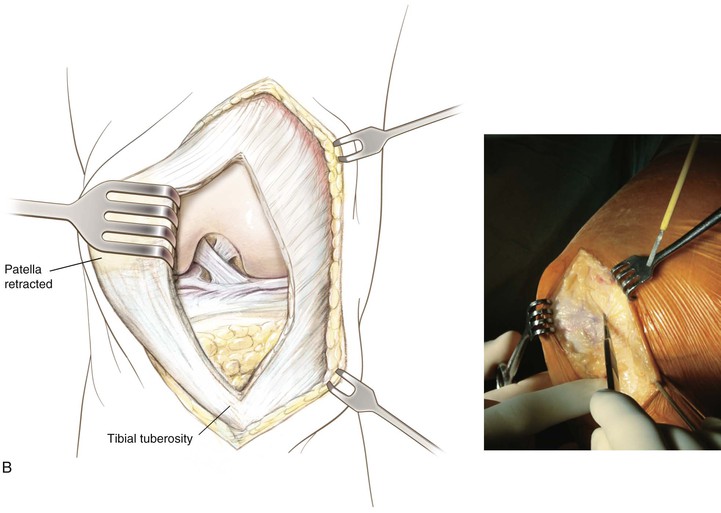
Superficial and Deep Dissection (Fig. 7-17, B and C)
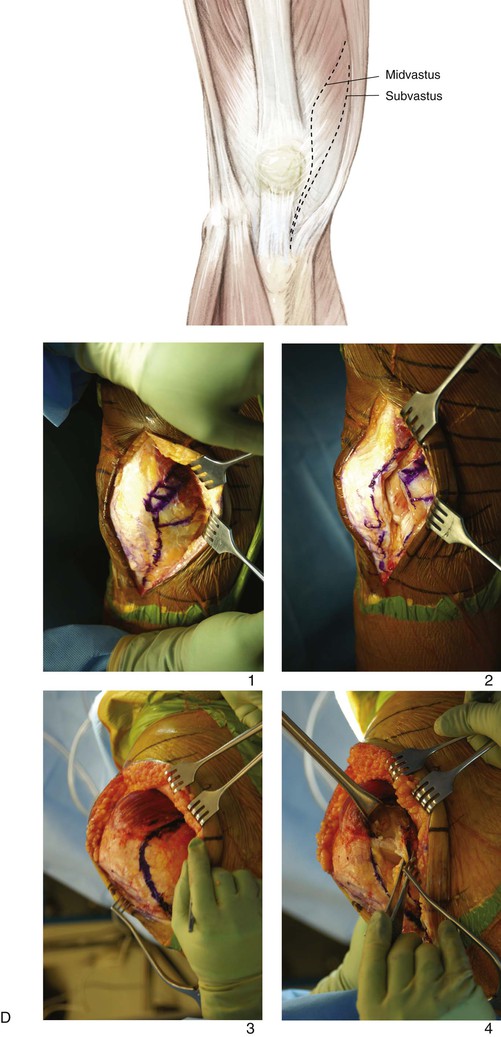
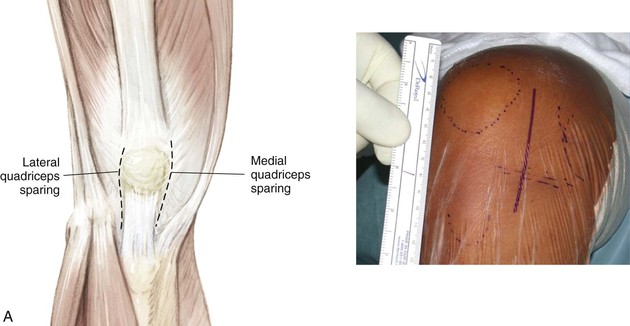
Limited Anterior Incision (Quadriceps Sparing; Fig. 7-18, A)
Positioning
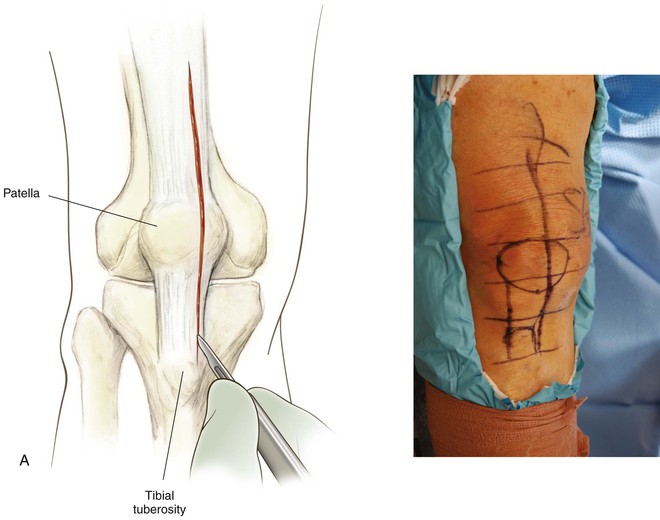
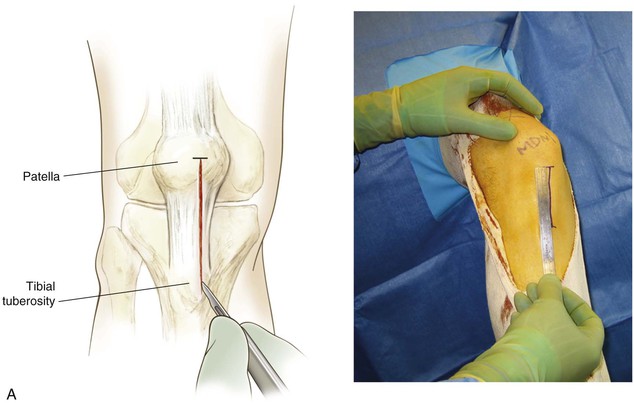
Anterior Approach for Patella Tendon Harvest
Positioning
Commercially available leg holders or positioners may be helpful
The end of the table is dropped to allow the knee to drop into flexion
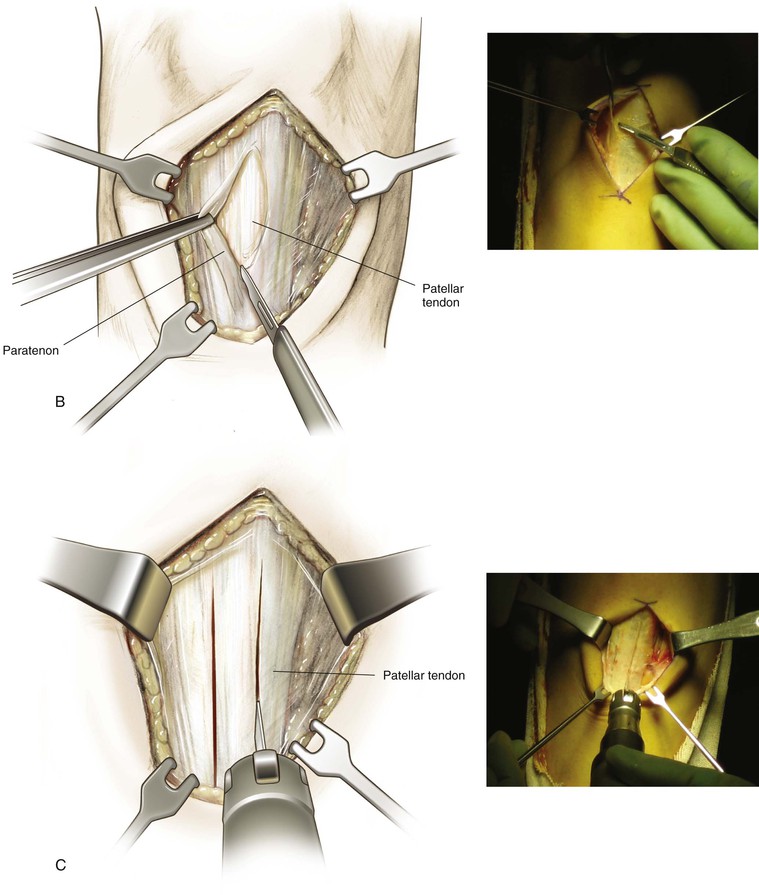
