Knee
Analysis: the checklists
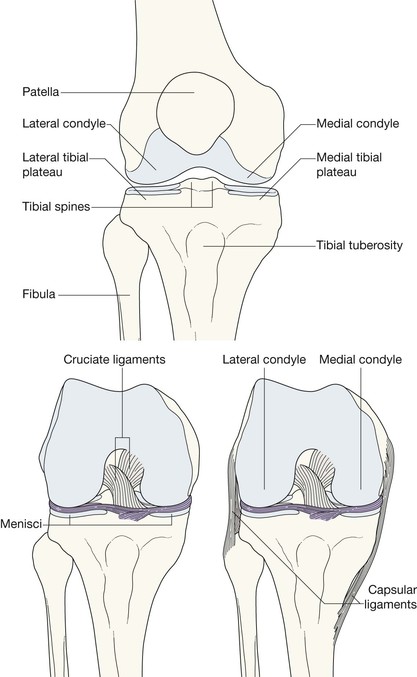
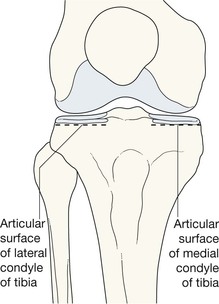
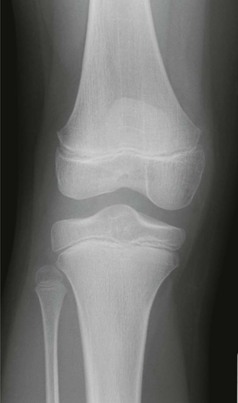
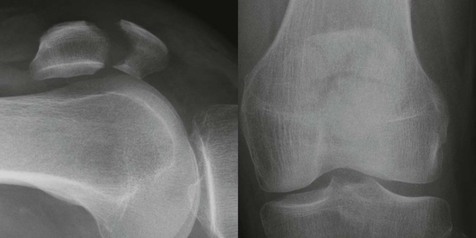
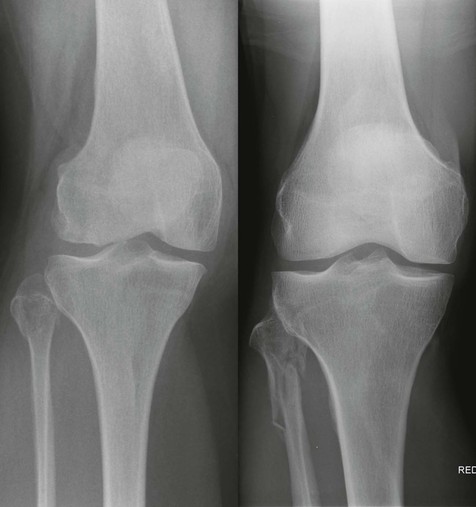
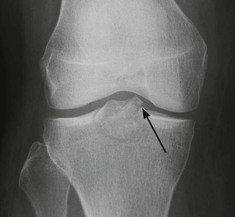
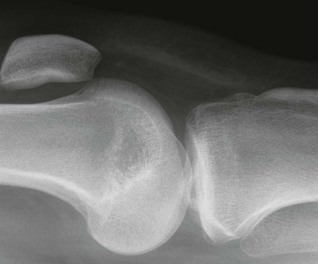
The AP radiograph
Adults: a five-point checklist
Check:
2. The head and neck of the fibula.
□ Each plateau should be smooth. No steps, no layering, no disruptions.
□ The subchondral bone should not show any focal increase in density.
4. The patella. Look through the superimposed femur.
5. Finally, check for any small fragments of bone—anywhere at all.
Children: an eight-point checklist
1–5 as for adults, but also check:
6. The growth plates of femur, tibia, and fibula. Is there an epiphyseal fracture? (See pp. 14–17).
7. The cortex of the femur and tibia. Is there a Greenstick or Torus fracture? (See pp. 18–19.)
8. The condylar surfaces of the femur. Is there an osteochondral lesion/fracture? (See pp. 28–29.)
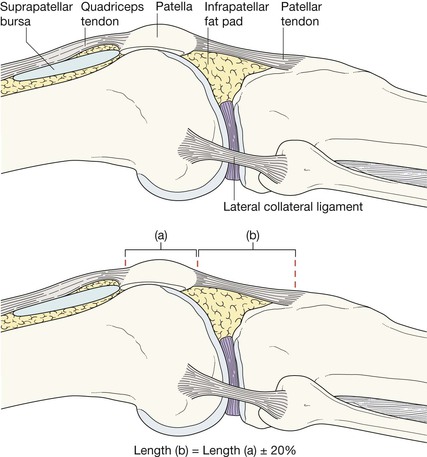
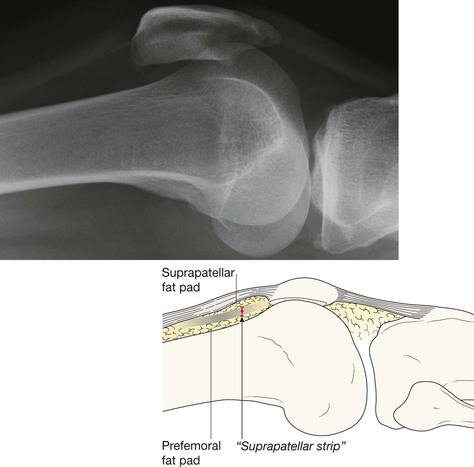
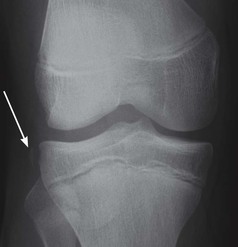
The lateral radiograph
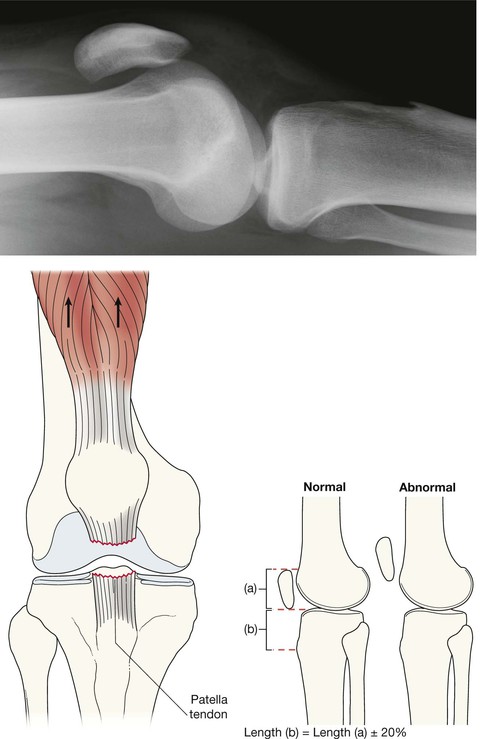
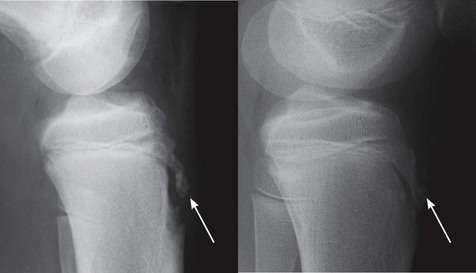
It is important to understand the normal and abnormal appearance of the suprapatellar bursa—if abnormal, this often suggests a fracture or ligament damage4–6.
Adults and children: a six-point checklist
Check:
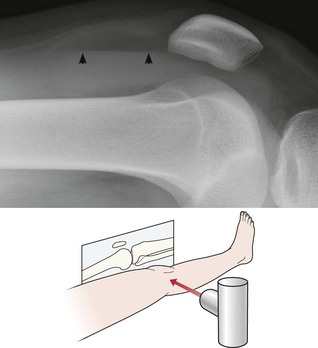
1. For a joint effusion4–7. Present if the suprapatellar strip exceeds 5 mm (see below).
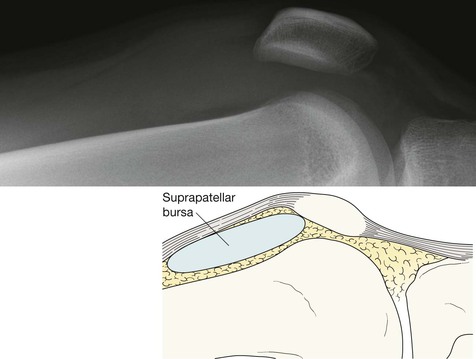
2. For a fat–fluid level in the suprapatellar bursa… an intra-articular fracture.
3. The condylar surfaces of the femur. Are they smooth?
4. The patella. Is the articular surface smooth?
The common fractures
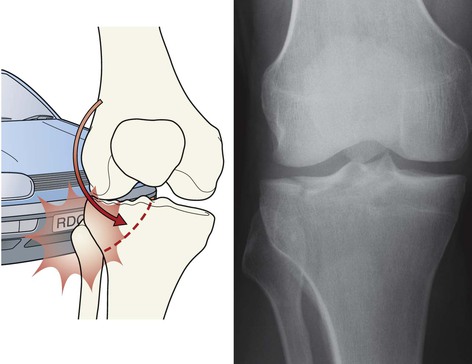
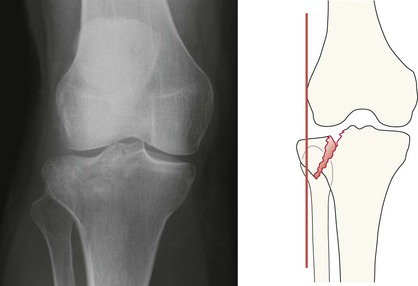
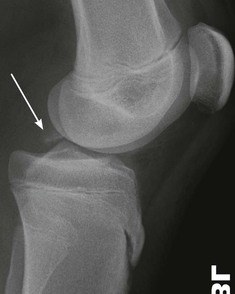
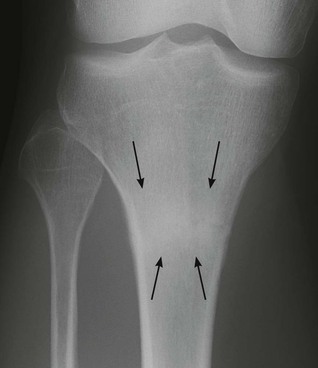
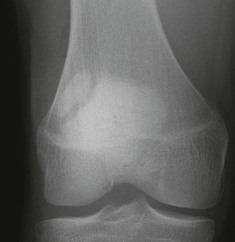
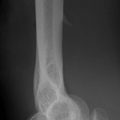
Tibial plateau fracture
Usually seen as a depression in the lateral plateau following violent impaction by the lateral femoral condyle. The so-called ‘car bumper’ or ‘fender’ fracture. Many, but by no means all, are true car bumper injuries. Sports injuries and falls at home are other frequent causes.
▪ Radiographic evidence of an impacted fracture may be subtle. There are four features to look for (see pp. 252–253). Sometimes only one or two will be present.
Fracture through the body of the patella
Usually caused by a direct blow. Vertical, horizontal and comminuted fractures occur. A violent contraction of the quadriceps can cause a transverse fracture in an athlete.
Osteochondral fracture: articular surface of the patella
Often consequent on high energy trauma in young patients. Articular surfaces shear against each other. The medial surface of the patella is usually affected.
Neck of fibula fracture
Don’t dismiss an isolated fracture too lightly. These fractures of the fibula are often consequent on high energy trauma. Damage to the collateral or cruciate ligaments within the joint are well recognised associations.
Osteochondritis dissecans of the knee
Repetitive trauma may cause a defect in the articular surface of the femur. Most commonly affecting the lateral aspect of the medial femoral condyle. See pp. 28–29.
Supracondylar and intracondylar fractures of the femur
Most commonly consequent on high energy trauma in the young; typically a road traffic accident. These fractures also occur in elderly patients with severe osteoporosis who have fallen. Detecting the fracture on the radiographs is straightforward.
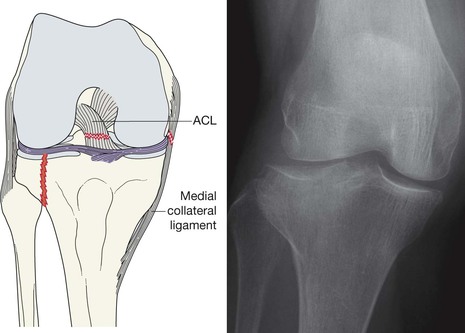
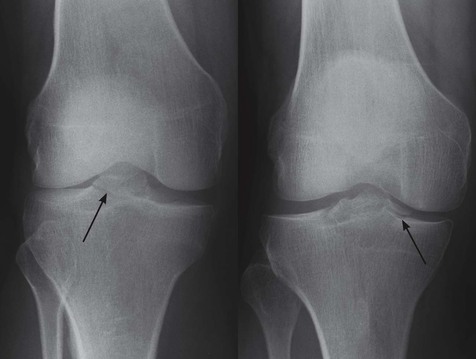
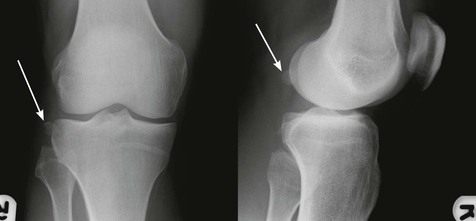
Fracture/avulsion of the tibial spine
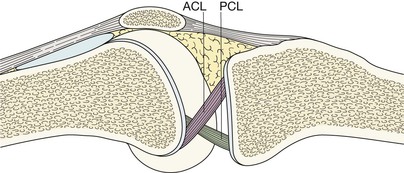
An avulsion fracture of the tibial spine (the intercondylar eminence) indicates a cruciate ligament injury because this area is the site of attachment of these ligaments.
