12 Kidney Diseases
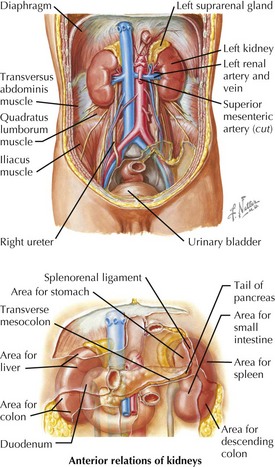
Anatomy of the Kidneys
Position of the Kidneys
• Kidneys and adrenals lie within perirenal (perinephric) fat that is enclosed by fibrous renal fascia (Gerota’s).
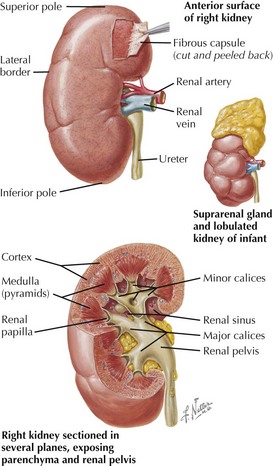
Internal Renal Structure
• Cortex: contains Bowman’s capsules and glomeruli (renal corpuscles), proximal and distal convoluted tubules, proximal collecting ducts, arcuate arteries and veins, cortical capillary plexus
• Medulla, pyramids: contain loops of Henle, distal collecting ducts, vasa rectae, medullary capillary plexus
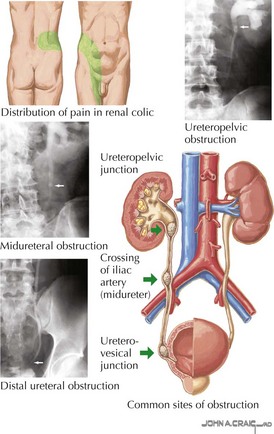
Ureter
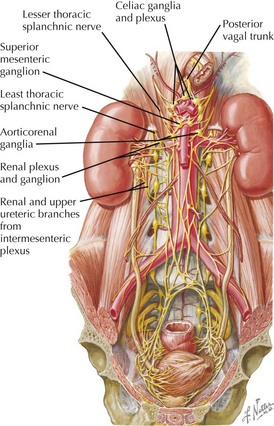
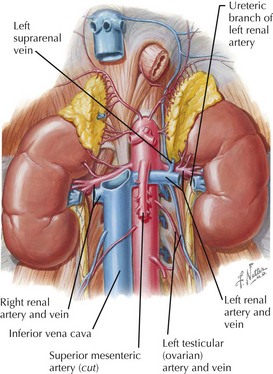
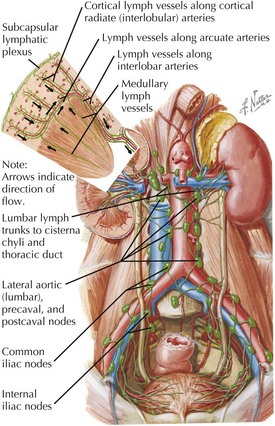
Vessels and lymphatics
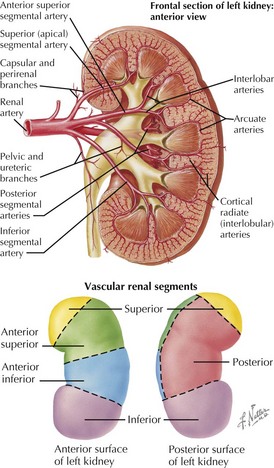
Arterial Supply
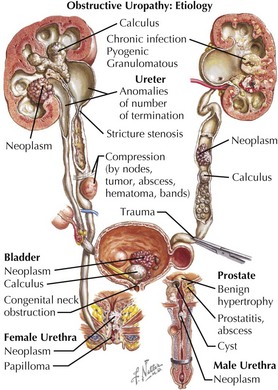
Clinical Correlates
Stones
• Magnesium ammonium phosphate (struvite) stones (~15%) are radiopaque and can occur with infections producing urease (e.g., Proteus mirabilis).
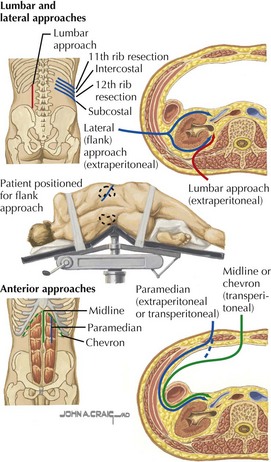
Surgical Approaches to the Kidneys
• Multiple different surgical approaches to kidneys: anterior, lateral or flank, lumbar or posterior, laparoscopic
• Preferred approach depends on disease, size and extent of lesion, obstruction, trauma, cancer or resection, and failure or transplant.