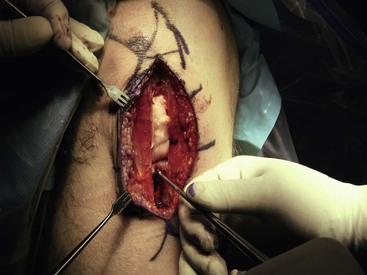
Superficial and Deep Dissection (Fig. 7-21)
The paratenon is carefully dissected off the underlying tendon fibers
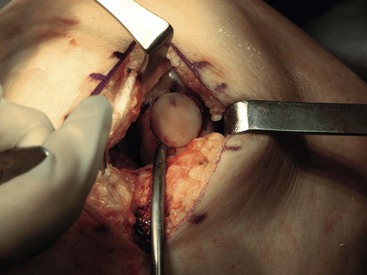
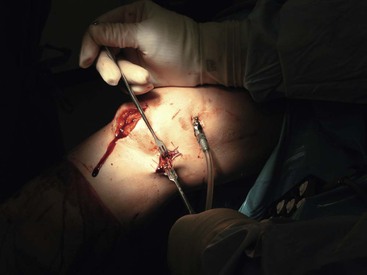
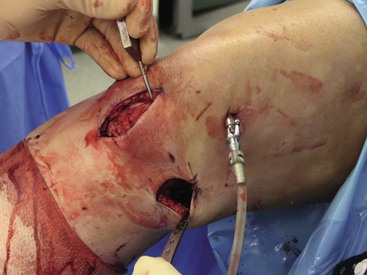
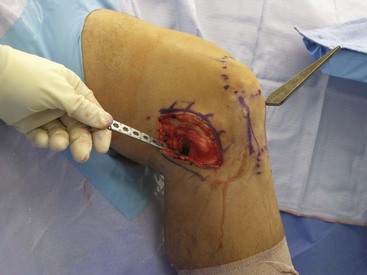
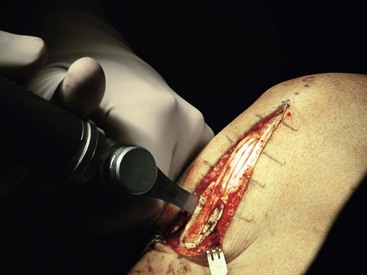
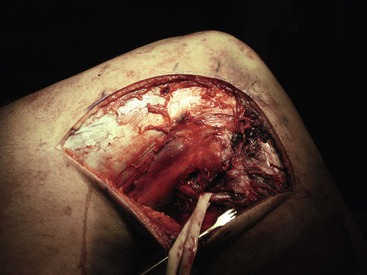
An appropriate graft is harvested with 20 to 25 mm of bone from the patella and the tibial tubercle (Fig. 7-22)