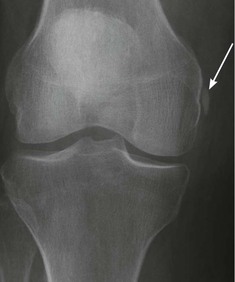
Small fragments around the knee
Any small fragment is important. It will warn you that an important soft tissue injury is likely.
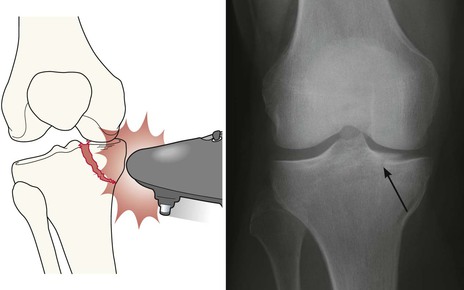
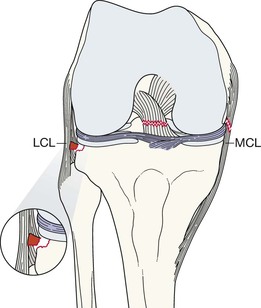
Cruciate ligament or meniscus injury—Segond fracture11–14
A tear of the lateral capsular ligament may cause a cortical avulsion where it is attached to the tibia. The tear is consequent on forceful internal rotation and varus stress. This cortical avulsion is termed a Segond fracture.
A Segond fracture has a strong association with a tear of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and/or a meniscal injury. More than 75% of patients with a Segond fracture have torn the ACL.
A Segond fracture is regarded as the most frequent indirect sign of an ACL tear seen on a plain radiograph.
A common dislocation
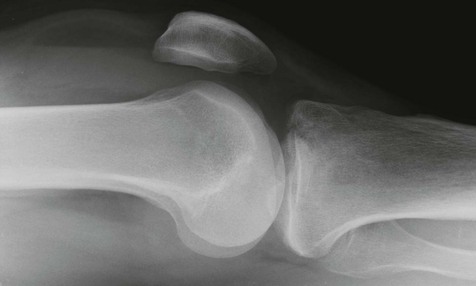
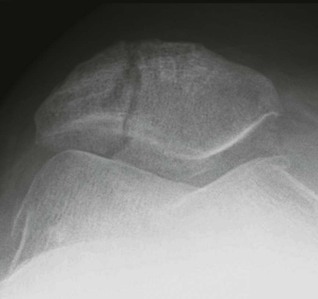
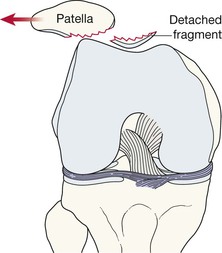
Patella dislocation15,16
The knee joint is most vulnerable when the leg is extended. It is then that the patella is least stable and most vulnerable to an external force.
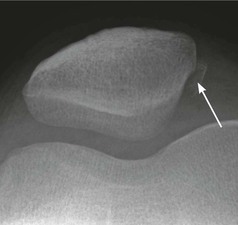
Fracture complication: in approximately 20% of patients who have dislocated the patella there will be a small sliver of bone detectable on the plain radiographs. This fragment detaches from the patella or from the lateral femoral articular surface as part of a shearing injury during the dislocation.
With many patients, who have suffered a transient patella dislocation and subsequently attend the Emergency Department, the dislocation will already have reduced spontaneously. In these patients it is wise to obtain a patellar view (skyline view) as well as the standard knee radiographs as this will increase the chances of detecting a fragment that might have sheared off at the time of dislocation.