A bone graft is placed into the patellar defect before closure (Fig. 7-23)
Inferomedial Approach for Hamstring Harvest (Video 7-1)
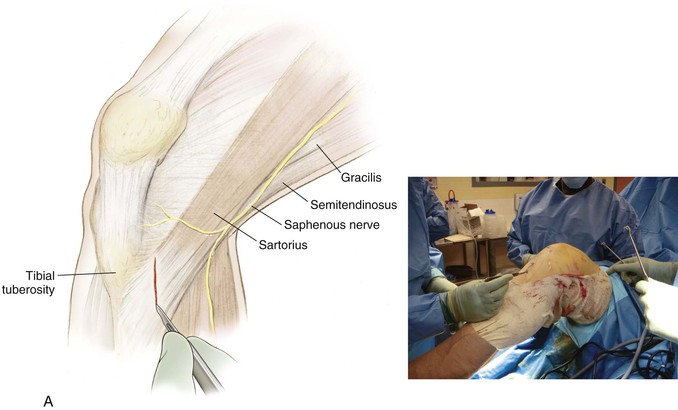
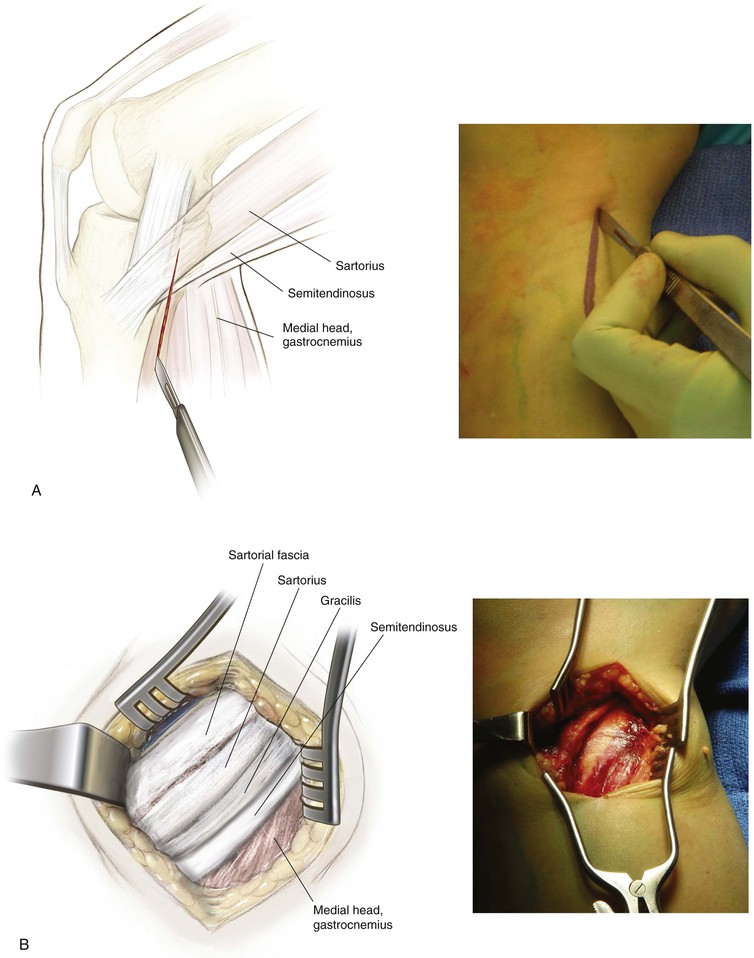
Incision (Fig. 7-24, A)
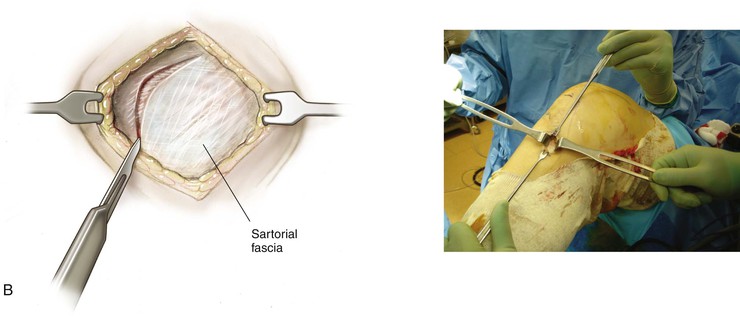
Superficial Dissection (Fig. 7-24, B)
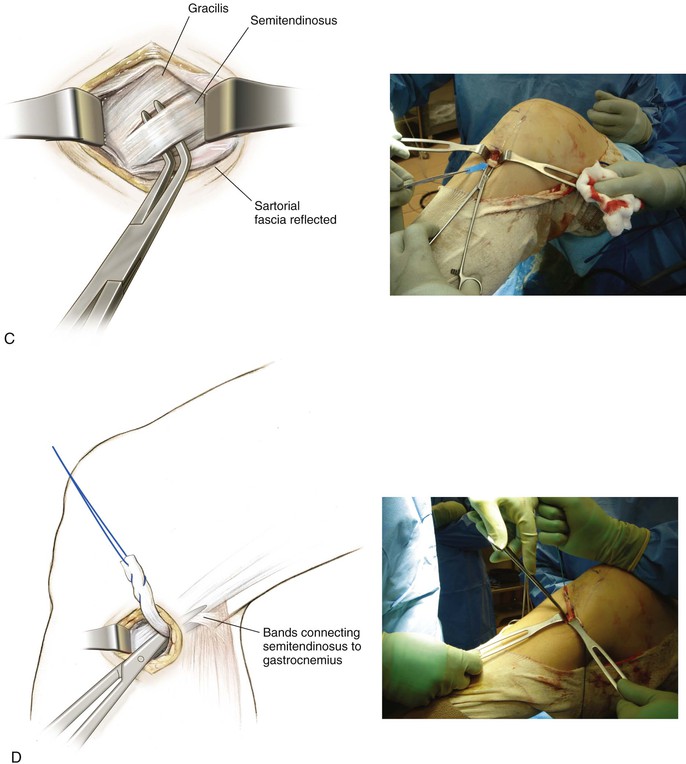
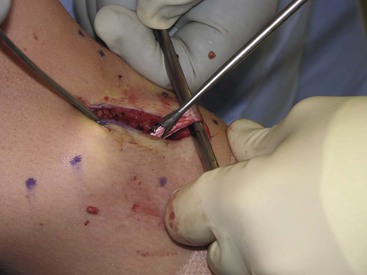
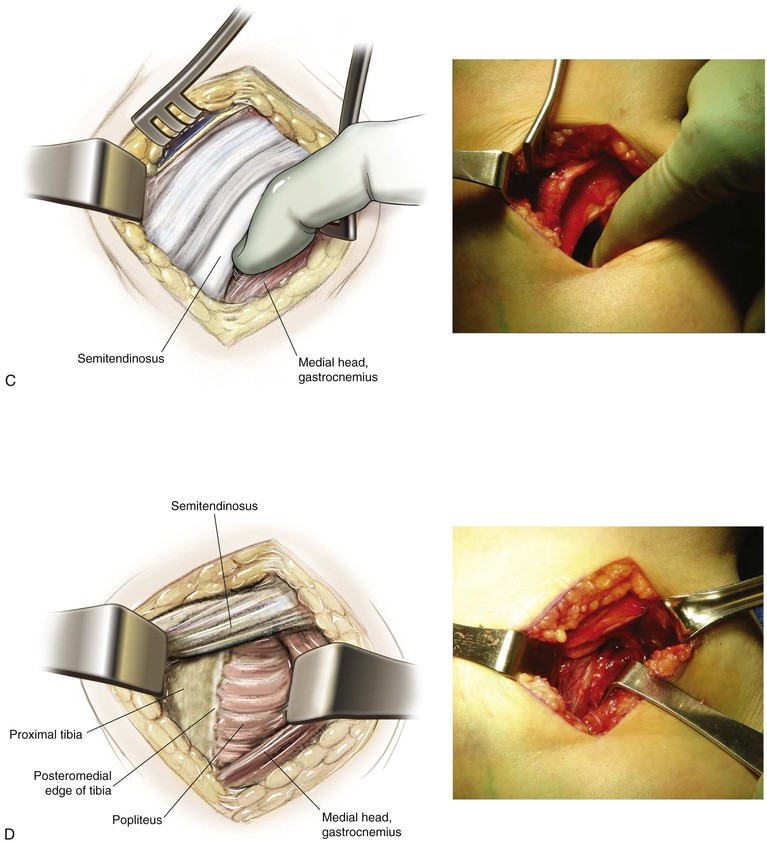
Deep Dissection (Fig. 7-24, C and D)
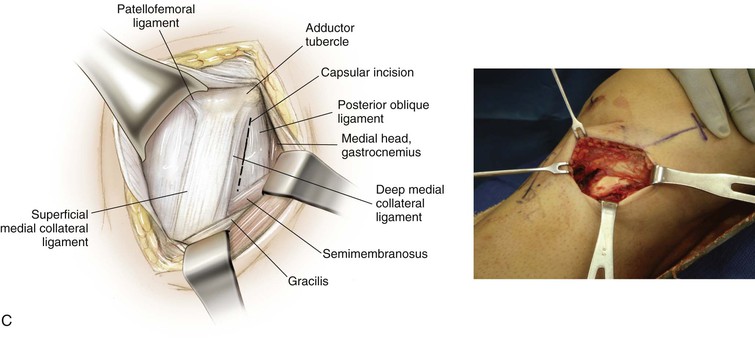
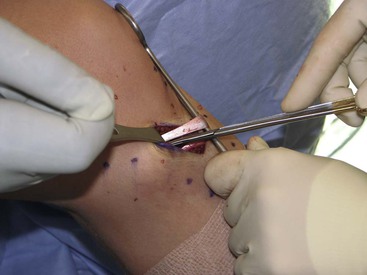
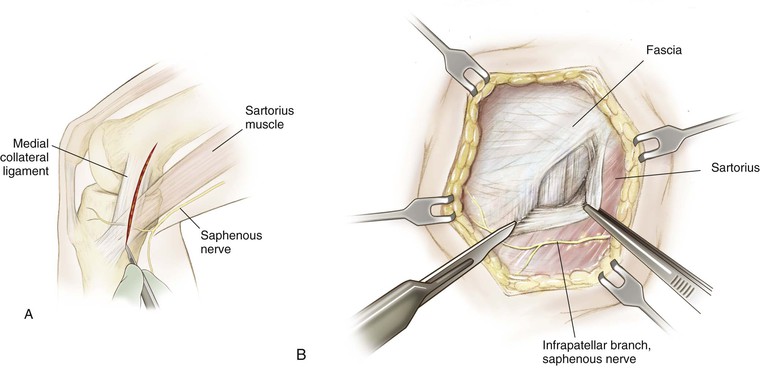
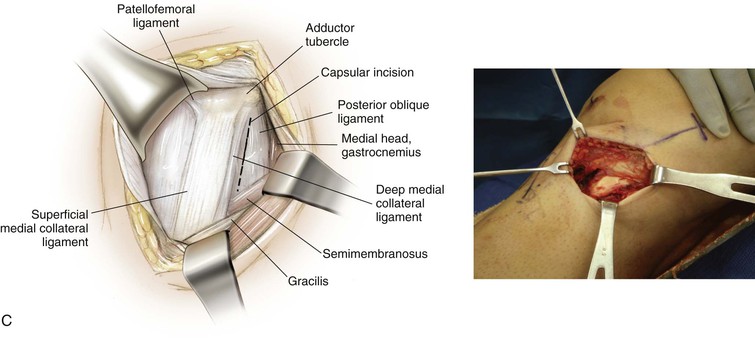
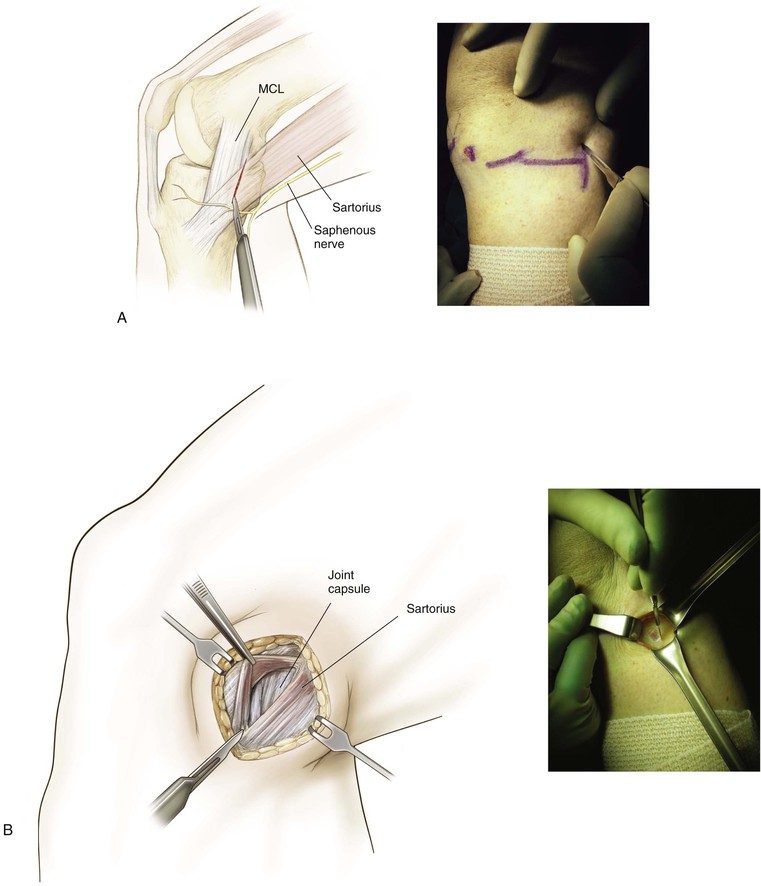
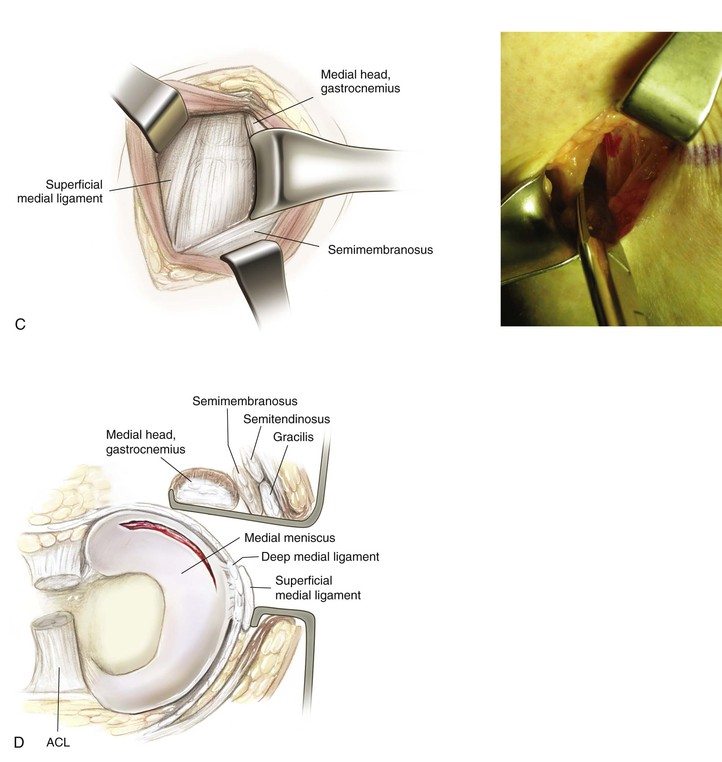
Medial Approach to the Knee (Fig. 7-27 and Video 7-2)
Indications
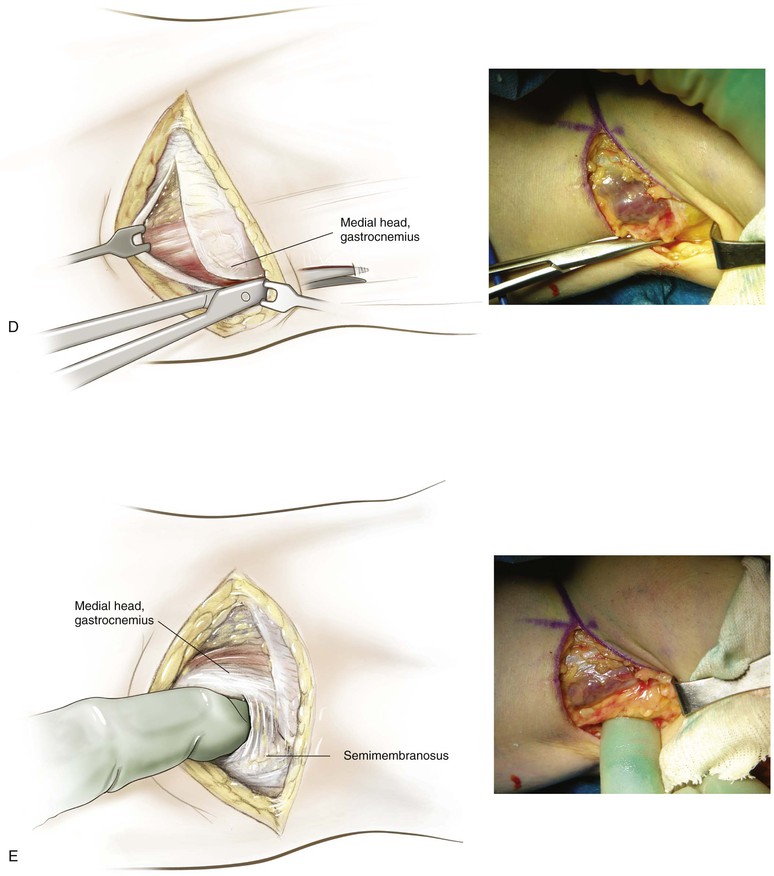
Deep Dissection
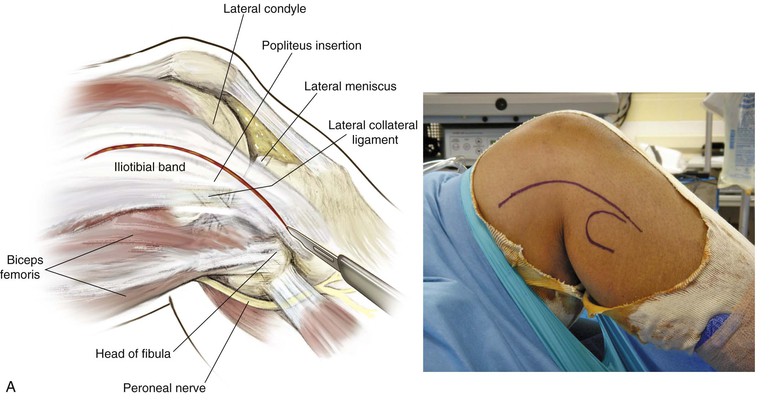
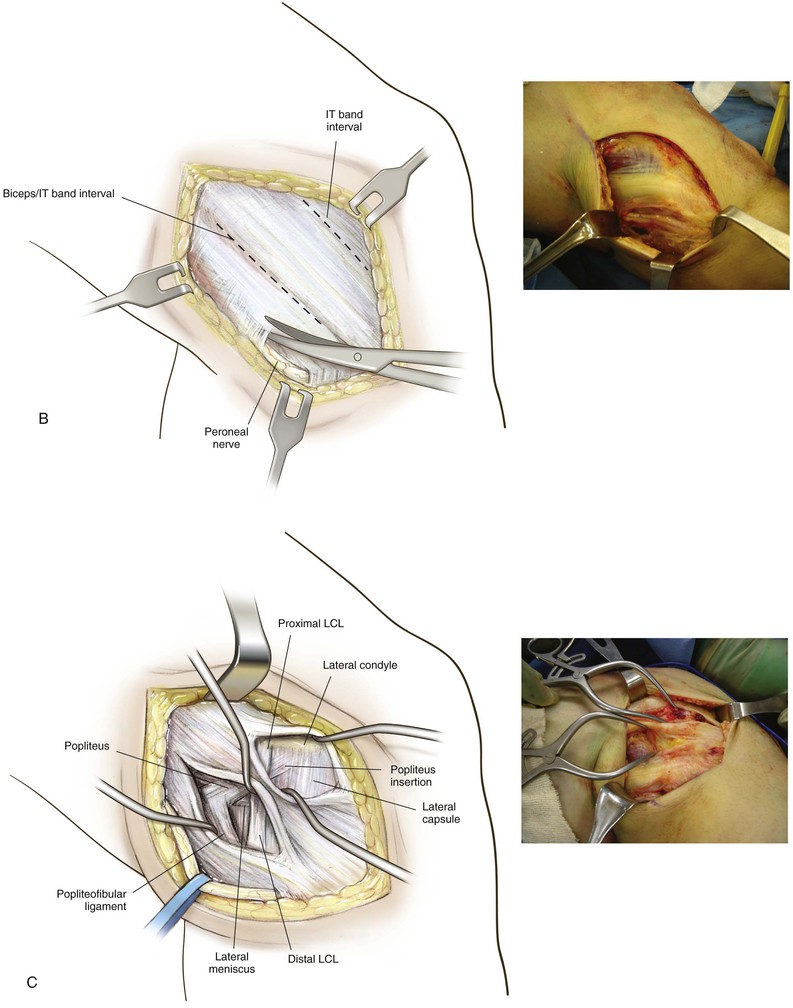
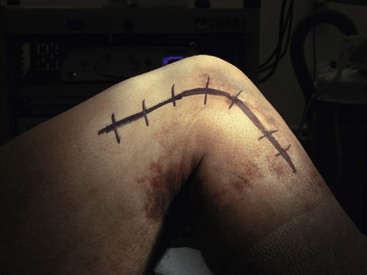
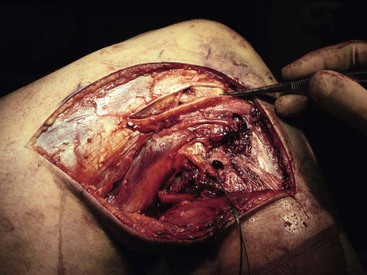
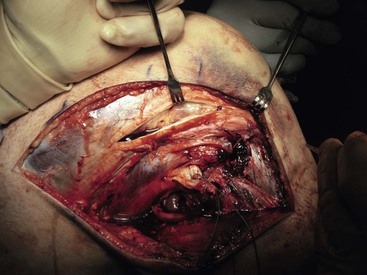
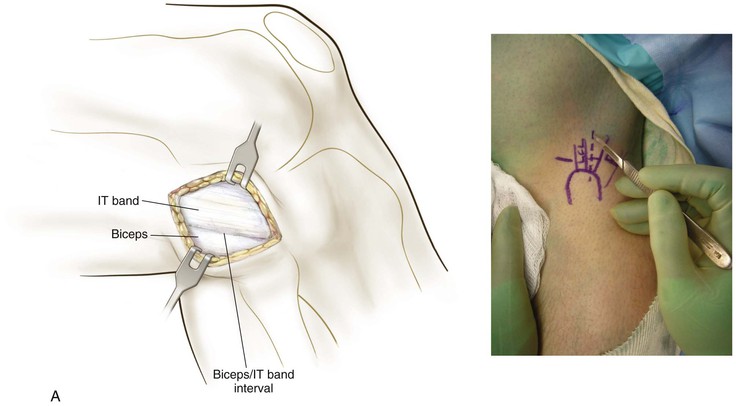
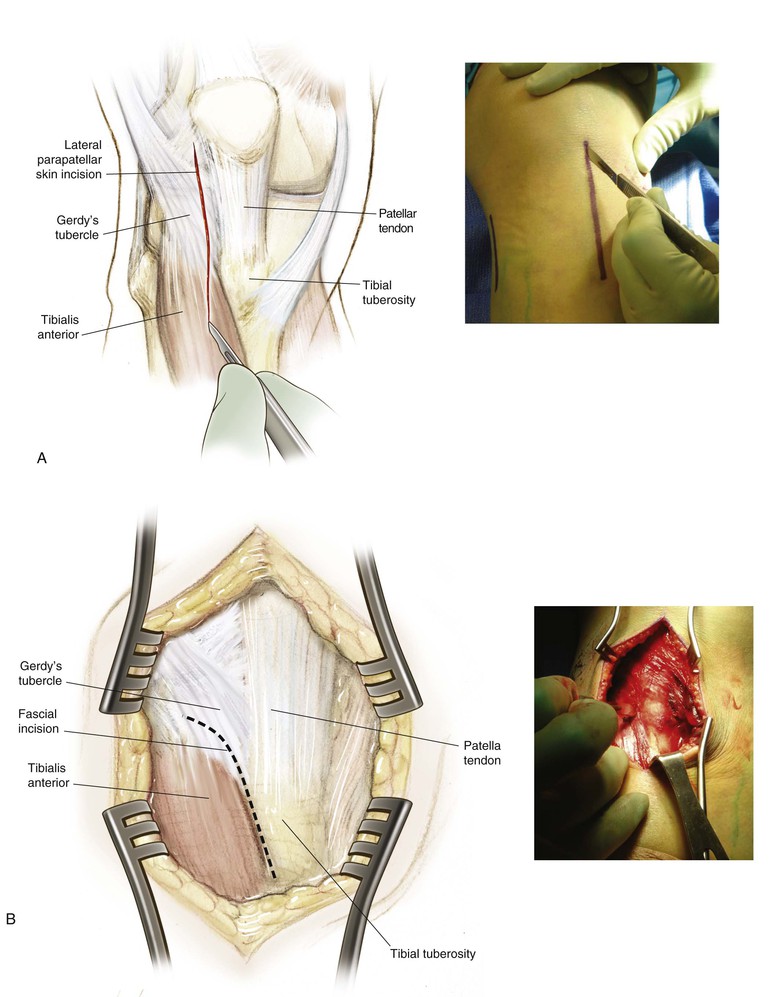
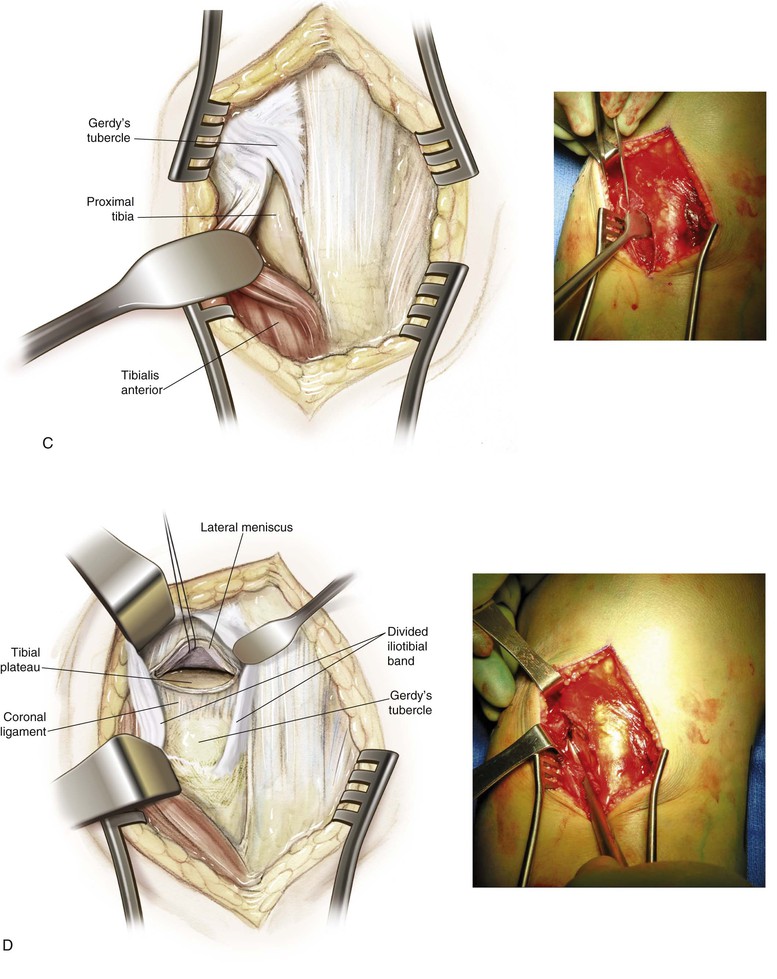
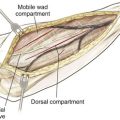
Lateral Approach to the Knee (Fig. 7-31 and Video 7-3)
Indications
Deep Dissection
Identify and protect the peroneal nerve (just posterior to the biceps muscle); carefully dissect the nerve across the neck of the fibula (Fig. 7-34)
Develop the interval between the iliotibial band and the biceps (interval 1) as needed
• Developing the interval allows identification of the tibial attachments of the lateral joint capsule
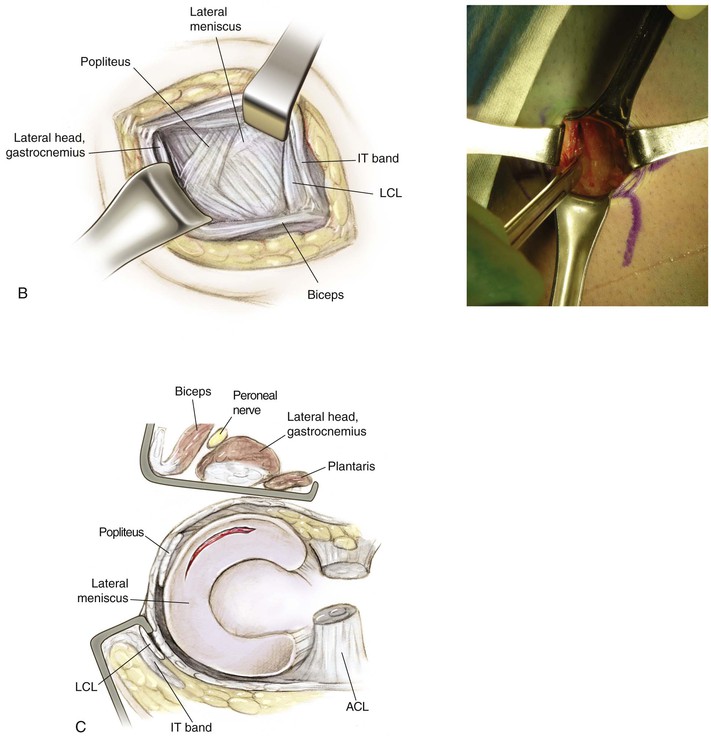
Split the midportion of the iliotibial band (interval 2; Fig. 7-35)
• This procedure allows identification of the lateral femoral epicondyle and the femoral attachments of the LCL and popliteus tendon (Fig. 7-36)
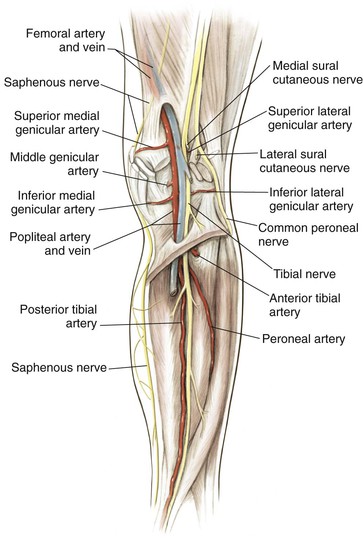
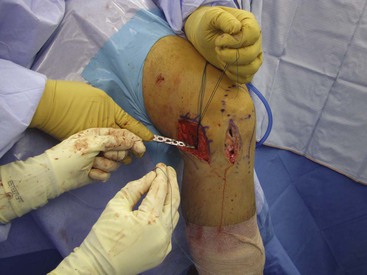
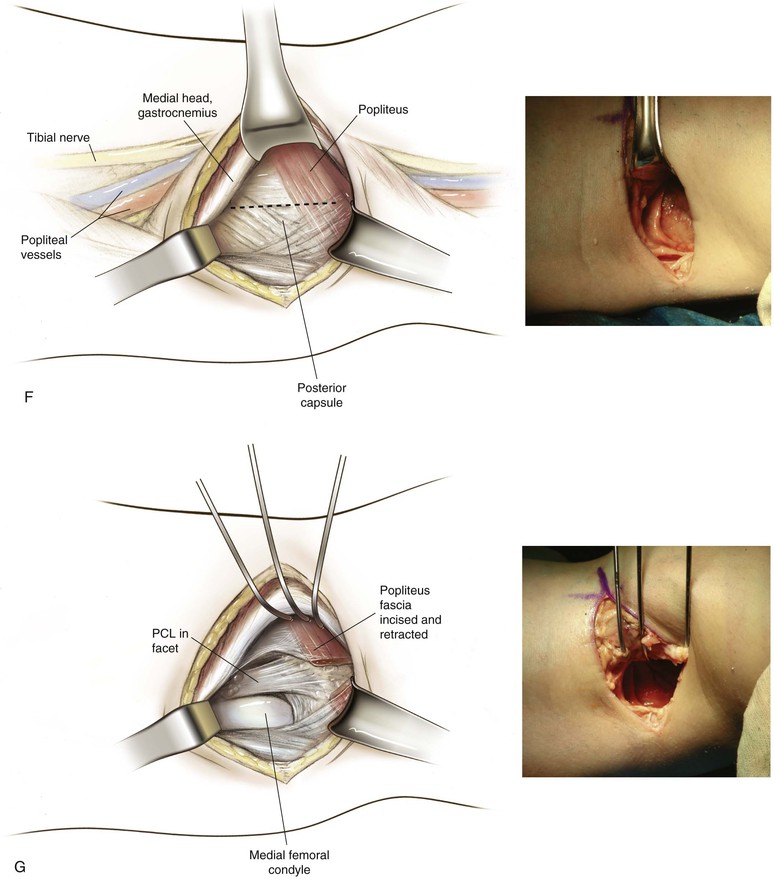
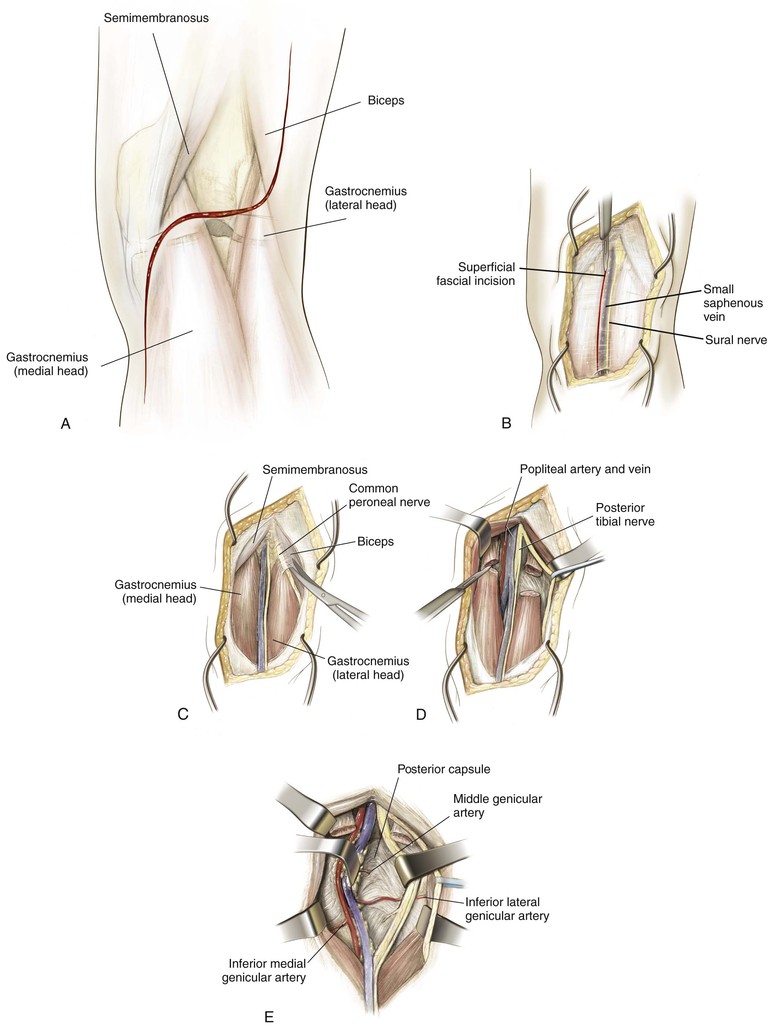
Posterior Approach to the Knee (Figs. 7-40 and 7-41 and Video 7-4 )
)
Indications
Lateral Approach to the Proximal Tibia (Fig. 7-42)
Indications
Medial Approach to the Proximal Tibia (Fig. 7-43)
Indications
Deep Dissection
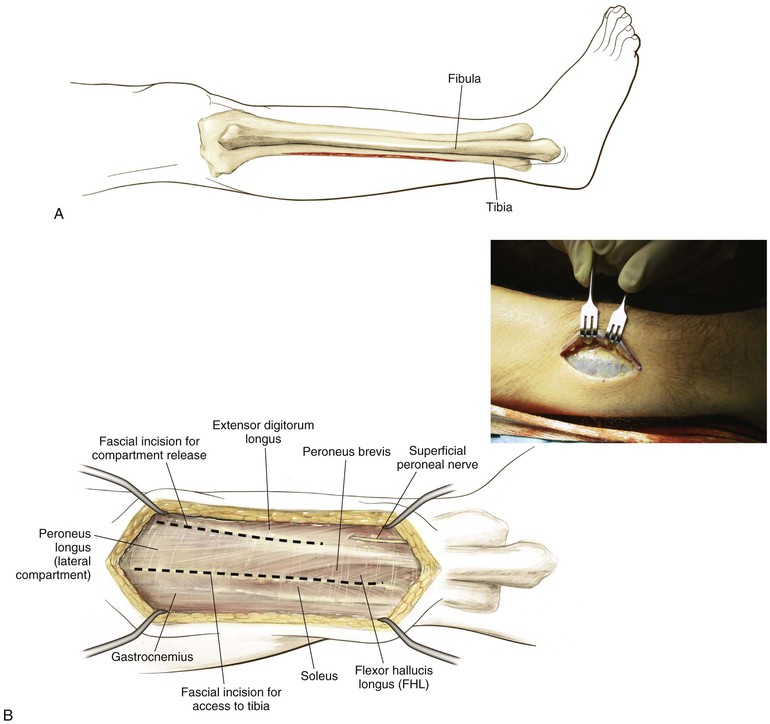
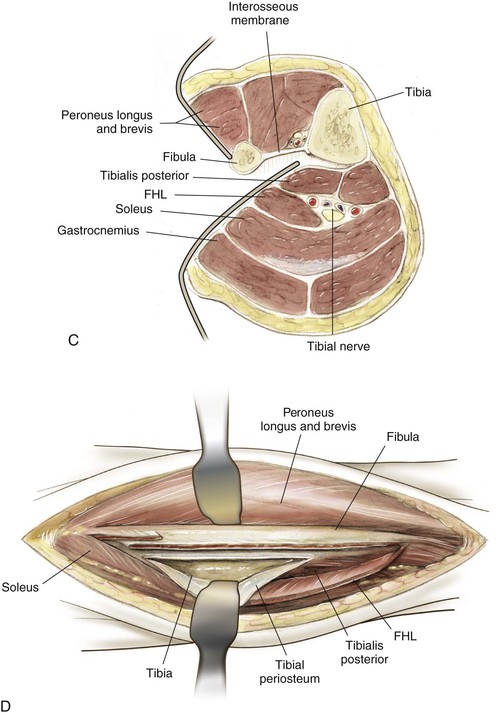
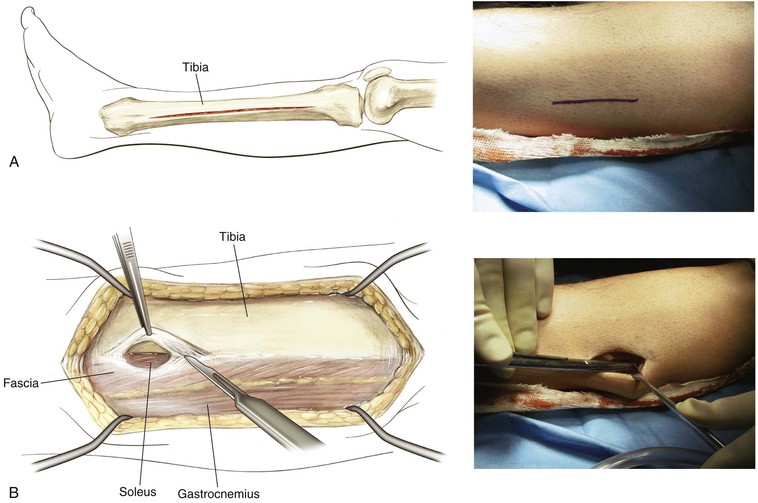
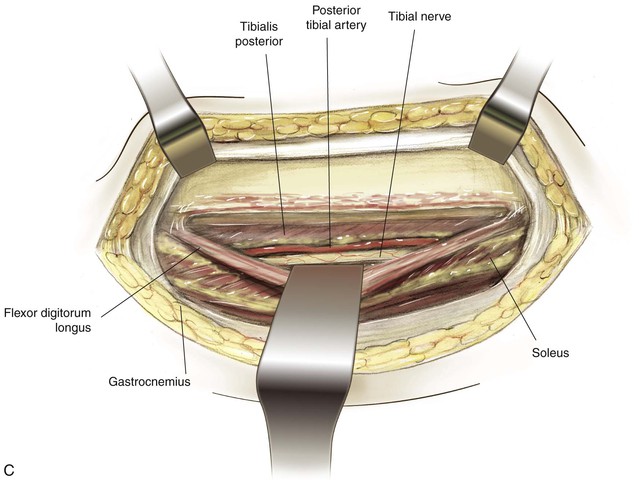
Lateral Approach to the Leg (Fig. 7-44)
Indications
Superficial Dissection
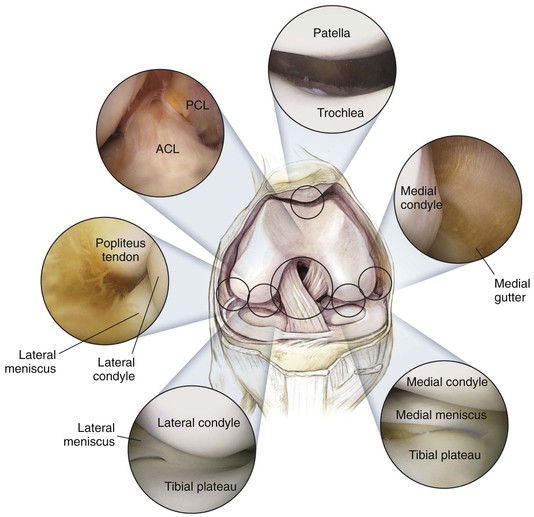
Knee Arthroscopy
Indications
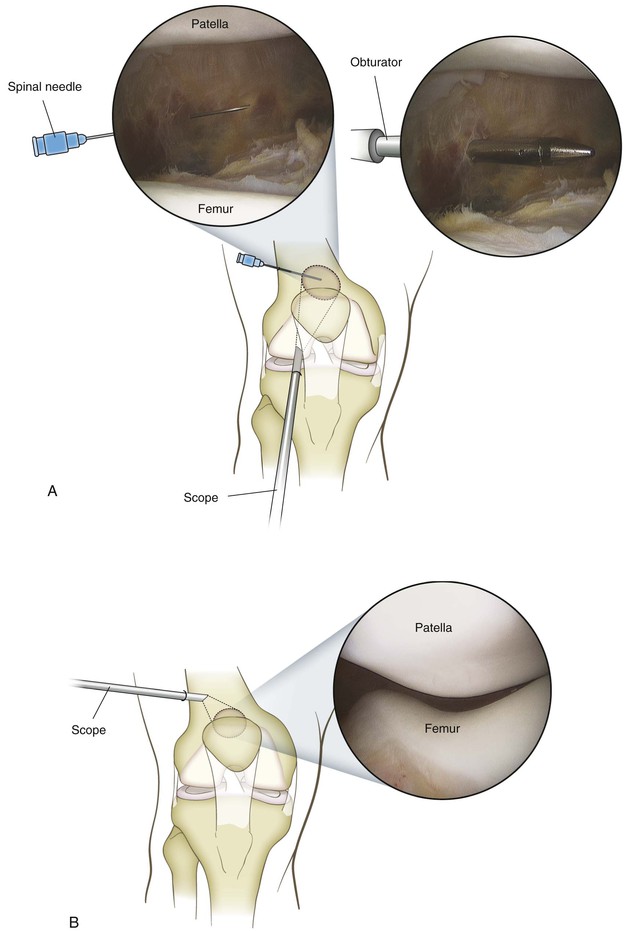
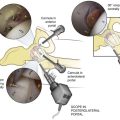
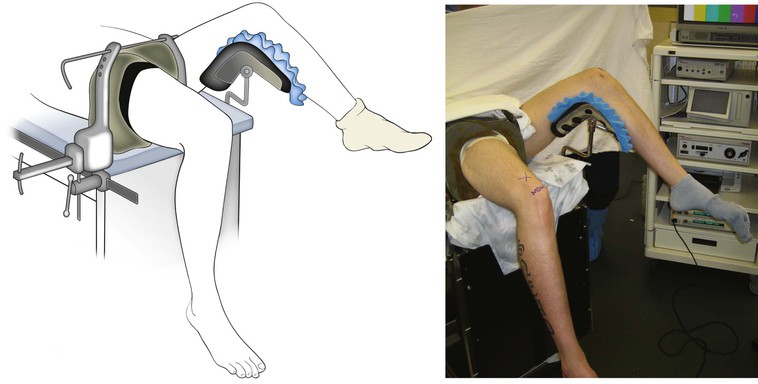
Positioning (Fig. 7-46)
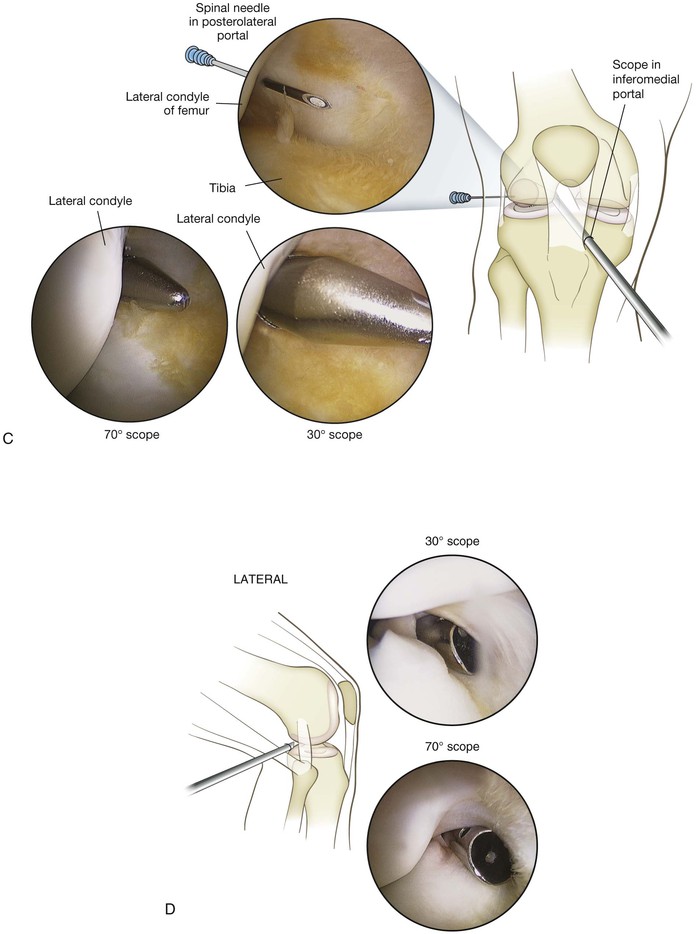
Portals (Figs. 7-47 through 7-50)
Inferolateral
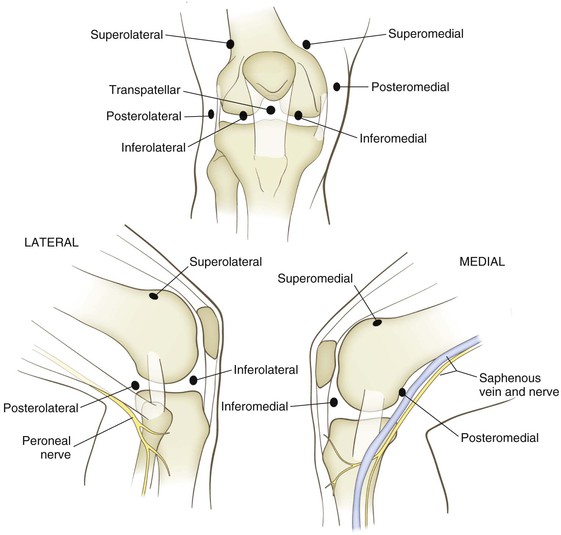
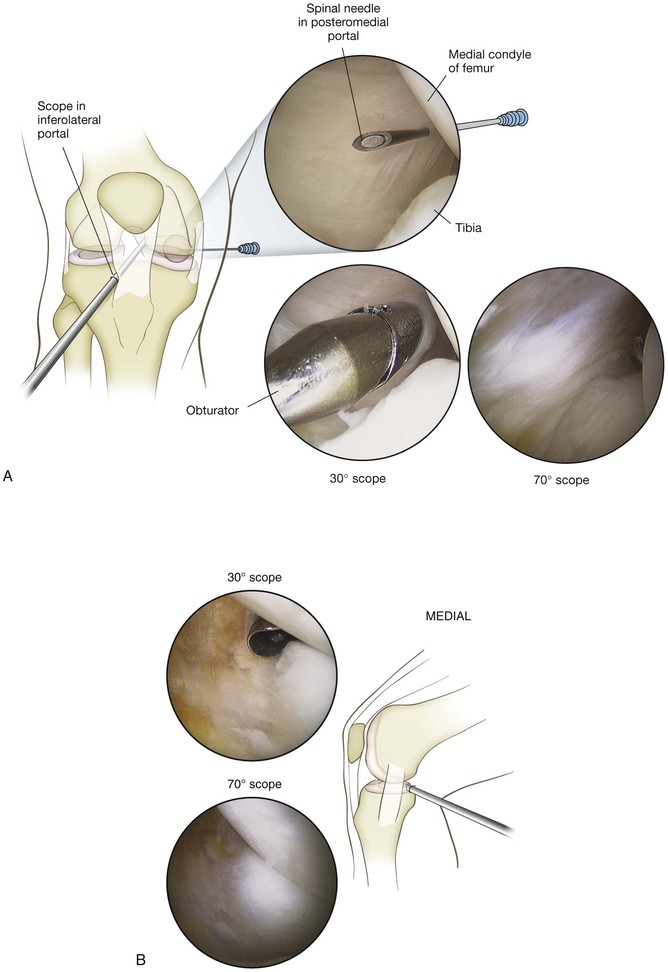
Posteromedial Portal
Location: just above the joint line, posterior to the joint
• Typically located with a spinal needle while viewing the posteromedial aspect of the knee through a Gillquist or modified Gillquist portal (a cannula is introduced into the back of the knee along the inferolateral aspect of the medial femoral condyle)
• Care must be taken to avoid injuring the saphenous vein or nerve while establishing this portal